离子液体在TIPS法制备PVDF膜中的应用毕业论文
2020-06-16 20:37:06
摘 要
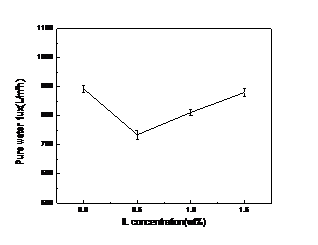
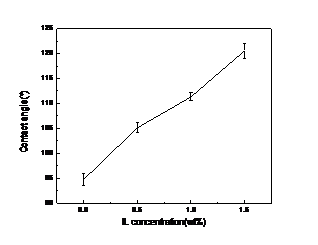
本论文以聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)为聚合物膜材料,选用环保稀释剂乙酰柠檬酸三丁酯(ATBC)代替有机溶剂作为稀释剂,在实验过程加入离子液体1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑六氟磷酸盐([BMIM][PF6])作为添加剂,采用热致相分离法(TIPS)制备PVDF平板微孔膜,并对PVDF平板微孔膜的结构性能进行研究。本实验研究过程中将聚合物PVDF的质量分数固定为20%,添加剂离子液体[BMIM][PF6]的质量分数分别为0%、0.5%、1.0%和1.5%。PVDF聚合物膜的表征主要包括膜的纯水通量测试,膜的机械性性能测试,PVDF晶型测试,膜的孔隙率以及聚合物膜的微观形貌。实验结果表明,添加剂[BMIM][PF6]含量的逐渐加入,膜孔隙率、纯水通量、断裂伸长率会先出现相应的减小后,又逐渐增大,而拉伸强度则会先相应增强后,随之逐渐减弱。当[BMIM][PF6]含量为0%和0.5%时,PVDF聚合物PVDF的晶型为α晶型;当[BMIM][PF6]含量为1.0%和1.5%时,PVDF聚合物膜的结晶类型为β晶型。此结果表明,当加入1%的添加剂[BMIM][PF6]时,膜的结晶类型就可以发生改变,为压电性PVDF膜的制备提供了捷径。
关键词:聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF);1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑六氟磷酸盐([BMIM][PF6]);离子液体;乙酰柠檬酸三丁酯(ATBC);热致相分离法
Abstract
In this paper, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) as the polymer membrane material, the use of environmentally friendly diluent acetyl tributyl citrate (ATBC) instead of organic solvents as a diluent, in the course of the process of adding ionic liquid 1-butyl-3 (BMIM) [PF6] was used as additive. PVDF microporous membrane was prepared by thermally induced phase separation (TIPS), and the structural properties of PVDF microporous membrane were studied. In the course of this study, the mass fraction of polymer PVDF was fixed at 20%, and the mass fraction of additive ionic liquid [BMIM] [PF6] was 0%, 0.5%, 1.0% and 1.5%, respectively. The characterization of PVDF polymer films mainly includes the pure water flux test of the membrane, the mechanical properties of the film, the PVDF crystal test, the porosity of the film and the microstructure of the polymer film. The experimental results show that when the additive [BMIM] [PF6] is added, the pure water flux, porosity and elongation at break of the film decrease first, and gradually increase with the increase of the content of the additive. Changes are increased first and then gradually reduced. When the mass fraction of [BMIM] [PF6] is 0% and 0.5%, the crystal form of PVDF polymer PVDF is α crystal form. When the mass fraction of [BMIM] [PF6] is 1.0% and 1.5%, the crystallization of PVDF polymer film Type β crystal type. The results show that the crystallization type of the membrane can be changed when 1% of the additive [BMIM] [PF6] is added, providing a shortcut for the preparation of a piezoelectric PVDF film.
Key words: polyvinylidene fluoride; 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate; ionic liquid; acetyl tributyl citrate; thermally induced phase separation
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
目录 III
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1膜分离技术的发展 1
1.2膜材料的选择及其性质 3
1.3 PVDF微孔膜制备方法研究进展 4
1.3.1浸没沉淀法 4
1.3.2热致相分离法 5
1.3.3溶剂蒸发凝胶法 5
1.4稀释剂的选择及其性质 5
1.5添加剂的选择及其性质 6
第二章 实验部分 9
2.1实验原料 9
2.2主要仪器 10
2.3实验方法与表征 10
2.3.1 PVDF膜的制备 10
2.3.2膜的形貌结构表征 10
2.3.3 膜的纯水通量测试 11
2.3.4膜的孔隙率测试 11
2.3.5膜的机械性能测试 11
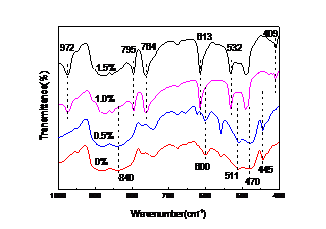
2.3.6膜的FTIR和XRD测试 11
2.4.7膜的接触角测试 12
第三章 结果与讨论 13
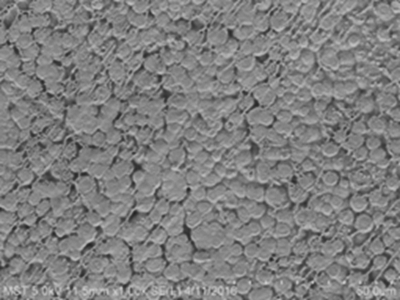
3.1膜的形貌 13
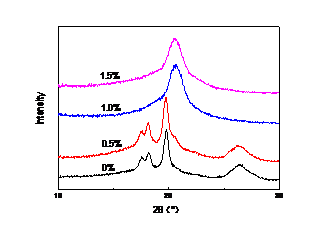
3.2膜中PVDF的晶体类型 15
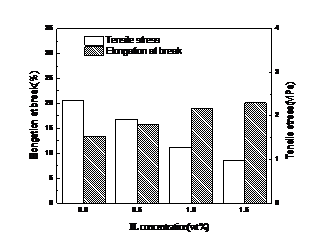
3.3膜的拉伸强度和断裂伸长率 15
3.4膜的纯水通量 16
3.5膜的孔隙率 16
3.6膜的接触角 17
参考文献 19
致 谢 22
第一章 文献综述
1.1膜分离技术的发展
现如今,在全球水资源正变成一种宝贵的稀缺资源,生态环境的保护和治理中,膜技术得到了全世界史无前例的高度重视。超微滤和反渗透技术在污水处理与回用中,由于超微滤和反渗透技术具备极强的高效节能等优势,现已在污水处理等领域得到广泛应用。全球膜应用领域中废水处理与再利用占了很大比例,具体应用主要有饮用水、工业、膜生物反应器、反渗透预处理等领域[1]。
生物膜渗透现象最早于Nollet于18世纪被Nollet发现,随之对生物膜渗析过程的不断探究中,膜技术渐渐形成。膜分离技术是在二十世纪七十年代得到应用和发展。Greham发表有关膜渗透的文章;Traubl,Fick以及Pfeffer等利用人工合成的膜进行关联渗透压与溶液浓度以及渗透压的相关实验[2-9]。膜技术的发展里程碑[10]如下表1-1:
相关图片展示: