化学气相沉积法制备ZIF-8@SBA-15复合材料及其性能探究毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:50:57
摘 要
金属有机骨架(Metal-organic frameworks,MOFs)材料通常是指无机的金属中心(金属离子或金属簇)与有机配体通过共价键或离子-共价键相互联接,通过配位自组装形成的具有周期性网络结构的晶体多孔材料。它是近十几年发展起来的一类新型多孔材料, 通过改变金属离子和有机配体的种类,我们可以“定制”不同结构的MOFs材料,由于其结构的多样性,比表面积大、孔隙率高以及结晶度高,MOFs材料在吸附脱硫、催化、气体储存与分离、药物传输等方面得到了广泛的研究。但是,大部分的MOFs材料都是微孔材料,虽然微孔MOFs有利于对小分子气体的吸附,但是分子在微孔孔道内扩散速度慢,并且阻碍了大分子接触其活性位,这限制了其在大分子方面的应用。合成介孔的MOFs是解决这个问题的方法之一,但是目前合成介孔MOFs具有一定的难度。
本文以MOFs材料作为研究对象,将MOFs材料引入到SBA-15的介孔孔道内,制备得到的复合材料既具有二氧化硅材料的介孔孔道,又有MOFs材料的活性位点,形成了一种类似于介孔MOFs结构的复合材料。本实验我们将ZnNO3·6H2O与SBA-15进行固相研磨,利用原粉SBA-15的限阈空间,在SBA-15孔道内得到了高分散的锌,然后将复合材料通过高温焙烧转化为ZnO@SBA-15,再通过化学气相沉积法(Chemical Vapor Deposition, 简称CVD),让复合材料中的Zn2 与易升华的2-甲基咪唑进行配位原位生成ZIF-8,从而得到高度分散的ZIF-8@SBA-15复合材料。它既拓展MOFs材料在大分子领域的应用,同时也提升SBA-15的应用价值,该复合材料能够高效吸附大分子,有望在吸附大分子例如染料大分子和生物酶大分子等方面有新的进展。
关键词:MOFs SBA-15 化学气相沉积法 大分子吸附
Preparation and Properties of ZIF-8@SBA-15 Composites by Chemical Vapor deposition
Abstract
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) materials usually refer to inorganic metal centers (metal ions or clusters) that are interlinked with organic ligands through covalent or ion-covalent bonds. Crystal porous materials with periodic network structure are formed by coordination self-assembly. Organometallic skeleton materials are a new kind of porous materials developed in recent years. By changing the types of metal ions and organic ligands, we can "customize" MOFs materials with different structures, because of their diversity of structure and large specific surface area. High porosity and high crystallinity of MOFs materials have been widely studied in adsorption, desulfurization, catalysis, gas storage and separation, drug delivery and so on. However, most of the MOFs materials are microporous materials. Although microporous MOFs are conducive to the adsorption of small molecular gases, the diffusion rate of molecules in the micropore channels is slow, and the active sites of macromolecules are hindered. This limits its application to macromolecules. Synthesis of mesoporous MOFs is one of the methods to solve this problem, but it is difficult to synthesize mesoporous MOFs.
In this paper, the MOFs material was introduced into the mesoporous channel of SBA-15. The composite material has not only the mesoporous channel of silica material, but also the active site of MOFs material. A composite material similar to mesoporous MOFs structure was formed. In this experiment, ZnNO3·6H2O and SBA-15 were ground in solid phase, and the highly dispersed zinc was obtained in the SBA-15 pore by using the confined space of SBA-15. Then the composites were calcined at high temperature and converted to ZnO@ SBA-15, and then the Zn2 in the composite was prepared by chemical vapor deposition. The Zn2 in the composite was coordinated with the easily sublimated 2-methylimidazole to form ZIF-8 in situ, and a highly dispersed ZIF-8@SBA-15 composite was obtained. It not only extends the application of MOFs materials in the field of macromolecules, but also enhances the application value of SBA-15. This composite can adsorb macromolecules efficiently, and it is expected to make new progress in adsorption of macromolecules such as dye and enzyme.
keyword : MOFs; SBA-15; Chemical vaporous depositon; bulky molecules adsorption
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 3
1.1 金属有机骨架材料(MOFs)材料 3
1.1.1 MOFs概述 3
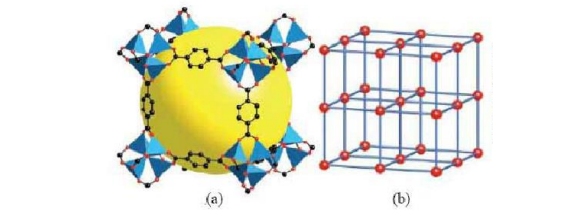
图1-1 三种常见的MOF材料 3
1.1.2 MOFs的合成方法 4
1.1.3 MOFs的研究进展 4
1.1.4 MOFs的缺点和局限性 6
1.2 介孔氧化硅SBA-15 7
1.2.1 SBA-15的组成及结构 7
1.2.2 SBA-15功能化的方法 8
1.3 ZIF-8@SBA-15的合成 9
1.3.1介孔MOFs 9
1.3.2 MOF@SBA-15最近的一些进展 9
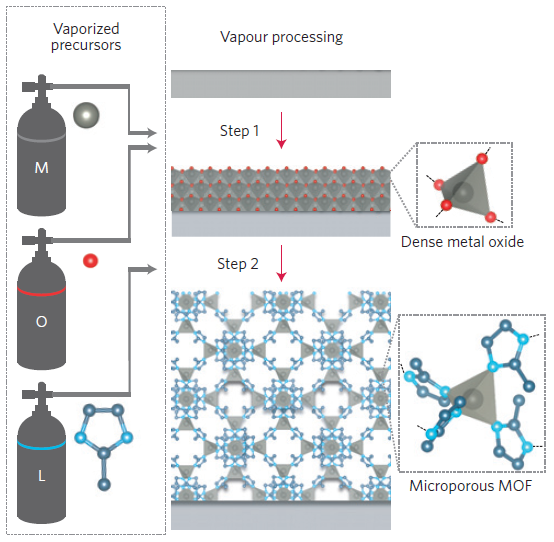
1.3.3化学气相沉积法(CVD) 11
1.4本论文的研究目的和主要研究内容 13
第二章 实验部分 14
2.1 实验器材及试剂 14
2.2 实验方法和步骤 15
2.2.1 制备载体介孔氧化硅SBA-15 15
2.2.2 制备复合材料ZIF-8@SBA-15 15
2.3 材料的表征 17
2.3.1 X射线衍射(XRD) 17
2.3.2 红外光谱(IR)分析 17
2.3.3 热重(TG)分析 17
2.4 吸附性能测试 17
第三章 实验结果与讨论 19
3.1 样品的表征 19
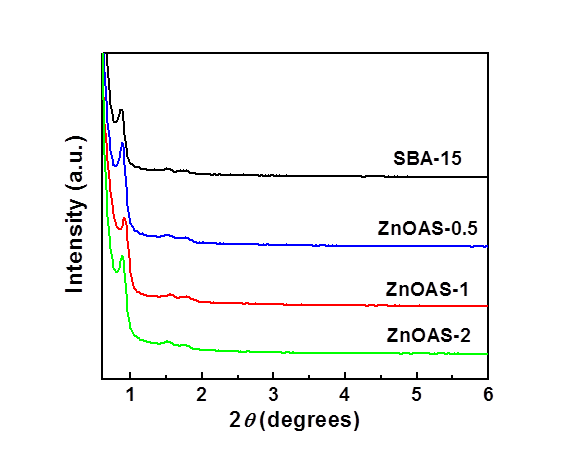
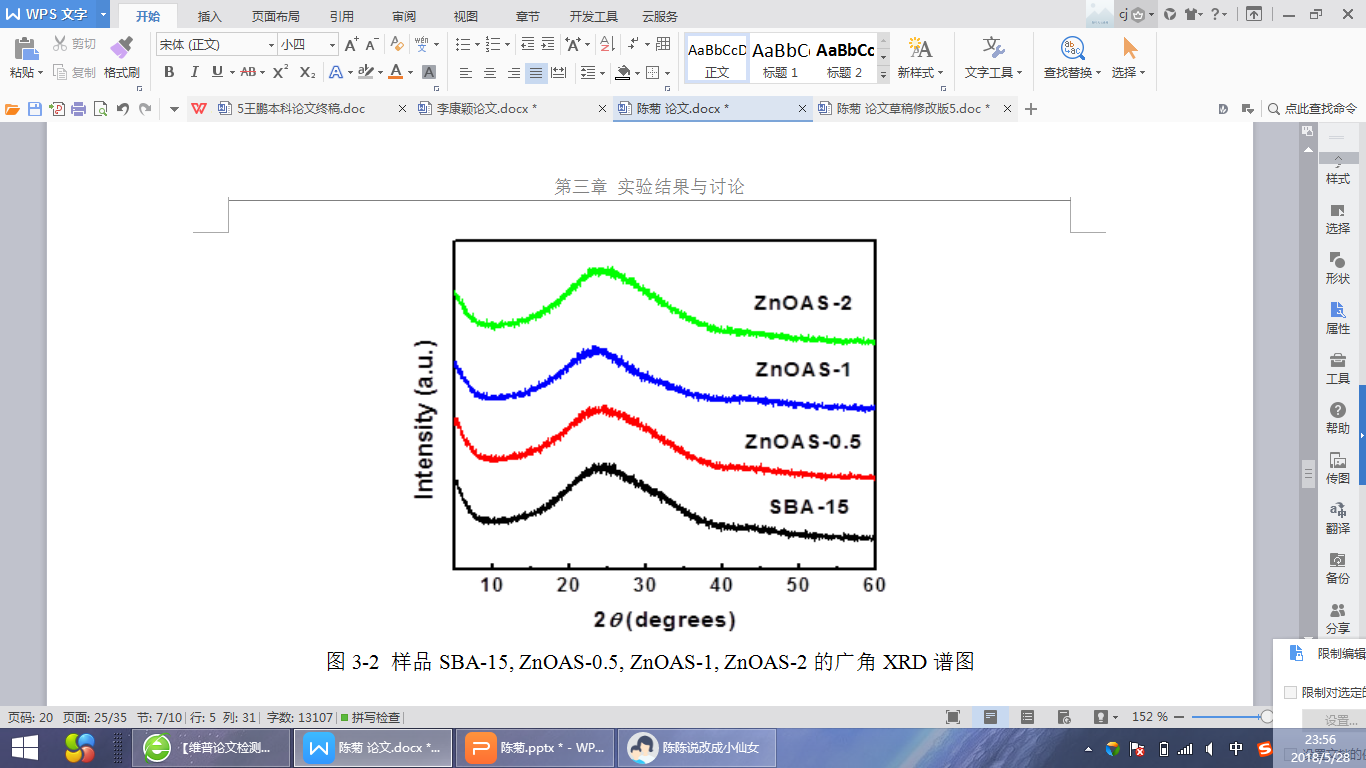
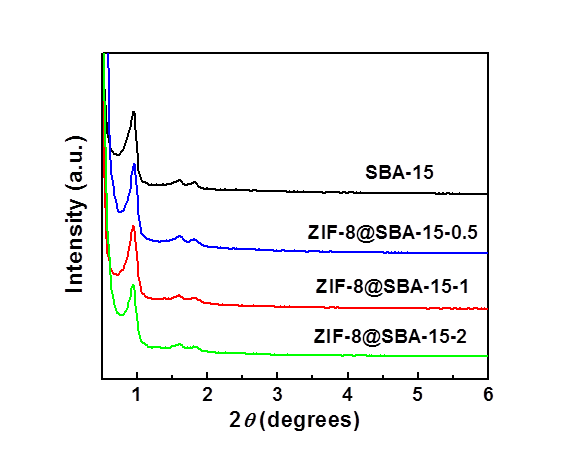
3.1.1样品的 XRD分析 19
3.1.2 红外光谱表征 22
3.1.3 热重表征 23
3.2吸附性能测试结果 24
第四章 结论与展望 25
参考文献 26
致谢 30
第一章 绪论
金属有机骨架材料(Metal-oganic frameworks, MOFs),是一类新型类沸石多孔材料[1-2]。近来该材料广受关注,因为它具有独特的性能,不寻常的光效应,含大量的重金属离子,过渡金属离子以及许多有机配体可供选择。另一方面,传统的分子筛合成方法复杂,而MOFs有不同的孔隙形状,合成条件比较温和,合成方法比较简单,孔径和大小都可以调节。再加上MOFs材料热稳定性好,其结构具有多样性,而且有较大的比表面积和孔隙率,因此在很多领域又有着广阔的应用前景,例如在储能、分离、光学材料、磁性材料以及催化等方面。这里我们主要将它通过化学气相沉积法合成并附着在介孔氧化硅SBA-15孔道内,从而形成类似于介孔材料用来吸附染料或者大分子蛋白酶。
1.1 金属有机骨架材料(MOFs)材料
1.1.1 MOFs概述
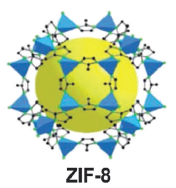
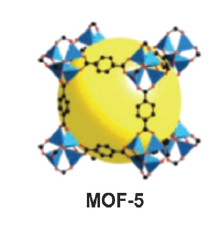
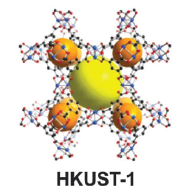
图1-1 三种常见的MOF材料
MOFs是近期发展起来的一类新型多孔材料,由无机的金属中心(金属离子或金属簇)与含氮、氧等多齿有机配体通过共价键或离子-共价键相互联接而成的,具有周期性网络结构的晶体材料(如图1-1所示)。同时MOFs也被称为配位聚合物,是一种有机-无机杂化材料,它与普通有机复合物和无机多孔材料不同,但又具有无机材料的硬度和有机材料的柔性。
与传统的硅铝分子筛相比,它具有稳定的化学性质、大孔体积、、高比表面积,可调节的微孔尺寸和结构、结构和功能的多样性等特点,使这种材料在吸附脱硫、手性催化和对环境有害气体的储气和分离被广泛的研究[3-4]。
1.1.2 MOFs的合成方法
目前MOFs的研究中最为常用的合成方法为水热法(溶剂热法):在溶剂中倒入具有一定摩尔比的金属离子和有机配体,在适当的温度和原位压力下他们会进行配位反应生成我们想要的配位化合物。一般是在密闭容器(如带有聚四氟乙烯内衬的不锈钢高压反应釜)中放入混合好的极性低沸点的溶剂如无机金属盐、有机配体、甲醇、乙醇、模板剂与去离子水、有机胺等然后密封放到烘箱里,利用自生压力在一定温度下会发生反应。该方法能解决常温常压下反应物不溶或难溶的问题,因为反应过程中反应物会随温度升高而逐渐溶解。 根据实验的实际需要,可以使用各种不同极性,不同沸点,不同官能团,不同介电常数或混合溶剂的有机溶剂来获得各种具有高维和稳定热力学性质的拓扑骨架结构材料。水(溶剂)热合成的晶体生长完美,同时反应装置简单、节能。此外,还存在其它制备方法,如扩散法、搅拌法、微波法、超声法,化学气相沉积法等,本实验采用的是化学气相沉积法,在后面的章节中会详细介绍。
1.1.3 MOFs的研究进展
早在1706年就发现第一个具有三维网络结构的化合物——普鲁士蓝,但直到1977年才被科学家们所确定[5]。1959年有报道[6]提出bis(adiponitrilo)copper(I) nitrate的晶体结构,它由过渡金属络合物[Cu(adiPonitrile)2]和硝酸阴离子合成。这就是我们现在所说的MOFs。“配位聚合物”一词最早出现于1964年,其合成策略是用分子模块构造出所需的骨架结构。
相关图片展示: