改性活性炭上苯和低浓度氯气制氯化苯的催化性能毕业论文
2020-07-02 22:38:31
摘 要
在许多涉氯化工品生产中,常产生一些低浓度Cl2与HCl等混合气体,这不仅不利于HCl的生产利用,还会造成环境污染。将低浓度Cl2直接运用于有机物氯化尤其是芳烃氯化的产品生产是探索氯资源利用的有效途径之一。传统氯化苯的制备是以FeCl3作催化剂将苯氯化,但其工艺过程复杂且产生大量对环境有污染的废水废渣。因此开发一种固体颗粒催化剂代替FeCl3,不仅能提高低浓度Cl2的利用效率,同时可缓解废酸污染和工艺流程长的问题。本论文验证了低浓度氯气运用于苯氯化反应的可行性,制备并考察了活性炭固体催化剂对苯氯化反应的催化性能。
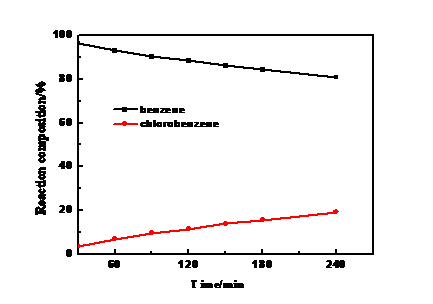
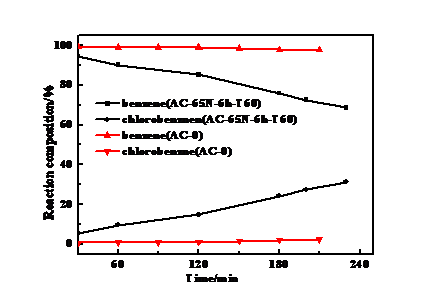
本文以HCl为氯源,经催化氧化制备了不同组成的HCl和Cl2等的混合气体,研究了改性活性炭上苯氯化反应的催化性能。探讨了HNO3改性活性炭的工艺条件(HNO3浓度、浸渍时间、浸渍温度和活化温度)对催化剂性能的影响。结果表明:在HNO3浓度为65%,浸渍时间为6h,浸渍温度为60℃,活化温度为100℃条件下制备AC-65N-6h-T60是活性最好的催化剂。AC-65N-6h-T60催化下,反应3h时,反应液中苯含量为75.87%,氯化苯含量为24.13%,苯的转化率能达到18.08%,氯化苯平均生成速率能达到4.9 g/(g·h);反应4h时,反应液中苯含量为67.5%,氯化苯含量能达到32.5%。结合表征数据可知:HNO3浓度增加使得表面含氧基团特别是羧基和酚羟基数量大大增加;浸渍6h活性炭表面氧化已达到饱和;较高温度改性导致活性炭的石墨化现象严重,造成活性炭表面被侵蚀,使活性炭孔道结构被剧烈破坏,这对催化活性是不利的;TG结果也表明活性炭表面基团在250℃以上会出现分解,活性炭载体在更高温度也会出现结构损失。以上结果可以得出:活性炭在剧烈氧化作用或高温焙烧下其孔道结构变化才会影响苯氯化反应,活性炭表面的酸性含氧基团可直接作为苯氯化反应的催化活性位点。
关键词:苯氯化 氯化苯 活性炭 酸催化
Catalytic Performance of Reaction of Benzene with Low Concentration of Chlorine on Modified Activated Carbon to Benzene Chloride
ABSTRACT
In many chlorinated work products, some mixed gases such as Cl2 and HCl are often produced, which is not only unfavorable for the production and utilization of HCl, but also causes environmental pollution. The direct application of low-concentration Cl2 to the chlorination of organic compounds, especially aromatics, is one of the effective ways to explore the utilization of chlorine resources. Traditional chlorinated benzene is prepared by chlorination of benzene with FeCl3 as a catalyst, but the process is complicated and a large amount of wastewater wastes that are polluted to the environment are generated. Therefore, the development of a solid particle catalyst instead of FeCl3 can not only improve the utilization efficiency of low-concentration Cl2, but also alleviate the problem of waste acid pollution and long process flow. This paper verifies the feasibility of using low-concentration chlorine gas for the benzene chlorination reaction. The catalytic performance of the activated carbon solid catalyst for the chlorination of benzene has been prepared and investigated.
In this paper, HCl was used as the chlorine source, and HCl and Cl2 mixed gases with different compositions were prepared by catalytic oxidation. The catalytic performance of benzene chlorination on modified activated carbon was studied. Then, the effect of the process conditions (HNO3 concentration, immersion time, impregnation temperature, and activation temperature) on the performance of the catalyst with HNO3 modified activated carbon was investigated. The results showed that the catalyst with the best activity was prepared with HNO3 concentration of 65%, impregnation time of 6 h, impregnation temperature of 60 °C and activation temperature of 100 °C. Under the catalysis of AC-65N-6h-T60, the content of benzene in the reaction solution was 75.87%, the chlorinated benzene content was 24.13%, the conversion of benzene could reach 18.08%, and the average formation rate of chlorinated benzene could reach 4.9 g/(g·h); In the reaction for 4 h, the benzene content in the reaction liquid was 67.5%, and the chlorinated benzene content could reach 32.5%. Combined with the characterization data, it can be seen that the increase of HNO3 concentration greatly increases the amount of surface oxygen-containing groups, especially carboxyl groups and phenolic hydroxyl groups; the surface oxidation of activated carbon after saturation of 6 h has reached saturation; the higher temperature modification leads to a serious graphitization of activated carbon, resulting in the surface of activated carbon being Erosion causes the pore structure of the activated carbon to be severely destroyed, which is detrimental to the catalytic activity. The TG results also show that the surface groups of the activated carbon will decompose above 250° C, and the active carbon carrier will also suffer structural loss at higher temperatures. The above results can be concluded that the change of the pore structure of activated carbon will affect the benzene chlorination reaction under severe oxidation or high-temperature calcination, and the acidic oxygen-containing groups on the surface of activated carbon can be directly used as the catalytic active sites of benzene chlorination.
KEYWORDS: benzene chlorination;chlorobenzene ;activated carbon;acid catalysis
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 低浓度Cl2现状 1
1.1.1 低浓度Cl2的产生与危害 1
1.1.2 低浓度Cl2的综合利用方法 1
1.2 苯沸腾氯化制氯化苯工艺 2
1.2.1 氯化苯装置在氯碱厂中平衡Cl2的重要作用 2
1.2.2 沸腾连续氯化工艺难以克服的缺陷 2
1.3 苯氯化反应机理 3
1.4 活性炭用作苯氯化固体催化剂的研究 5
第二章 实验部分 7
2.1 实验原料及仪器 7
2.1.1 实验气体及试剂 7
2.1.2 实验仪器 7
2.2 催化剂表征 8
2.2.1 X-射线衍射(XRD) 8
2.2.2 N2吸附-脱附等温线 (N2-Adsorption Desorption) 8
2.2.3 氨气程序升温脱附(NH3-TPD) 8
2.2.4 Boehm滴定 9
2.2.5 热重分析(TG) 9
2.2.6 傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR) 9
2.3 活性评价装置及产物分析方法 9
2.3.1 催化剂评价装置 9
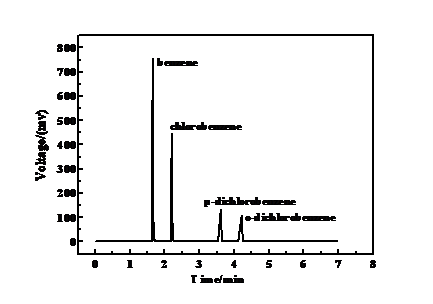
2.3.2 产物分析方法 10
第三章 改性活性炭催化苯和低浓度Cl2制氯化苯的性能 13
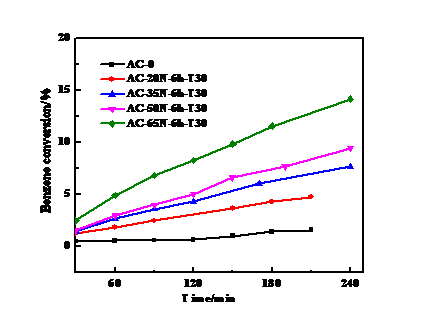
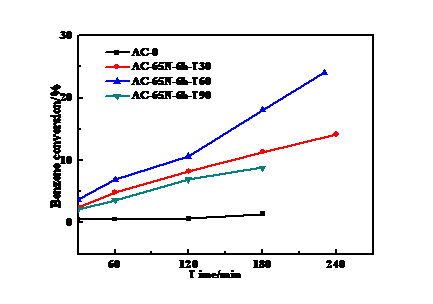
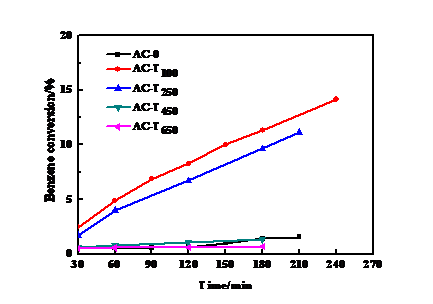
3.1 HNO3浓度的影响 13
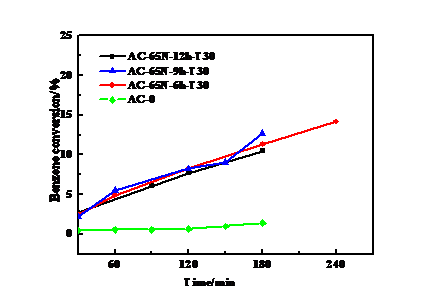
3.2 浸渍时间的影响 15
3.3 浸渍温度的影响 16
3.4 活化温度的影响 18
3.5 HNO3改性活性炭催化剂的物化性能表征 19
第四章 总结 25
参考文献 26
致谢 28
第一章 文献综述
1.1 低浓度Cl2现状
1.1.1 低浓度Cl2的产生与危害
在大量消耗Cl2的工业生产中,氯气的利用率只有50%。随着TDI、MDI、ADC发泡剂和甲烷氯化物等涉氯产品的大规模扩产和氯碱行业的发展,预计到2020年,副产HCl总量将超过500 万t/a[1]。
一些低浓度的Cl2常常作为副产品混合于HCl中,这不利于HCl的生产利用。同时 Cl2也是一种毒性很强的气体,也是众多的有机氯产品生产过程中的重要原料,这会造成环境污染和氯资源的浪费。综上,有效的回收利用低浓度氯气,可以使资源充分利用,做到安全作业和保护环境。
1.1.2 低浓度Cl2的综合利用方法
目前,工业上低浓度Cl2综合利用方法主要分为三大类[2]。碱液吸收法生产次氯酸钠、低浓度Cl2的富集利用[3]和低浓度Cl2生产氯化产品。
(1)碱液吸收产次氯酸钠
相关图片展示: