氧化硅基高容量锂离子电池负极材料构筑毕业论文
2020-02-27 10:48:46
摘 要
目前商业化的锂离子电池主要采用石墨作为负极材料,但石墨有限的理论比容量(372mAh g-1)极大地限制了它的应用,越来越不能满足当今社会对高容量锂离子电池的需求,故开发一种可替代石墨的高容量的新型锂离子电池负极材料已经迫在眉睫。具有高比容量的SiOx负极材料相较于Si负极和石墨有一定的优势,也很有希望可以取代石墨负极材料形成下一代高容量锂离子电池负极材料。在商业化的SiO中其制备主要是通过气相硅和二氧化按计算出来的化学计量比混合在真空条件下高温制备得到的,其制备成本大,反应条件难以控制,Si/O比例也难以调控,所以提出一种新的合成SiOx的方法是很有意义的。
针对这些问题,本文以氧化硅基材料作为锂离子电池负极材料为研究对象,运用有机硅烷作为硅源合成有机硅材料并在高温中热解有机基团直接得到SiOx-C材料, 这种方法成本低廉,工艺简单,环境友好,且具有优异的氧化硅基负极材料电化学性能,同时为高容量氧化硅基负极材料的产业化提供了思路。本论文运用SEM,XPS,XRD,拉曼光谱手段研究了SiOx的微观结构特点,探究了结构-性能相关性,并部分解释了材料具有优异电化学性能的原因,之后尝试了将金属和金属有机框架与其复合并探索其电化学性能。主要研究结果包括如下:
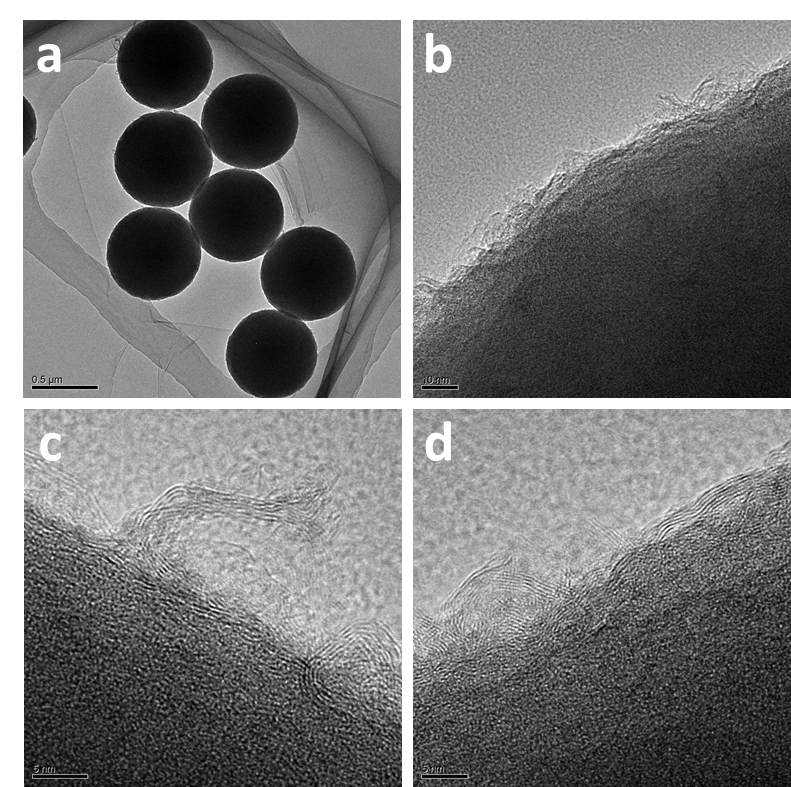
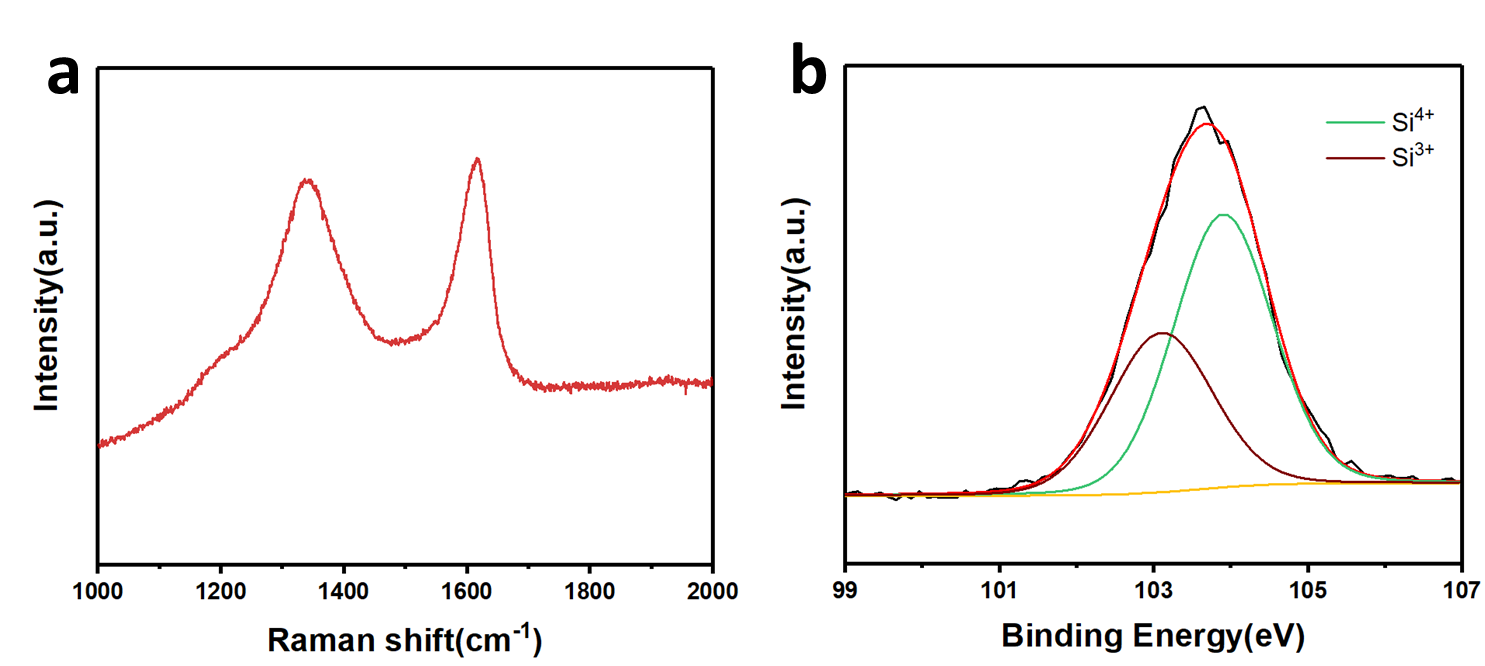
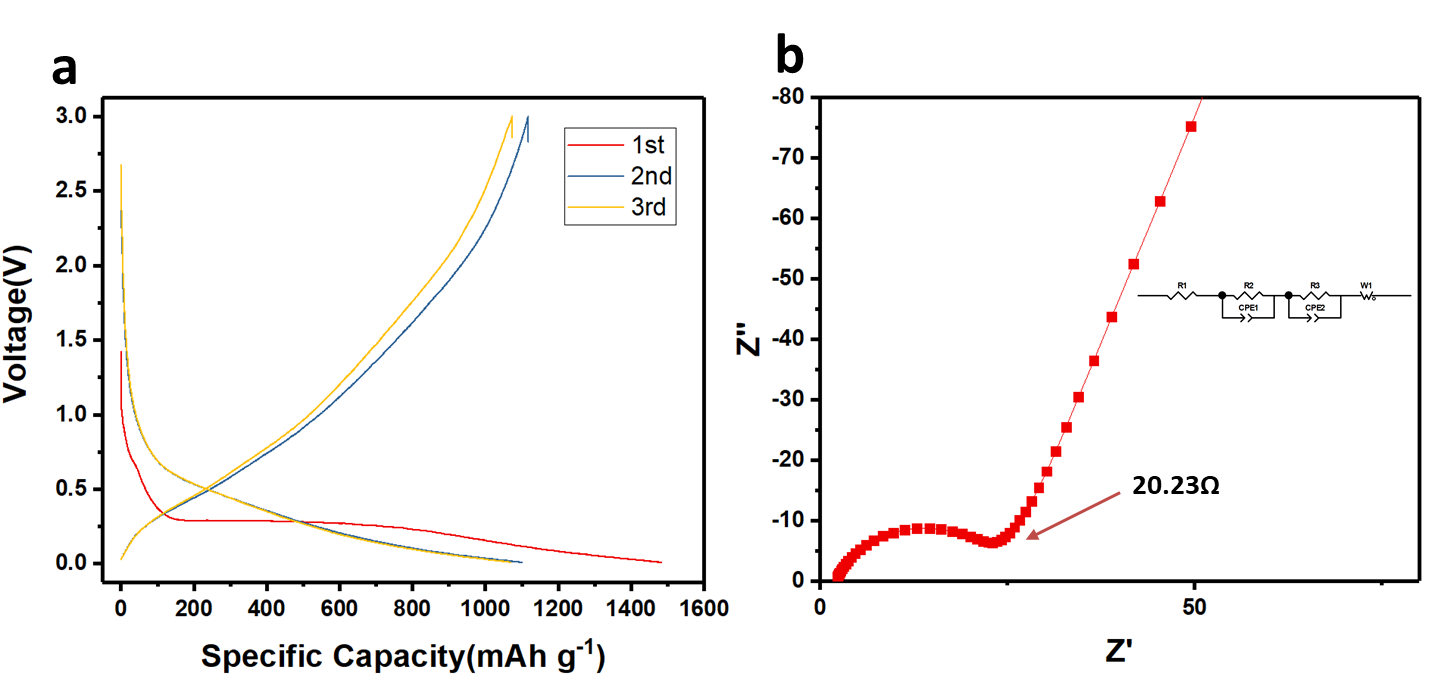
- 用stober法合成有机硅小球作为前驱体,经一步热解得到粒径400nm均一的SiOx-C小球,x值用XPS测试推测大约为1.81,拉曼结果显示D峰与G峰的比例较小,TEM图中可观察到明显的石墨晶格条纹,证明1000℃惰性气体烧结已经可以使碳有较高的石墨化程度,材料中的碳不仅可缓冲体积膨胀还可以提供良好的导电性;其电化学反应阻抗很小只有20.23Ω,SiOx-C小球负极材料有极高的首次库伦效率(74%),较高的可逆比容量,优异的循环性能和倍率性能,100mA g-1的电流密度下可逆比容量约为1000mAh g-1,在1A g-1的电流密度下,在循环300圈后依然有686.2mAh g-1的可逆容量,容量保持率高达97%。此材料合成成本低廉,工艺简单,环境友好,且有进行工业化生产的潜力。
- 将金属Sn与SiOx-C复合得到Sn/SiOx-C复合材料,通过一步惰性气体热解的方法在将有机硅材料碳化成SiOx-C的同时将Sn从氧化态还原成Sn直接形成Sn/SiOx-C复合材料。但合成Sn不和SiOx-C是在一个相里,前驱体合成部分还需再调控。Sn/SiOx-C在100mAh g-1下10圈后有709.2mAh g-1的可逆比容量,在1A g-1的电流密度下, 23圈后放电比容量为589.3 mAh g-1且呈现一个上升的趋势,且其中放电容量大于充电容量,推测是在循环过程中Sn与原本在硅基锂离子电池负极材料首圈产生的惰性的Li2O反应产生SiO2导致材料理论比容量上升所致。该材料合成成本低廉,工艺简单。
- 采用水热法合成了一种二维片晶在纵向搭接而形成的块体“书本状”铜基金属有机框架——对苯二甲铜。将带巯基的有机硅烷——γ-巯丙基三甲氧基硅烷与对“书状”结构有机框架通过Cu与S之间的强作用里相结合形成巯基有机硅烷包覆的对苯二甲铜金属有机框架,作为Cu/SiOx-C的前驱体,并因为Cu优异的导电性而具有合成优异循环性能负极材料的潜力。
关键词:氧化硅;碳掺杂;锂离子电池;负极材料;电化学性能
Abstract
Nowadays graphite is the most commonly used commercial lithium ion batteries anode material. However graphite with a low theoretical capacity of 372 mAh g-1 greatly restrict its improvement so long as our society develops currently. So it’s highly urgent to explore new anode material with high theoretical capacities to replace graphite in the next-generation high energy lithium ion battery. In preparation in the commercialized SiO, it’s mainly through a complex, energy-consuming, high cost process in which the gas phase silicon dioxide and Si are mixed according to the calculated the stoichiometric ratio in vacuum conditions at high temperature. Si/O ratio is also difficult to control the whole process is not environmental friendly. So it’s urgent and meaningful to bring up a new method which is both low-cost and simple for the direct synthesis of SiOx.
So as to solve these problems, this paper studies on SiOx as lithium ion battery anode material. Organic silane is applied as silicon source to synthesize organic silicon material as precursor, followed by a high temperature calcination in inert gas to pyrolyze and carbonize the organic groups to obtain SiOx - C material directly with extraordinary electrochemical performance. This method is simple,low-cost environmental friendly,and provide inspiration for industrialization for the SiOx anode material. In this paper,we analysis microstructure and composition of SiOx anode material by SEM, XPS, XRD, Raman spectra,explore the structure -electrochemical performance correlation, and explain why the material has excellent electrochemical performance at a certain extent. We further attempt to composite metal and metal organic framework respectively to organic silicon material and explore the electrochemical performance. The result are as follows:
- we use stober method to synthesis the organic silicon sphere as precursor then we obtain uniform SiOx-C sphere with the diameter of 400 nm through a one-step calcination. By XPS result we calculate x is around 1.81, Raman result shows that the ratio of D peaks and G peaks are relatively small, indicating the high degree of graphitization, and the carbon in the SiOx-C material perform not only as the buffer for the structure expansion/contraction but also as a conductive agent. For the electrochemical performance, SiOx-C sphere has good rate performance and high reversible specific capacity which is over 1000 mAh g-1 under the current density of 100 mAh g-1, and under the current density of 1A g-1, it still has the specific capacity of 686.2 mAh g-1 after 300 cycles with the capacity retention of 97%. The synthesis of the SiOx-C sphere is low cost, simple environmental friendly has the potential to be magnified to industrialized scale.
- We try compositing metal Sn and SiOx-C to acquire Sn/SiOx-C composition, and we manage to reduce Sn from oxidation state to metal state while carbonize the organic silicon material to SiOx-C through a one-step calcination in inert gas. However, we are still unable to acquire homogeneous phase of Sn/SiOx-C, which need further improvement. When applied as lithium ion battery anode, Sn/SiOx-C has a reversible capacity of 709.2 mAh g-1 after 10 cycles, and under the current density of 1A g-1, it still has the specific capacity of 589.3 mAh g-1 after 23 cycles with an increasing trend, surprisingly. We speculate that Sn may react with Li2O which is the inert product from the redox reaction of SiOx and Li in the first cycle to form SiO2 phase and increase the total theoretical specific capacity. The synthesis of the SiOx-C sphere is both low cost and simple.
- We use hydrothermal method to synthesize "book-like" structure copper based metal organic framework which is a bulk stacked by numerous two-dimensional sheets——copper terephthalate metal organic framework. We manage to coat γ-Mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane onto copper terephthalate metal organic framework through the strong interaction between Cu and S to acquire the precursor of Cu/SiOx-C. We believe it has the potential to fabricate lithium ion battery anode material with excellent cycling performance due to cupper’s good conductivity.
Key Words:Silicon suboxide; Carbon-doped; Anode material; Lithium ion battery; electrochemical properties
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract III
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 锂离子电池 2
1.2.1 锂离子电池工的原理 2
1.2.2 硅锂离子电池负极材料 3
1.2.2 氧化硅锂离子电池负极材料 3
1.4 本论文的选题意义及主要研究内容 6
第2章 实验原料/仪器及测试方法 7
2.1实验药品及主要仪器设备 7
2.1.1 实验药品 7
2.1.2 实验主要仪器设备 7
2.2材料表征方法 8
2.2.1 微观形貌分析 8
2.2.2 物相分析 8
2.2.3 其它相关分析 8
2.3材料电化学性能表征方法 9
2.3.1 锂电负极的制备及纽扣式电池的组装 9
2.3.2 电化学性能测试 10
第3章 SiOx-C小球作为高容量锂离子电池负极材料的制备以及电化学性能 11
3. 1 引言 11
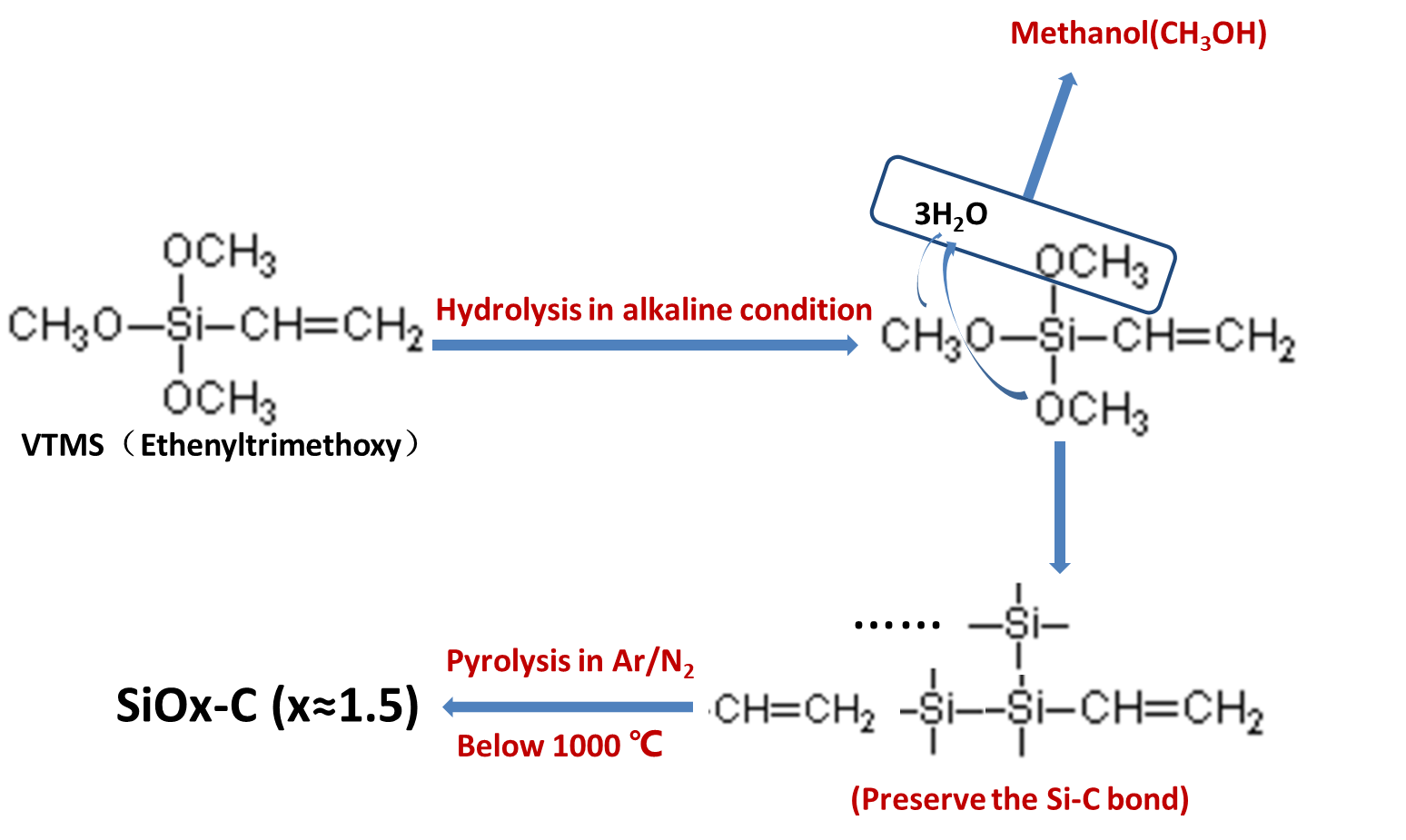
3. 2 SiOx-C小球电极材料的制备 11
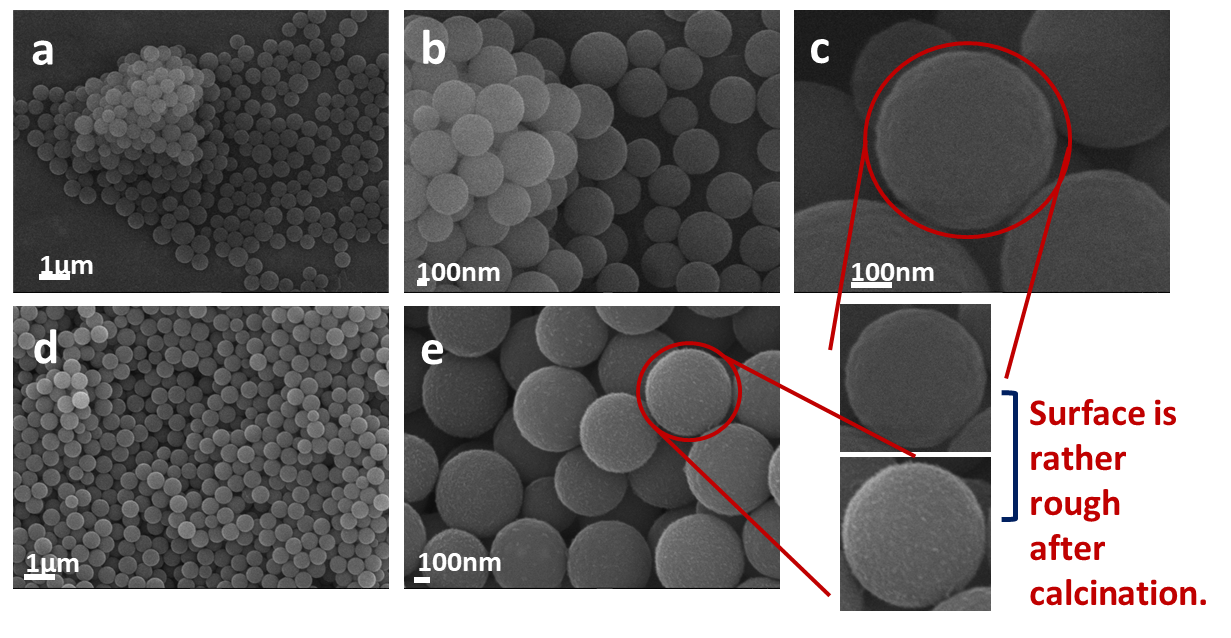
3. 3 SiOx-C小球电极材料的结构表征 12
3. 4 SiOx-C小球电极材料的电化学性能 14
3.6 本章小结与展望 16
第4章 Sn/SiOx-C作为高循环性能锂离子电池负极材料的制备 18
4.1 引言 18
4.2 Sn/SiOx-C电极材料的制备 18
4.3 Sn/SiOx-C电极材料的结构表征 19
4.4 Sn/SiOx-C小球电极材料的电化学性能 20
4.5 本章小结与展望 21
第5章 金属有机框架为模板合成Cu/SiOx-C前驱体的初步尝试 23
5.1 引言 23
5.2 以金属有机框架为模板合成Cu/SiOx-C的材料制备 23
5.3 有机硅包覆对苯二甲铜的结构表征 24
5.4 本章小结与展望 25
第5章 结论 26
5.1 结论 26
参考文献 27
致 谢 29
第1章 绪论
1.1 引言
随着社会,经济,科技的进步,人类对能源得需求也日益增加,而目前我们普遍使用的能源物质主要是传统的不可再生能源如石油,煤炭,天然气等,同时这类化石能源得大量使用导致了严重的环境污染。所以为了实现可持续发展,两种观点同时被提出:一个是能源和资源最充分被利用(Maximum Energy and Resources Utilization),另一个是环境最弱影响(Minimum Environment Impact)。绿色能源因而渐渐成为人们研究和发展的热点,绿色能源包括太阳能,核能,地热能,潮汐能,风能等,而其中太阳能,潮汐能,风能等间歇式能源难以直接投入电网使用[1],仍很大程度上依赖于大规模高效储能系统装置,故开发新型储能装置,储能技术已经迫在眉睫。
电化学储能技术是目前能源存储技术(相比于智能电网,电磁波储能和化学储能)相对来说最为方便的一种,化学电源又具有充电效率高,体积小等优势,所以其被认为是非常理想的储能器件[2]。二次电池里主要有铅酸电池,镍镉电池,镍氢电池,锂离子电池等,而锂离子电池由于其无记忆效应,工作电压高,充放电速度快,对环境友好等优点成为目前应用最为广泛的二次电池。如今锂离子电池已经被广泛应用于各种电子产品(手机,笔记本电脑等)、电动工具以及电瓶车中,并已经向纯电动汽车(特斯拉,比亚迪等),混合动力汽车和大型储能设备方向进军。
负极材料是锂离子电池中非常关键的一部分,目前商业化锂离子电池负极材料为石墨类碳质材料,但由于其低的理论比容量(372 mAh g-1),较低的充放电电位,较差的倍率性能以及会与电解液发生共嵌入现象,石墨已经逐渐无法担当锂离子电池发展中负极的重任,所以发展高比容量,高安全性的新型负极材料已经成为如今锂离子电池研究中的热点。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: