石墨烯纤维布复合气凝胶的制备及性能毕业论文
2020-07-11 18:20:02
摘 要
石墨烯是碳的一种异形体,自2004年被发现以来,由于其高电子迁移率,高比表面积(2630m2/g)和高透明度等特性,在碳材料领域得到了广泛关注。然而,由于石墨烯片层之间存在着强烈的π-π键和范德华力,使得氧化石墨烯很容易发生团聚,导致它实际的比表面积远低于理论比表面积,极大地降低了吸附性能,较难应用。本文通过二维石墨烯的自组装将石墨烯结构三维化,以增强其孔隙率和疏水性能,有效地缓解团聚现象,制备出一种对CCl4的吸附量达到148g/g的石墨烯气凝胶材料,这对于石墨烯吸附性能的研究具有重大意义。以氧化石墨烯为原料,将其还原,可制备出具有三维网络结构的石墨烯气凝胶作为吸附剂,通过与不同的物质进行复合反应,对比研究其密度、吸附倍数等性能,找出最佳制备方法,得到实现对不同吸附质的快速吸附,在水处理和环境保护等领域有重大意义。本文采取MTMS作为硅源来复合石墨烯/PTFE气凝胶,得到对NMP吸附量为10.87g/g, 环己烷9.24 g/g,乙醇8.32g/g的气凝胶材料,由于其良好的吸附性和较为经济的生产成本,有望投入产业化生产。
关键词: 石墨烯 氧化还原 三维结构 吸附
Preparation and Properties of Graphene/PTFE Composite Aerogels
Abstract
Graphene is a carbon isoform. Since its discovery in 2004, graphene has attracted wide attention in the field of carbon materials because of its high electron mobility, high specific surface area (2630 m2/g), and high transparency. However, due to the strong π-π bonds and Van der Waals forces between the graphene sheets, the graphene oxide is easily agglomerated, resulting in its actual specific surface area far below the theoretical surface area, which greatly reduces the adsorption performance and makes it harder to apply. In this paper, the graphene structure is three-dimensionalized by two-dimensional graphene self-assembly to enhance its porosity and hydrophobicity, and the agglomeration phenomenon is effectively mitigated. A graphene aerogel material with an adsorption capacity of 148 g/g for CCl4 is prepared , which have great significance for the study of the adsorption properties of graphene. Using graphene oxide as a raw material and reducing it, a graphene aerogel with a three-dimensional network structure can be prepared as an adsorbent. Through the composite reaction with different substances, the density, adsorption multiple and other properties can be compared to find out the most. The good preparation method realizes rapid adsorption of different adsorbates, and has great significance in the fields of water treatment and environmental protection. In this paper, MTMS is used as a silicon source to compose graphene/PTFE aerogels, and an aerogel material with an NMP adsorption capacity of 10.87 g/g, cyclohexane 9.24 g/g, and ethanol 8.32 g/g is obtained due to its good Adsorptive and relatively economical production costs are expected to be put into industrial production.
Key Words: Graphene; Redox; Three-dimensional structure; Adsorption
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2石墨烯气凝胶的介绍 2
1.3石墨烯气凝胶的制备方法 2
1.3.1 化学还原自组装法 2
1.3.2 模板法 2
1.3.3 化学交联组装法 3
1.4 石墨烯气凝胶的应用 3
1.4.1吸附剂 3
1.4.2催化剂 3
1.4.3超电导材料 3
1.4.4储氢材料 3
1.5 研究目的和内容 4
1.5.1 研究目的 4
1.5.2 研究内容 4
第二章 实验部分 5
2.1 实验药品与实验仪器 5
2.1.1 实验药品 5
2.1.2 实验仪器 5
2.2 实验方法 6
2.2.1 石墨烯气凝胶的制备 6
2.2.2 GO/SiO2复合气凝胶的制备 7
2.2.3 石墨烯/PTFE复合气凝胶的制备 7
第三章 结果与讨论 8
3.1 表征手段 8
3.1.1 表观密度 8
3.1.2 拉曼光谱(Raman) 8
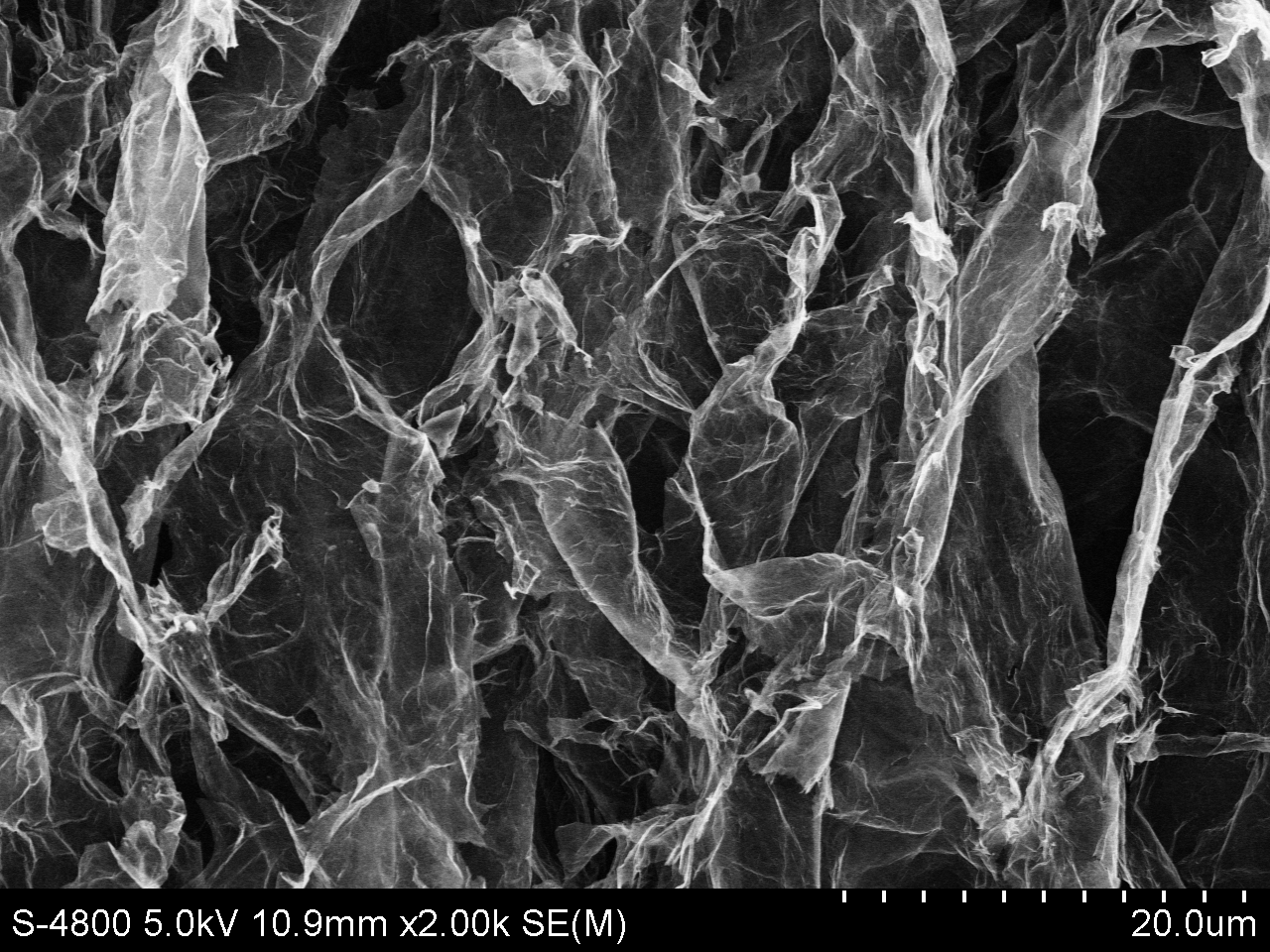
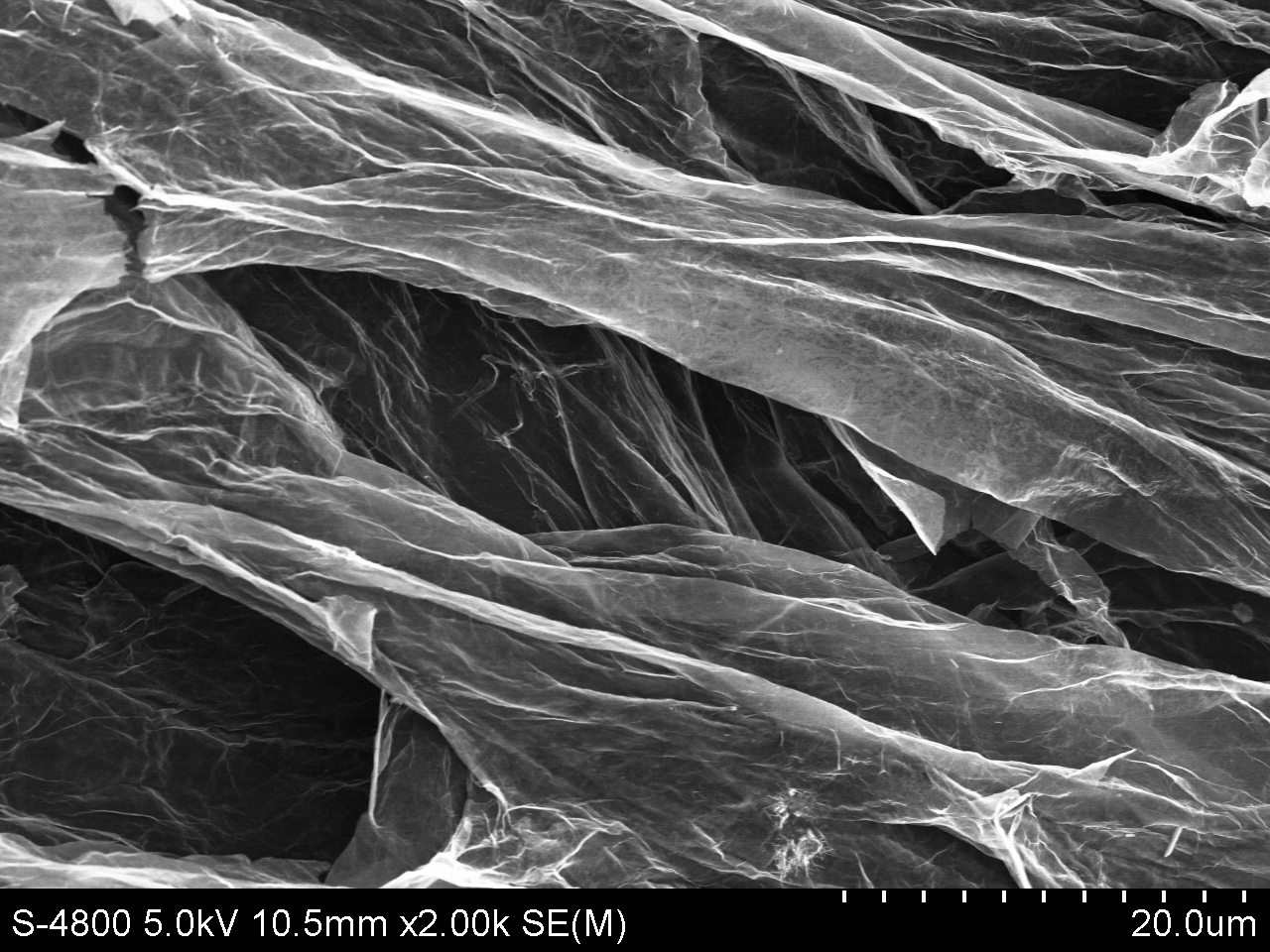
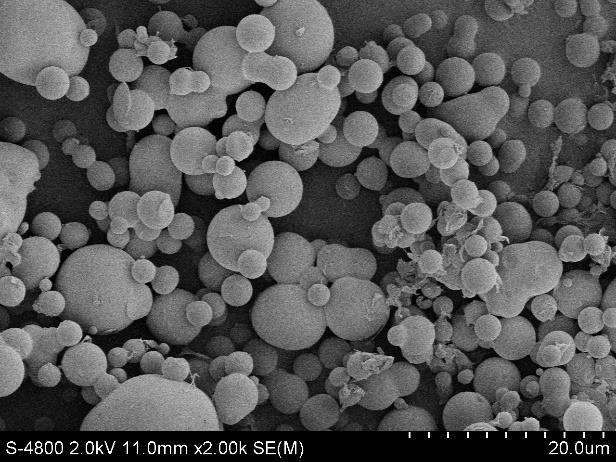
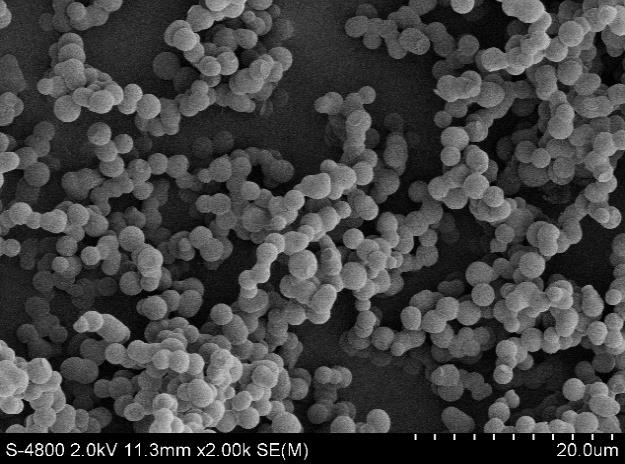
3.1.3 扫描电子显微镜(SEM) 8
3.1.4 傅立叶红外线光谱(FTIR)分析 8
3.1.5 比表面积和孔径分布测试 9
3.1.6 吸附率 9
3.2 石墨烯气凝胶材料制备结果与分析 9
3.2.1 密度分析 10
3.2.2 拉曼分析 11
3.2.3 SEM分析 11
3.3 GO/SiO2复合气凝胶材料的结果与分析 12
3.3.1 密度分析 12
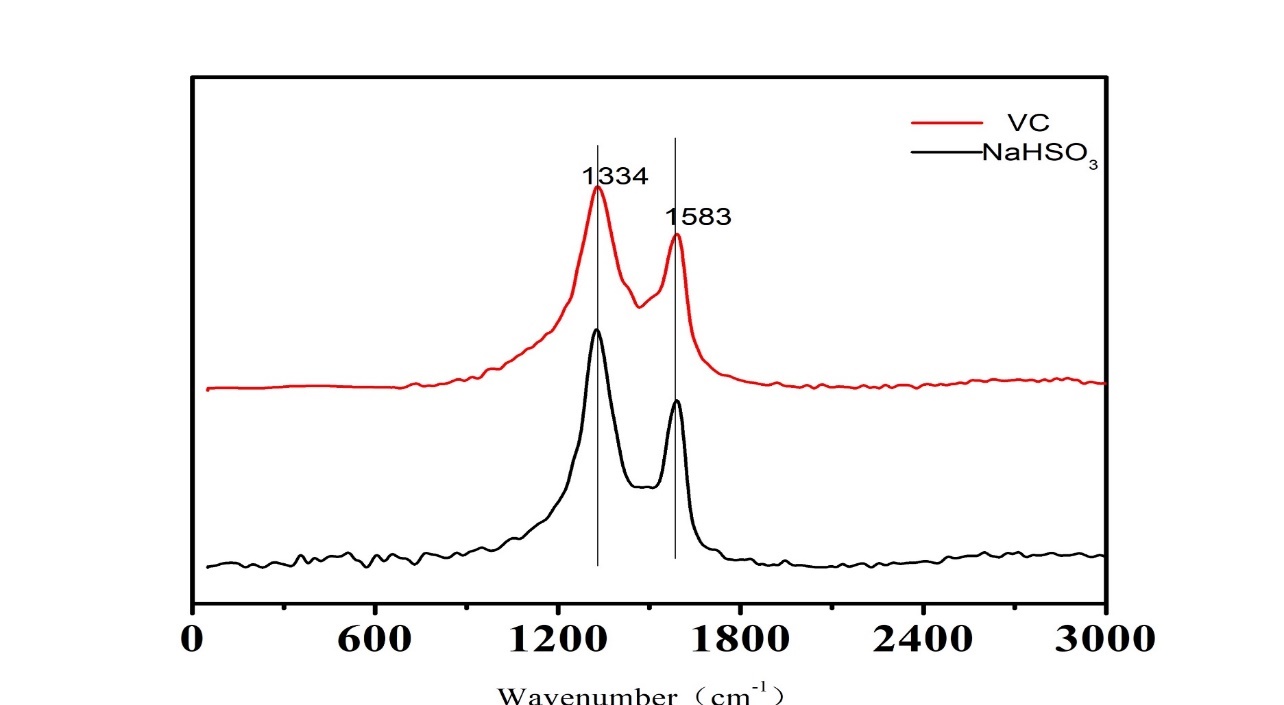
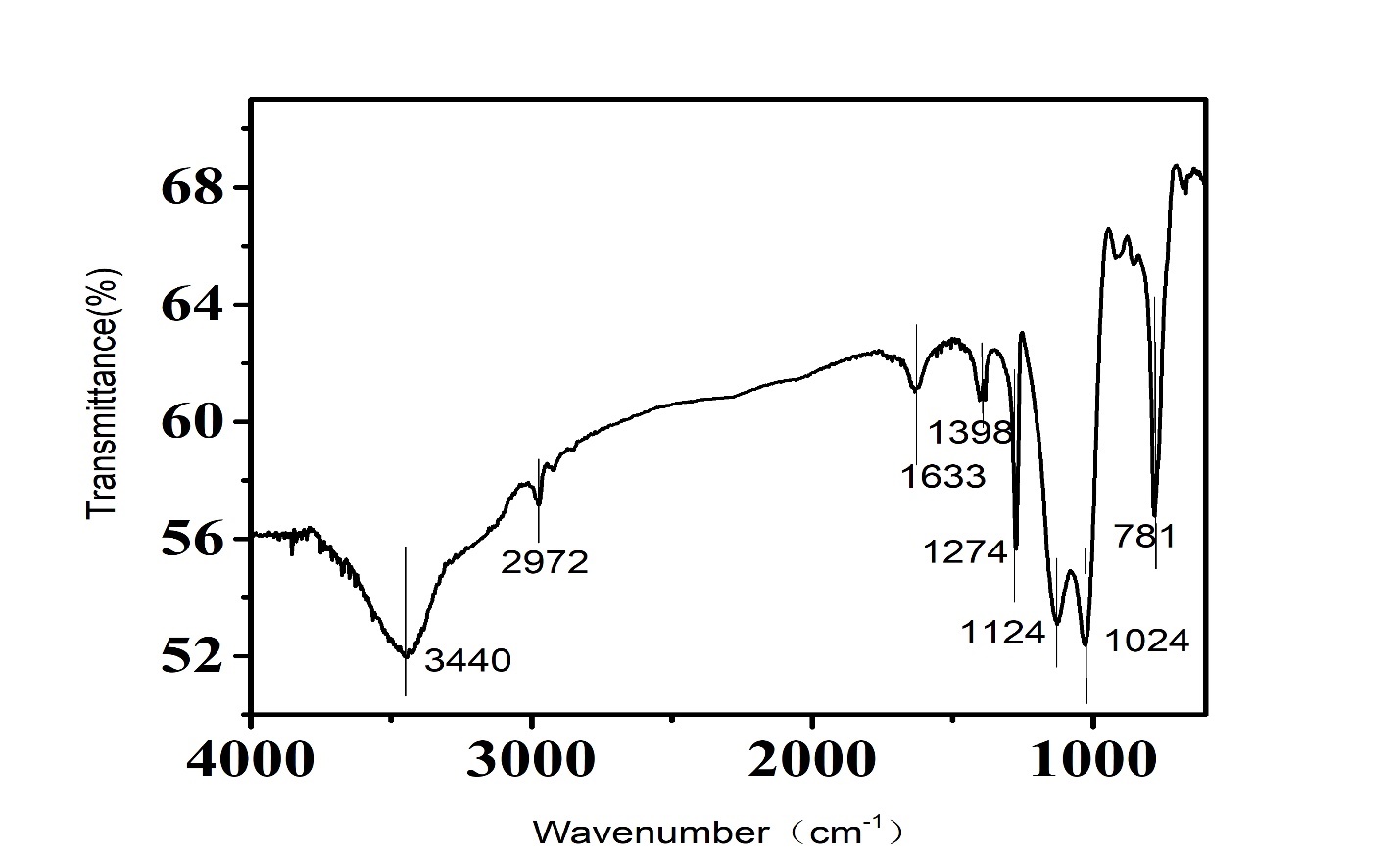
3.3.2 红外分析 13
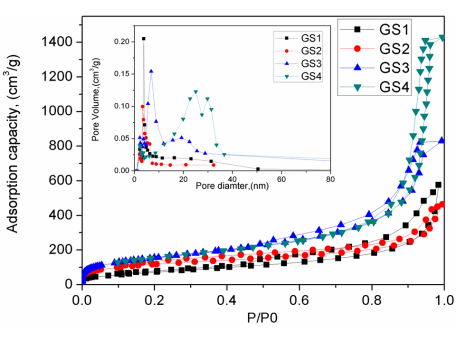
3.3.3 GO/SiO2气凝胶的比表面积和孔结构分析 13
3.3.4 SEM分析 15
3.3.5 吸附量分析 16
第四章 结论与展望 17
4.1 结论 17
4.2 展望 18
参考文献 19
致谢 21
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
气凝胶材料是一种三维网络结构的纳米级多孔骨架材料[1]。近几年来,受到科学家们的广泛关注。制备气凝胶的过程并不复杂:首先通过溶胶凝胶法制得水凝胶,然后采用乙醇等置换液进行溶剂交换,目的是除去水凝胶的网络结构中表面张力较大的溶剂分子,也就是所谓的老化过程,最后经过CO2超临界干燥将其干燥成气凝胶。气凝胶具有优异的物化特性,在吸附、催化等领域被广泛应用。
氧化石墨烯(GO)是纳米级碳材料,它具有二维片层状的平面结构[2]。理论上,GO的比表面积相当大,可达2630m2/g[3],同时拥有高达2998W·m-1·K-1的热导率和1050GPa的杨氏模量,具备很好的导热性能和力学性能。凭借其较高的比表面积和结构中所具有的大量官能团[4],GO在吸附水中的有机物和重金属等方面被赋予了极大地期望[5],但由于石墨烯的片层间存在着π-π键的堆叠,会产生极大的分子间作用力,这种作用大多是范德华力,范德华力的存在会使GO在水溶液中发生团聚[6],减小它的比表面积,因此GO在实际中比表面积数值远远小于理论值(2630m2/g),从而降低它的吸附性能。此外,在实际应用中,粉末状的石墨烯吸附剂很难进行分离,纳米尺寸的石墨烯还可能存在毒性。为了解决这些问题,研究人员试着将GO制备成气凝胶。
相关图片展示: