基于金属有机骨架材料MIL-101(Cr)的新型吸附剂的制备及其性能研究毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:52:19
摘 要
金属有机骨架材料(MOFs)是近些年来研究很火热的材料,相比于传统材料,这一类新型的材料具有较大的比表面积、可调的孔径、并且存在大量不饱和金属位等突出优异点。有一批研究者已经在目前致力于深度脱硫方面领域中MOFs的应用了。本文以燃料油深度脱硫为出发点,利用MOFs孔道内外部亲疏水性的不同,通过毛细作用使得活性组分Cu(I)完全进入载体的孔道内,能够提高吸附剂的吸附性能。
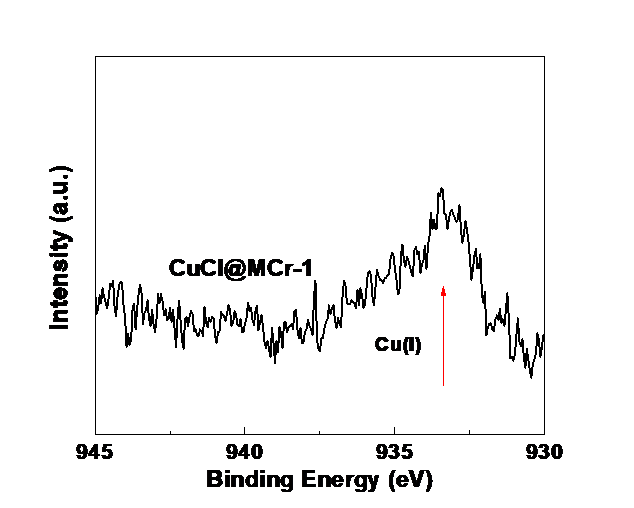
我们选用金属有机骨架材料MIL-101(Cr)为载体,采用双溶剂法,将前驱体Cu(II)和还原剂完全引入MIL-101(Cr)孔内,再结合液相还原法,还原剂可以在孔道内完全的还原Cu(II),得到吸附剂CuCl@MCr。这种方法实现了传统方法难以做到的的在温和条件下制备得到高分散的Cu(I)负载的MOFs吸附剂。制备得到的样品通过X射线衍射(XRD)和77 K氮气吸附等温线等一系列的表征,确定了复合材料CuCl@MCr良仍很好的保持了MIL-101(Cr)骨架结构。X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和滴定实验表明液相还原法结合双溶剂法能够将Cu(II)还原成Cu(I)。
最后,我们将制备得到的不同铜含量的吸附剂样品CuCl@MCr用于吸附脱除模型油中的噻吩硫化物。实验结果表明,当铜负载量为3 mmol/g时,吸附剂的脱硫性能最优,饱和吸附量为0.086mmol S∙g−1吸附剂,优于未引入活性组分的MIL-101(Cr)。
关键字:MIL-101Cr、Cu(I)、Cu(II)、氧化还原、新型吸附剂
Preparation and properties of new adsorbent based on metal organic frameworks MIL-101
abstract
Metal organic framework material (MOFs) is a very hot material in recent years. Compared with traditional materials, this new type of material has a larger specific surface area, adjustable aperture, and a large number of outstanding points, such as unsaturated metal. A number of researchers have been working on the application of MOFs in the field of deep desulfurization. In this paper, using the deep desulfurization of fuel oil as the starting point, using the difference of hydrophobicity inside and outside the MOFs channel, through the capillary action, the active component Cu (I) is completely entered into the channel of the carrier, and the adsorption properties of the adsorbent can be improved.
MIL-101 (Cr) is used as the carrier. The precursor Cu (II) and reducing agent are completely introduced into the MIL-101 (Cr) hole by double solvent method. The reductant can completely restore Cu (II) in the channel, and the CuCl @MCr of the adsorbent is obtained. This method has achieved a high degree of dispersion of Cu (I) MOFs adsorbent under mild conditions, which is difficult to achieve by traditional methods. The prepared samples were characterized by X ray diffraction (XRD) and 77 K nitrogen adsorption isotherms. It was determined that the composite CuCl@MCr good remains the MIL-101 (Cr) skeleton well. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and titration experiments showed that Cu (II) could be reduced to Cu (I) by liquid phase reduction and double solvent method.
Finally, we prepared the adsorbent CuCl@MCr with different copper content to adsorb the thiophene sulfide in the model oil. The experimental results show that when the load of copper is 3 mmol/g, the sorbent has the best desulfurization performance, and the saturated adsorption capacity is 0.086mmol S G - 1 adsorbent, which is better than that of MIL-101 (Cr) without the active component.
Keywords: MIL-101Cr, Cu (I), Cu (II), oxidation-reduction, new adsorbent.
目录
摘要 I
Abstract I
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1引言 1
1.2吸附分离基础 1
1.2.1 吸附类型 1
1.2.2 吸附机理 2
1.3金属有机骨架材料的研究进展 2
1.4 π络合吸附剂的研究进展 4
1.4.1 制备方法 4
1.4.2 络合吸附剂的类型 5
1.5络合吸附剂的应用 7
1.5.1 烯烃和烷烃的吸附分离 7
1.5.2 燃料油中的噻吩类化合物的吸附脱除 7
1.5.3 一氧化碳的分离和提纯 8
1.5.4 其他应用 9
1.6 本文的研究意义和内容 9
第二章 实验部分 10
2.1 实验材料 10
2.2 制备吸附剂 11
2.2.1 MIL–101(Cr)的合成 11
2.2.2 CuCl@ MCr的合成 12
2.3 样品表征 12
2.3.1 X射线衍射 12
2.3.2 比表面积和孔结构 12
2.3.3 傅立叶变换红外光谱分析 13
2.3.4 固体紫外-可见漫反射光谱 13
2.3.5 热重分析 13
2.3.6 X射线光电子能谱 13
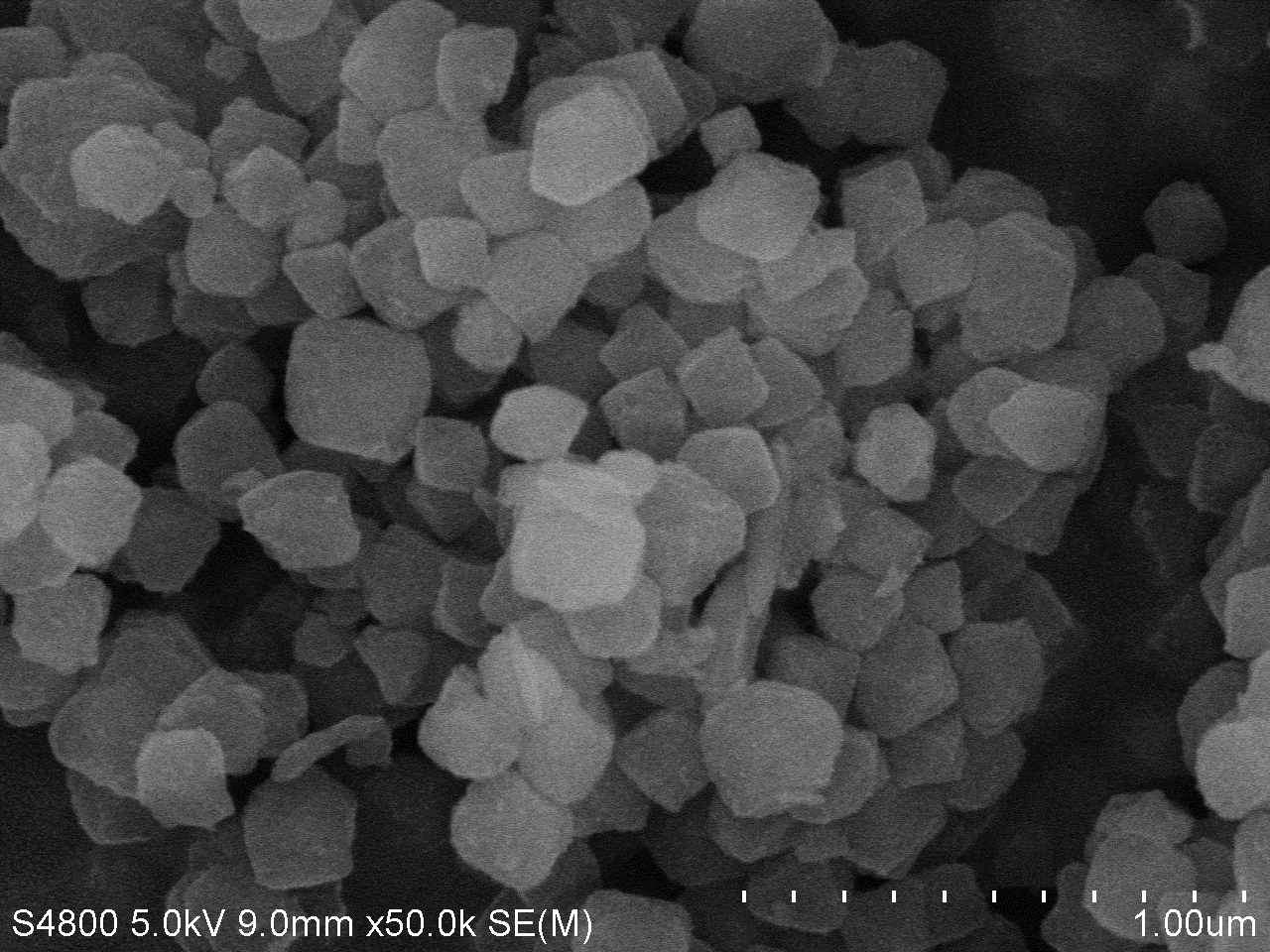
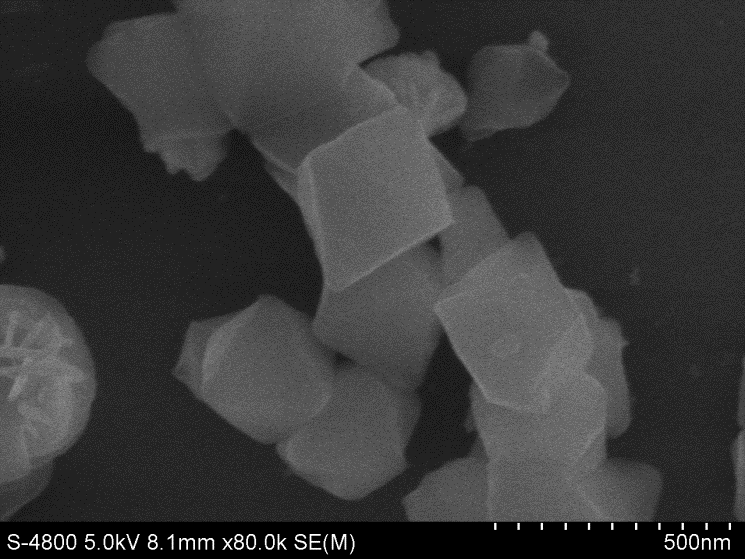
2.3.7 扫描电子显微镜 13
2.3.8 滴定法测定样品中Cu(I)的含量 14
2.4 吸附脱硫性能测试 15
2.4.1 模型溶液配置 15
2.4.2 吸附实验方法 15
第三章 实验结果与讨论 16
3.1 引言 16
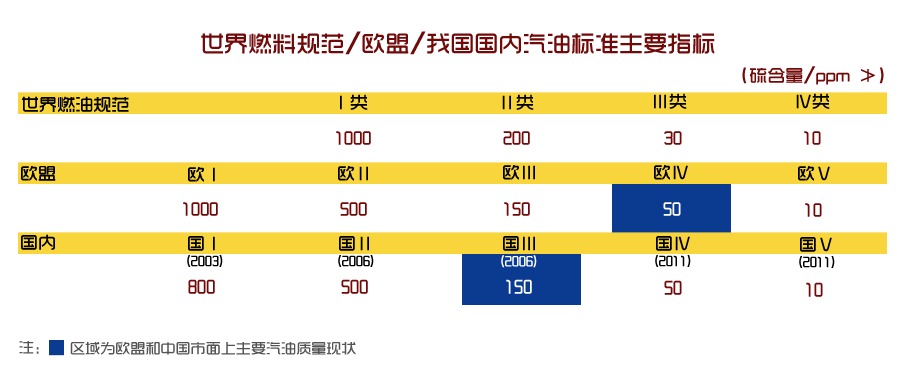
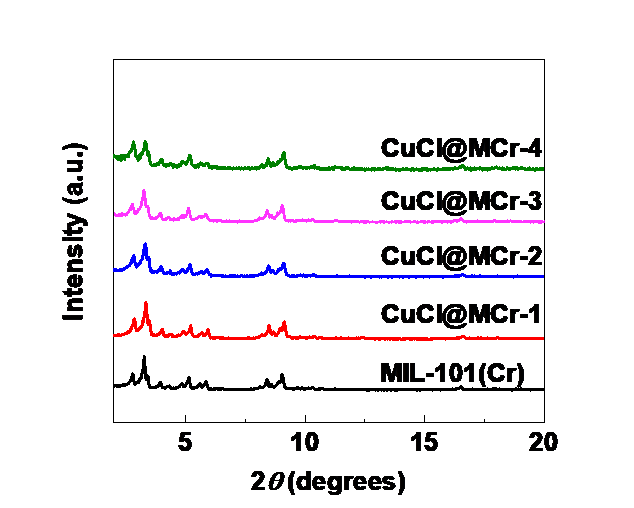
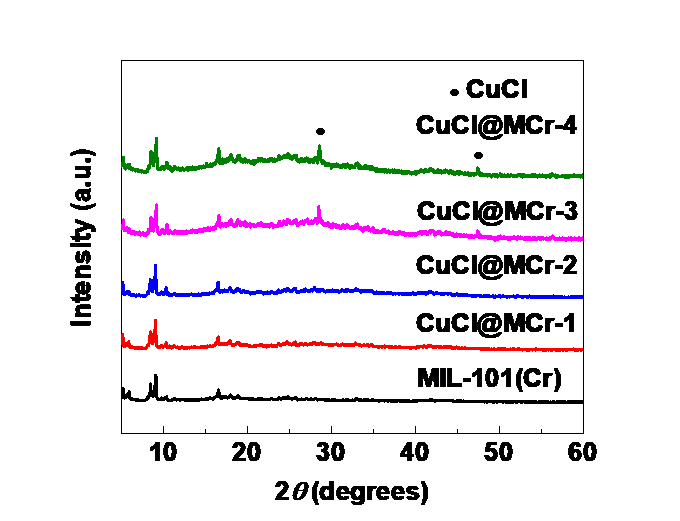
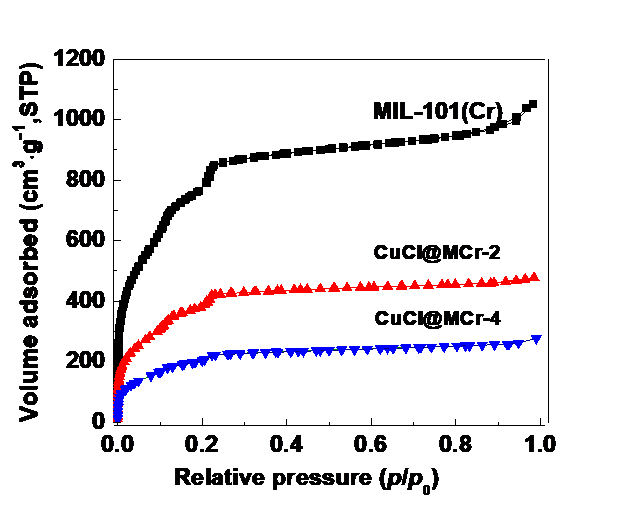
3.2 吸附剂的表征结果 16
3.3 吸附剂中Cu(II)的还原 19
3.4 吸附剂吸附脱硫性能 20
3.5 本章小结 22
第四章 结论与展望 24
4.1 结论 24
4.2 展望 24
参考文献 26
致 谢 29
文献综述
1.1引言
本论文主要以金属有机骨架MIL-101(Cr)为载体,设计新颖的功能化方案来引入活性组分Cu(I),从而制备出高效的新型的选择性吸附剂。
在化工生产过程中,吸附分离法是一种常见的分离方法。吸附分离技术的核心集中于开发高性能的吸附剂[1]。沸石、活性氧化铝、活性炭等是目前使用较为广泛的吸附剂[2]。基于其大比表面积和多孔结构的特性,这些类型的吸附剂主要是通过物理吸附的筛分效应来实现对吸附质的吸附作用。
本文针对上述问题,采用双溶剂法,利用MOFs内外部亲水性的不同,通过毛细作用,使得活性组分完全进入载体的孔道内,提高吸附剂的吸附性能。
首先,金属有机骨架材料MIL-101(Cr)为载体,采用双溶剂法,将前驱体Cu(II)完全引入MIL-101(Cr)孔内,再采用液相还原法结合双溶剂法,选择性地还原Cu(II),得到吸附剂Cu(I)@MIL-101(Cr)。这种方法实现了传统方法难以实现的在温和条件下有效得得到MOFs孔道内高度分散的Cu(I)。
1.2吸附分离基础
1.2.1 吸附类型
吸附是传质的过程,其主要原理是由于单组分或多组分在界面中的浓度有差异,从而发生了吸附现象。大致把吸附的类型简单的分为三种:第一种,物理吸附、第二种,化学吸附、第三种,选择性吸附。
相关图片展示: