超分子凝胶在受限空间中的性能研究毕业论文
2021-03-13 22:24:52
摘 要
本文合成了一种凝胶因子:BDT(十二烷基-Boc-L-酪氨酸),以BDT为原料制备了超分子凝胶,通过光学显微镜观察BDT在非受限空间的自组装行为,发现BDT自组装形成树枝状纤维,随机取向生长,这些纤维互相缠结、搭接,最后形成网络状结构。同时,本文将BDT和SA(海藻酸钠)制备成复合凝胶,发现复合凝胶内部的自组装行为与BDT凝胶类似,但在BDT浓度相同的情况下,复合凝胶比BDT凝胶的凝胶化性能更好,内部具有更密集的网络状结构。
此外,本文通过软刻蚀法制备了PDMS(聚二甲基硅氧烷)微通道,和载玻片一起构成了微通道装置。通过光学显微镜,观察BDT凝胶和复合凝胶中的凝胶因子在微通道装置中的自组装行为,发现BDT也会自组装形成纤维,再由这些纤维构成网络状结构。但是在微通道中,纤维会沿着微通道内壁方向取向生长,纤维之间排列更紧密,网络状结构更加密实,所得凝胶的相转变温度应该比非受限空间的高。而复合凝胶由于具有物理-离子复合交联网络,其纤维更密集,网络状结构更紧密。
关键词:超分子凝胶;凝胶因子;自组装;受限空间
Abstract
In this paper, a gelator: BDT (Boc-O-docy-L-tyrosine) was synthesized and the supramolecular gel was prepared from BDT. The self-assembly behavior of BDT in unrestricted space was observed by optical microscopy , BDT self-assembly was found to form dendritic fibers, which were randomly oriented, and these fibers were tangled and overlapped to form a network-like structure. At the same time, BDT and SA (sodium alginate) were prepared into composite gel. It was found that the self-assembly behavior of the composite gel was similar to that of the BDT gel. However, when the BDT concentration was the same, the gelation of the composite gel was better than that of the BDT gel, its internal has a more dense network-like structure.
In addition, PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) microchannels were prepared by soft etching, and the microchannels were formed together with slides. The self-assembly behavior of the gelator in the BDT gel and the composite gel in the microchannel device was observed by an optical microscope. It was found that the BDT will also form fibers self-assembly, and then the fibers constituted a network structure. However, in the microchannel, the fibers grow along the direction of the microchannel inner wall, the fibers are arranged more closely, the network structure is more compact, and the phase transition temperature of the resulting gel should be higher than that of the unrestricted space. Because of the physical - ion composite cross - linking network, the composite gel’s fiber is more intensive, and the composite gel have more compact network structure.
Key words: Supramolecular gel; geltors; self - assembly; confined space
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 凝胶 1
1.1.1 凝胶的定义 1
1.1.2 凝胶的分类 1
1.2 超分子凝胶 2
1.2.1 超分子凝胶的定义 2
1.2.2 超分子凝胶的结构 3
1.3 超分子水凝胶 4
1.3.1 超分子水凝胶 4
1.3.2 超分子水凝胶的应用 4
1.4 水凝胶因子 6
1.4.1 传统两亲的表明活性剂分子 7
1.4.2 双头基表面活性剂分子 7
1.4.3 双电荷表面活性剂分子 7
1.4.4 双组份体系 8
1.5 双组分凝胶 8
1.6 微通道 8
1.7 本论文的研究意义和主要内容 10
第2章 实验部分 11
2.1 非受限空间中凝胶因子的自组装 11
2.1.1 凝胶因子的合成制备 11
2.1.2 样品制备 13
2.1.3 热学性能 14
2.2 受限空间中凝胶因子的自组装 14
2.2.1微通道的制作 14
2.2.2样品制备 17
第3章 实验结果及分析 18
3.1 超分子凝胶相转变温度 18
3.2 非受限空间中凝胶因子的自组装 18
3.3 受限空间中凝胶因子的自组装 20
第4章 结论 22
参考文献 23
致谢 26
第1章 绪论
1.1 凝胶
1.1.1 凝胶的定义
凝胶是一种常见的物质形态,自然界中有许多东西都属于凝胶体系,比如我们常见的豆腐、琼脂、魔芋胶等,但凝胶并没有一个让所有人都接受的准确定义。接受范围最广的是Flory的说法,他认为凝胶体系至少要满足两个最基本的要求:(1)体系具有宏观尺寸的连续结构,并且在一定的时间内这种结构具有相对的稳定性 (2)体系具有类似于固体物质的流变力学行为[1]。这一概念比较全面和准确,接受范围最为广泛。凝胶同时具有固体和液体的某些性质,也具有一些独有的特性,不同于固体和液体,比如凝胶具有刺激响应性,当温度或pH改变,凝胶体系会相应于这些变化做出相应的改变。当温度、pH值等外界条件或者溶剂改变时,凝胶内部的微观结构也会发生改变的,导致凝胶宏观物理化学性质发生改变,从而使得凝胶体系功能化,因此凝胶被广泛地应用于各个领域。
1.1.2 凝胶的分类
凝胶的分类方法比较多,按照合成凝胶的原料来源可分为天然凝胶和人工合成凝胶,大部分天然凝胶都是一些糖类或蛋白衍生物(如琼脂、淀粉、胶原质、白明胶)与水形成的水凝胶;根据凝胶内部连续相的不同,可分为有机凝胶、水凝胶、气凝胶、离子液体凝胶;根据分子构成的不同,可分为无机颗粒凝胶、小分子凝胶、大分子凝胶;按照凝胶内部交联方式的不同,凝胶可分为物理凝胶和化学凝胶。详细的分类参见图1-1[2]:
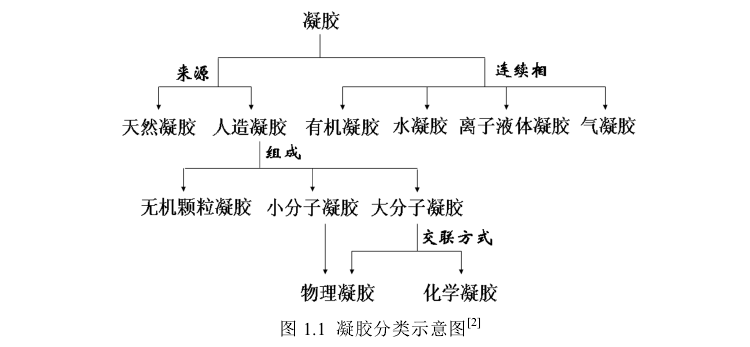 图1-1 凝胶分类[2]
图1-1 凝胶分类[2]
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 可聚合高分子模板增强制备高耐久超疏水涂层文献综述
- PVC/ABS合金的制备及性能研究开题报告
- 设计具有增强的赝电容及电催化性能的Co3O4/NiCo2O4双壳纳米笼结构外文翻译资料
- 光子上转换手性液晶:显著放大的上转换圆偏振发光外文翻译资料
- 氧空位型LiV3O8纳米片的快速稳定储锂性能研究外文翻译资料
- 应用于高性能钙钛矿太阳能电池的电子传输层的前体工程外文翻译资料
- 复合材料科学与技术 ——含碳纳米管的多孔导电弹性体复合材料悬浮在共连续聚合物的狭窄孔隙中的混合纳米复合材料外文翻译资料
- 一种用于先进锂硫电池源自聚罗丹宁纤维素的氮硫双掺杂碳外文翻译资料
- 短玻璃纤维增强聚丙烯控制界面和力学性能参数外文翻译资料
- 含Ca0的LaCO.0H纳米齿轮及其发光和脱NOx性能外文翻译资料




