填充床介质阻挡放电中流注发展过程的PIC/MCC模拟毕业论文
2021-12-02 13:04:37
论文总字数:22324字
摘 要
目前,对介质阻挡放电的研究大多集中在等离子催化这个新领域。等离子体协同催化介质阻挡放电由于结合了等离子体的高反应性和催化剂的选择性,在环境保护和污染物处理方面有着重要的应用。现在有很多工作研究了各种参数对放电的影响,包括有:顶部电压幅值、介质材料、放电间距等,但控制流注传播方向却没有得到研究。能控制流注的传播方向对如何更高效地得到大量的活性等离子体,提高等离子体催化的效率具有重要意义,进而也可以补充和完善填充床介质阻挡放电完整的放电机理。
本文通过利用PIC/MCC数值模拟的方法分别探讨了侧边电压以及侧边电极对填充床介质阻挡放电中流注发展的影响,完善了流注传播的控制问题。
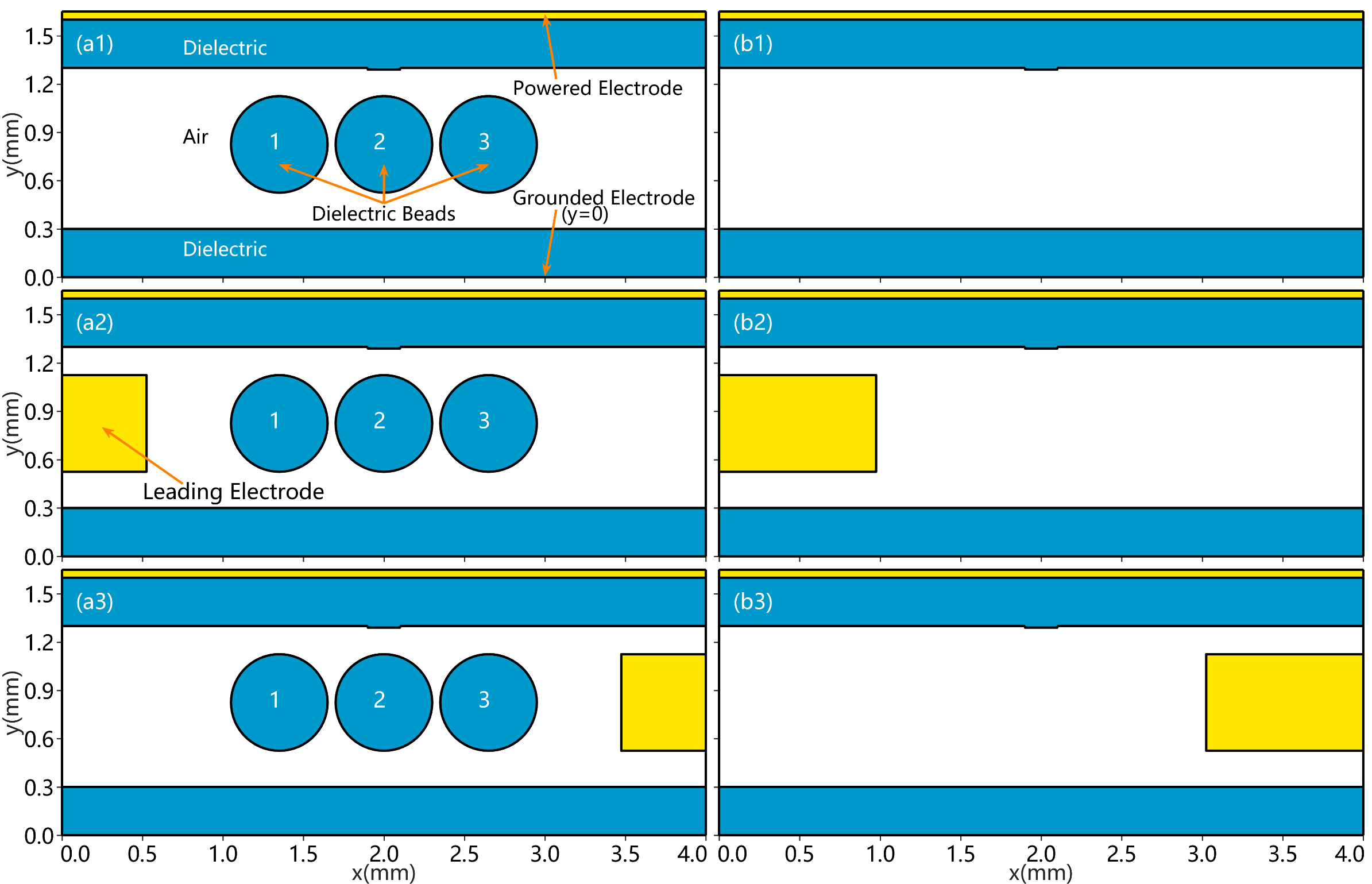
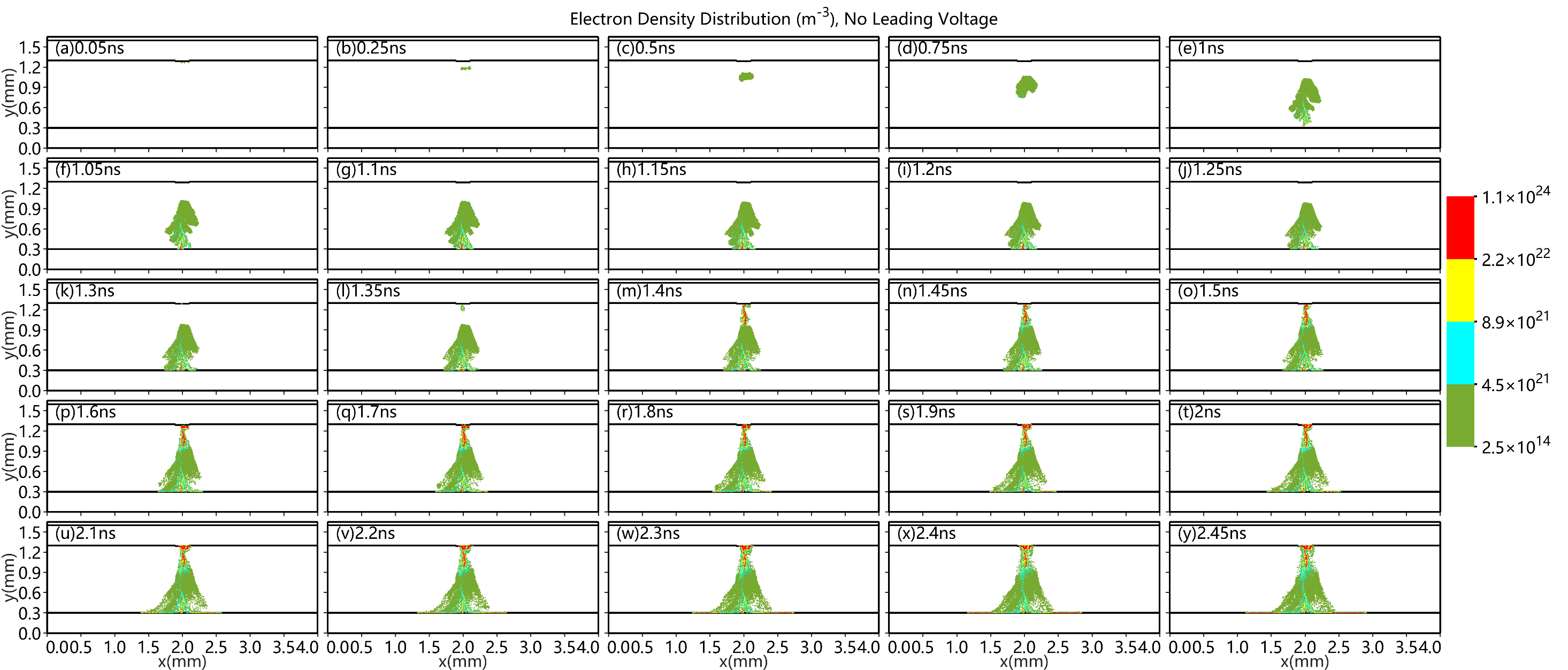
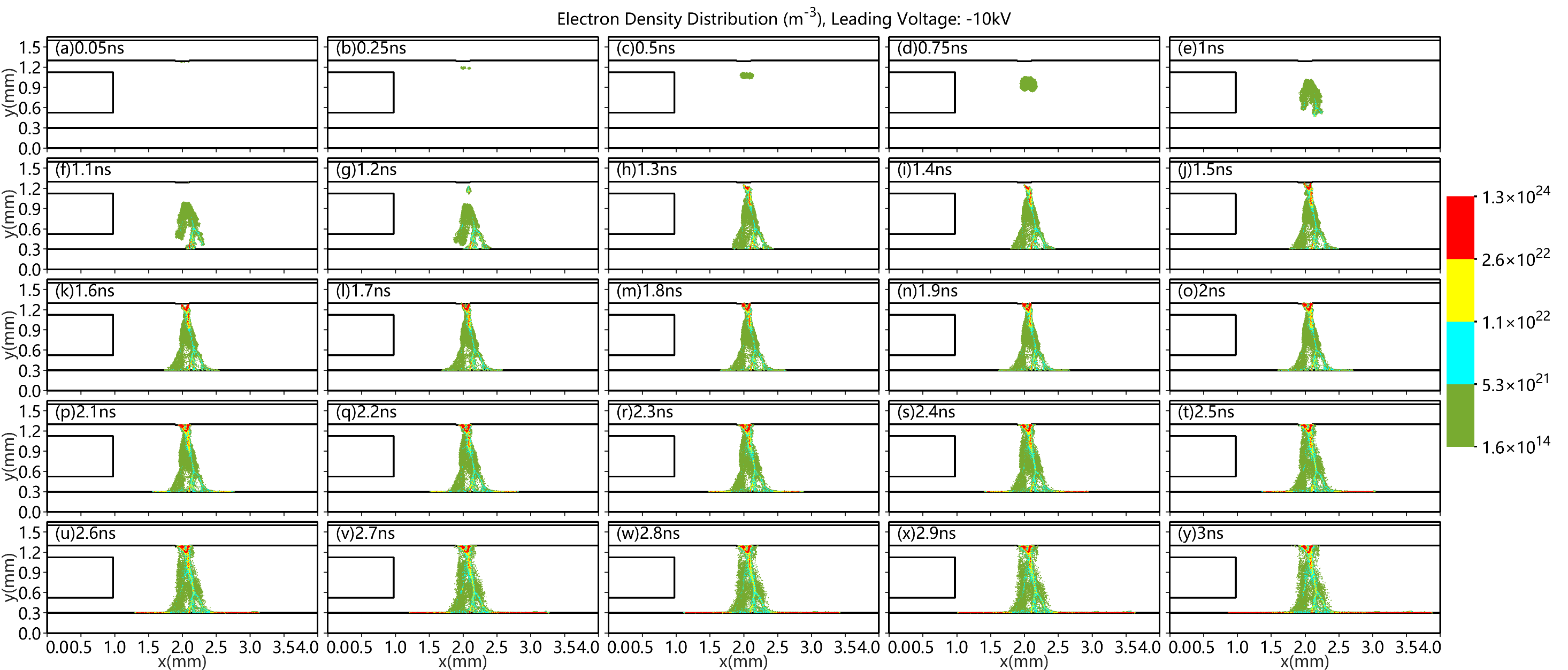
第一,使用二维显式PIC/MCC方法分别探讨填充介质球以及侧边电压对放电过程中流注的影响。通过对比几组PB-DBD反应器内电子密度的时间演化图,发现:(1)介质球的存在使带电粒子更集中在介质球的间隙和表面,使等离子体局部粒子密度变大,产生更多的活性粒子;(2)侧边电压越大,流注的传播通道越窄,偏转越明显;(3)即使侧边电压的大小相同,但侧边电极为正时流注的偏转效果更好。所以调节侧边电压的大小和方向可以控制流注的发展方向。
第二,为了设置最适合控制流注发展方向的装置参数,同样使用二维显式PIC/MCC方法探讨侧边电极的长度、宽度以及介质球的大小对放电过程中流注的影响。通过对比电子密度—时间的模拟图,发现:(1)侧边电极越短,流注越向中间分散发展,也就是偏转效果越弱,但侧边电极很长时,会发生丝状放电,不能形成狭窄的流注通道;(2)两倍介电球半径是比较合适的侧边电极宽度,流注通道最窄;(3)介质球越大,流注越集中在间隙两侧,流注通道越窄,偏转方面区别不大。所以,设置适当的侧边电极以及介质球的尺寸有利于控制流注的发展。
关键词:介质阻挡放电; PIC/MCC数值模拟;流注控制。
Abstract
Most of the research on dielectric barrier discharge is concentrated in plasma catalysis, a new field with important applications in pollutant disposal. Plasma synergistic catalytic barrier discharge effectively combines the selectivity of catalytic materials with the high activity of plasma.A lot of work has been done to investigate the effects of different parameters on discharge such as amplitude of top voltage, dielectric material and discharge gap, but none of them discussed how to control the direction of streamer propagation. In fact, the ability to control the direction of streamer propagation has important implications for obtaining a large number of active plasmas more efficiently and improving the efficiency of plasma catalysis.
To optimize the control of streamer propagation, the effects of side voltage and side electrode on streamer propagation during dielectric barrier discharge of packed bed were investigated by means of PIC/MCC numerical simulation.
First, a two-dimensional explicit PIC/MCC method was used to investigate the effects of dielectric sphere and side voltage on streamer during discharge. By comparing the time evolution of electron density in several PB-DBD reactions, it was found that: (1) due to the presence of dielectric sphere, charged particles were more concentrated in the gap and surface of sphere. As a result, more active particles were produced along with the increase in local particle density of plasma; (2) larger side voltage led to narrower channel of streamer propagation and more obvious deflection of streamer path; and (3) streamer showed a better deflection effect in the case of positive side electrode, even if the side voltage remained the same. Therefore, the direction of streamer propagation can be controlled by adjusting the value and direction of side voltage.
Second, for setting the suitable parameters of the equipment, the same method was also used to discuss how the length and width of side electrode and the size of dielectric sphere affect the streamer during discharge. By comparing the simulated diagram for the change of electron density over time, it was found that: (1) as the length of side electrode decreased, the streamer moved closer to the center, namely the deflection effect weakened; (2) The narrowest channel of streamer occurred when the width of side electrode was twice the radius of dielectric sphere; and (3) as the dielectric sphere became larger, the streamer was more concentrated on both sides of the gap and no significant change in deflection was found. Therefore, setting appropriate-sized side electrode and dielectric sphere is beneficial to the control of streamer.
Key words: dielectric barrier discharge; PIC/MCC numerical simulation; streamer control.
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1低温等离子体的简介 1
1.2介质阻挡放电 1
1.2.1常见的气体放电 1
1.2.2介质阻挡放电的放电机理 1
1.2.3 介质阻挡放电的构型 2
1.2.4 介质阻挡放电的研究进展 3
1.3 填充床介质阻挡放电及其研究进展 4
1.4 本文的研究意义以及结构安排 4
第2章 数值模拟 6
2.1 概述 6
2.2 PIC/MCC模型 6
2.2.1 PIC方法 7
2.2.2 MCC模型 8
2.3 PIC/MCC模拟的基本流程 8
2.3 采用VSIM软件完成PIC/MCC模拟 9
2.4 总结 10
第3章 探讨侧边电压对流注发展的影响 10
3.1 构建模型以及设置参数 11
3.2 探讨填充介质球对流注发展的影响 11
3.2.1 加入侧边电极后对放电的影响 11
3.2.2 填充介质球对流注的影响 14
3.3 侧边电压对流注发展的影响 14
3.3.1 改变侧边电压的大小 14
3.3.2 改变侧边电压的正负 16
3.4 总结 19
第4章 探讨侧边电极对流注发展的影响 19
4.1 侧边电极的长度对流注发展的影响 19
4.1.1 构建模型 19
4.1.2 模型结果与分析 20
4.2 侧边电极的宽度对流注发展的影响 22
4.1.2 构建模型 22
4.2.2 模拟结果与分析 22
4.3 介质球的大小对流注发展的影响 23
4.3.1 构建模型 23
4.3.2 模拟结果与分析 24
4.4 总结 25
第5章 总结 26
参考文献 27
附 录 29
致 谢 29
第1章 绪论
1.1低温等离子体的简介
等离子体是除了自然界中常见的固态、液态、气态以外的第四种物质聚集状态,常见于宇宙中的恒星中。有的等离子体电子温度一般超过一万电子伏特被称为高温等离子体,比如恒星的聚变反应、太阳风等;有的等离子体电子温度一般小于几十电子伏特被称为低温等离子体[1]。
目前,在实验室和工厂获取低温等离子体的方法除了经常用到的气体放电(比如:压电直接放电、介质阻挡放电等),也有光电离法、射线辐射等方法。根据热平衡的条件,低温等离子体可以分为热等离子体和冷等离子体。热等离子体处在热平衡的状态,比如自然界中的闪电、高频感应等离子体等;冷等离子体没有实现热平衡的状态,比如南北极上空的极光、二氧化碳红外激光器等。
非热平衡等离子体的气体密度一般为1014-1019m-3,因为粒子和电子的碰撞几率很低,同时非热平衡等离子体离子温度一般为300K,电子温度一般为1ev-10ev,所以冷等离子体的温度一般只需考虑离子温度。
低温等离子体在现代工程、实验室研究以及工业建设方面有着广泛的应用:(1)通过外加电磁场改变低温等离子体的能流运动方向来完成对半导体器件的注入和刻蚀[2]等。(2)因为低温等离子体不需要特定的高温就可以产生大量的活性粒子与带电粒子,所以能应用在材料的表面改性[3]以及环境保护,污染物处理[4]等方面。(3)在日常生活应用在LED显示屏以及居家照明设备等。(4)在工程建设领域应用等离子体焊接、切割、冶炼等。(5)在医学领域应用在杀菌消毒[5]和等离子体低温消融手术等。
1.2介质阻挡放电
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:22324字
相关图片展示: