氧化物在BaTiO3基陶瓷离子扩散及介电性能影响研究毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:34:22
论文总字数:27941字
摘 要
BaTiO3作为最早被发现的一种钙钛矿型铁电体,在室温下具有较高的介电常数(约1600左右),常被用作多层陶瓷电容器(MLCC)介质基体材料。近年来,电子信息产业的快速发展对电子设备的基本元件MLCC有了更高的要求,以此来提高电子设备在不同条件下的适应性。但是BaTiO3陶瓷存在介电常数随温度变化低等缺点,不可直接用作介质层材料,人们常常通过掺杂改性来提高BaTiO3陶瓷的性能,不同的掺杂材料对钛酸钡陶瓷的影响各异。
本文采用固相法来制备掺杂不同氧化物的原料粉体,经压制成型后排胶,在不同温度下烧结,测量陶瓷体积密度,得到体积密度最大的样品,即为烧结最致密的样品。对烧结好的样品进行X射线衍射分析(XRD)和扫描电子显微分析(SEM)测试,并对其介电性能进行测试。
实验结果表明,随着氧化锆和氧化镁掺杂含量的增加,改性效果越明显,居里峰被压得越低。XRD图谱表明氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷均为立方相,50nm氧化镁掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷和掺杂3%的200nm的钛酸钡基陶瓷物相结构也为立方相,而掺杂0.5%的200nm的钛酸钡基陶瓷物相结构为四方相。掺杂氧化锆的钛酸钡基陶瓷,介电损耗越小,介温稳定性就越高。而掺杂氧化镁的钛酸钡基陶瓷随着氧化镁粒径的增大介温稳定性也随之提高。对样品的微观形貌进行分析,发现不同粒径的氧化锆和氧化镁掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷对晶粒尺寸的影响区别不大。
不同粒径的氧化镁或氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡,陶瓷样品的晶粒尺寸不会发生明显变化;不同含量的氧化镁或氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡对陶瓷的晶粒尺寸也不会产生明显影响。随着掺杂氧化物粒径的增大,钛酸钡基陶瓷在居里温度的介电常数随之降低。
关键词:钛酸钡;不同氧化物;不同粒径;“核-壳”结构;介电性能;晶粒尺寸
Abstract
BaTiO3(BT), as one of the earliest perovkite-type ferroelectrics discovered, has a high dielectric constant (about 1600) at room temperature and is often used as a matrix material for multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCC).In recent years, the rapid development of electronic information industry has higher requirements on MLCC, the basic component of electronic equipment, so as to improve the adaptability of electronic equipment under different conditions.However,BT ceramics has the disadvantage of low dielectric constant changing with temperature, which cannot be directly used as a dielectric material. Doping modification is popular method toimprove the performance of BT ceramics , and different doping materials have different effects on BT ceramics.
In this paper, the solid state method was used to prepare BT powder doped with different oxides, which was pressed into shape and then sintered at different temperatures. The volume density of BT was measured, and the sample with the largest volume density was obtained.The BT –based samples were tested by X ray diffraction(XRD) and Scanning electron microscope(SEM), and their dielectric properties were also tested.
The experimental results show that with the increase of oxide coating content, the more obvious the modification effect is, the lower the Curie peak is.XRD patterns showed that zirconia doped BaTio3 ceramics were all cubic phase, 50nm magnesium oxide doped BaTio3 ceramics and 3% doped BaTio3 ceramics were also cubic phase, while 0.5% doped BaTio3 ceramics were tetragonal phase.The lower the dielectric loss is, the higher the mesothermal sta bility is.The mesothermal stability of barium titanate ceramics doped with magnesium oxide increased with the size of magnesium oxide.The effect of zirconia and magnesium oxide doped barium titanate ceramics on grain size was not significant.
The grain size of ceramic samples did not change obviously when magnesium oxide or zirconia were doped with barium titanate.Different contents of magnesium oxide or zirconia doped barium titanate did not significantly affect the grain size of ceramics.With the increase of doped oxide particle size, the dielectric constant of batio3 ceramics decreased at Curie temperature.
Key words: Barium titanate;Different oxides;Different particle sizes;"Core-shell" structure;Dielectric properties;Grain size
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 BaTiO3结构、性能与改性机理 1
1.1.1 BaTiO3的晶体结构 1
1.1.2 BaTiO3的介电性能 2
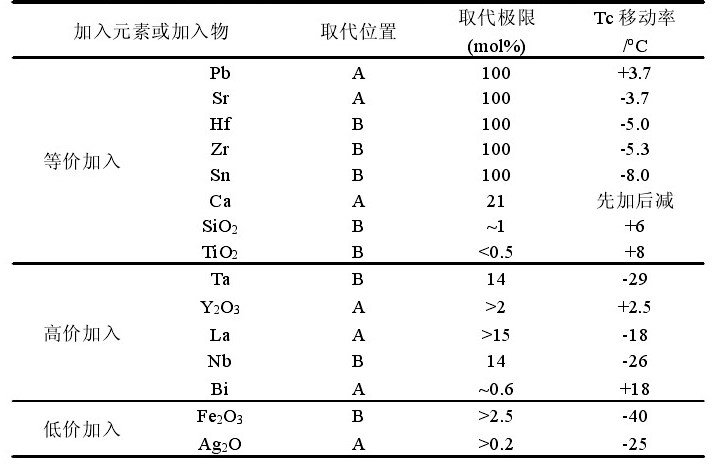
1.1.3 BaTiO3的改性机理 3
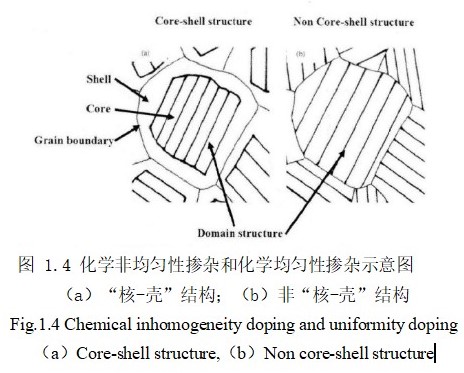
1.1.4 BaTiO3的“核-壳”结构(core-shell) 5
1.2 BaTiO3的掺杂改性技术 6
1.2.1 传统固相法 6
1.2.2 湿化学法 7
1.3 材料体系选择 7
1.4 论文研究目的及内容 7
第2章 BaTiO3基陶瓷的制备方法及其结构与性能测试 9
2.1 BaTiO3基陶瓷制备中的原料及仪器设备 9
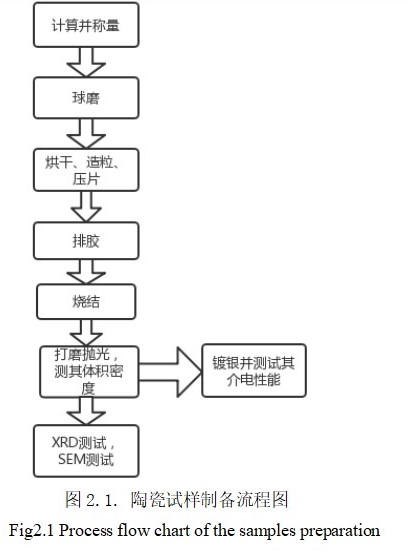
2.2 制备工艺 9
2.2.1 固相法制备不同氧化物掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷 9
2.3 测试方法与原理 11
2.3.1 体积密度 11
2.3.2 X射线衍射分析(XRD) 11
2.3.3扫描电子显微分析 12
2.3.4 能谱分析(EDS) 12
2.3.5 介电性能 12
第3章 不同粒径ZrO2掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的制备与表征 14
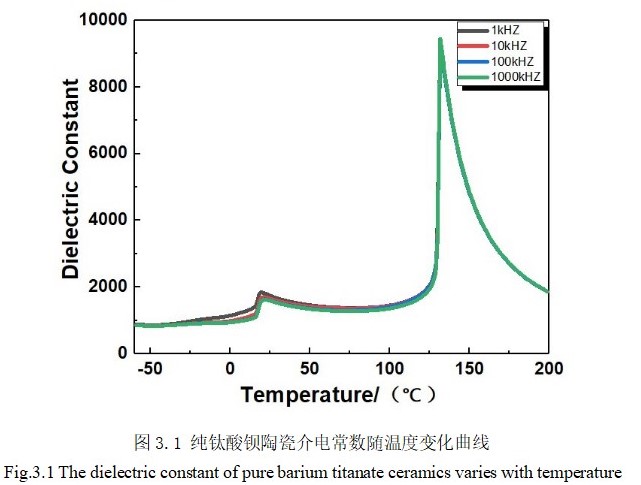
3.1 纯BaTiO3的介电性能 14
3.2 实验路线 14
3.3 不同粒径氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的物相结构与显微形貌 16
3.3.1 50nm氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷物相结构与微观形貌 16
3.3.1.1 物相结构 16
3.3.2 100nm氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷物相结构与微观形貌 17
3.3.2.1 物相结构 17
3.3.3.1 物相结构 19
3.4 不同粒径氧化锆掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的介电性能 20
3.4.1介温谱 20
3.4.2 容温特性 22
3.5 本章小结 24
第4章 不同粒径氧化镁掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的制备与表征 25
4.1 不同粒径氧化镁掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的物相结构与显微形貌 25
4.1.1 50nm氧化镁掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的物相结构与显微形貌 25
4.1.1.1 物相结构 25
4.2 不同粒径氧化镁掺杂钛酸钡基陶瓷的介电性能 27
4.2.1 介温谱 27
4.3 容温特性 28
4.3 本章小结 29
第5章 结论 30
参考文献 31
致 谢 33
- 绪论
多层陶瓷电容器(MLCC)作为电子器件的一种基本元件,被广泛应用于微电子产品、汽车、航天工业等领域。随着电子产品换代更新速度的加快,人们对MLCC的需求也越来越大,MLCC的性能也必须能够适应不同环境。这就对MLCC的介质基体材料提出了更高的要求。
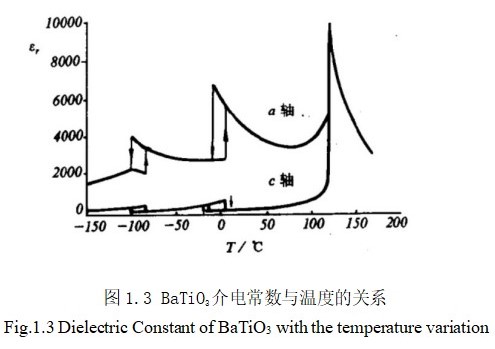
常见的作为MLCC的介质材料体系由钛酸钡体系、铅基钙钛矿体系、钨青铜结构体系。钛酸钡具有高介电常数、价格便宜等优点,因此较早被应用于多层陶瓷电容器的制备。但是,钛酸钡在居里点介电常数会发生突变,介电峰变得异常尖锐,温度超过130℃后,介电常数又会急剧下降,这些缺点使得钛酸钡不能直接被用作多层陶瓷电容器的制备。因此,人们不断地探索钛酸钡的改性方法,以此提高钛酸钡基陶瓷的温度稳定性。
- BaTiO3结构、性能与改性机理
- BaTiO3的晶体结构
- BaTiO3结构、性能与改性机理
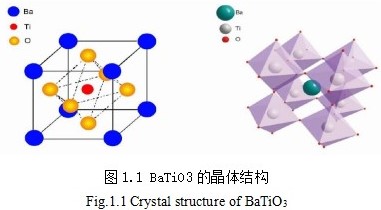
钛酸钡是一种拥有钙钛矿结构的物质,在一般情况下钛酸钡的晶体结构是立方晶系,如图1.1所示。在钛酸钡的晶体结构中钡离子与氧离子共同组成了面心立方堆积,钡离子、氧离子分别位于晶体结构中的顶角和面心,钛离子位于体心。钡离子、氧离子、钛离子-的配位数分别为12、6和6。钛离子占据八面体空隙的1/4。[TiO6]八面体共顶连接形成三维结构。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:27941字
相关图片展示: