R2O含量对R2O-RO-Al2O3-SiO2微晶玻璃结构和应能的影响毕业论文
2020-04-06 11:11:15
摘 要
Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(NCAS)系微晶玻璃具有高硬度、突出的抗折强度和耐冲击强度,而且膨胀系数较低等特点,通过控制晶化工艺,可实现透明、半透明、不透明产品的制备。因此,Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(NCAS)微晶玻璃具有突出的理化性能,广泛应用于光电显示、电子元器件等领域,并引起国内外学者的广泛关注。
论文主要研究单掺K2O以及双掺K2O和Li2O对NCAS系微晶玻璃析晶和性能的影响,并采用高温黏度计、差式扫描量热、热膨胀分析、X射线衍射和扫描电镜,探讨了K2O和Li2O对玻璃的高温粘度、核化温度、晶化温度、和微观结构的影响。同时对不同微晶玻璃进行离子交换,通过表面应力仪、电子探针、显微硬度计对交换后的表面应力、应力深度、截面的离子分布情况、硬度等进行表征。通过对各种数据的分析得到最合适的K2O的引入量,以及K2O和Li2O对析晶和性能的影响规律。
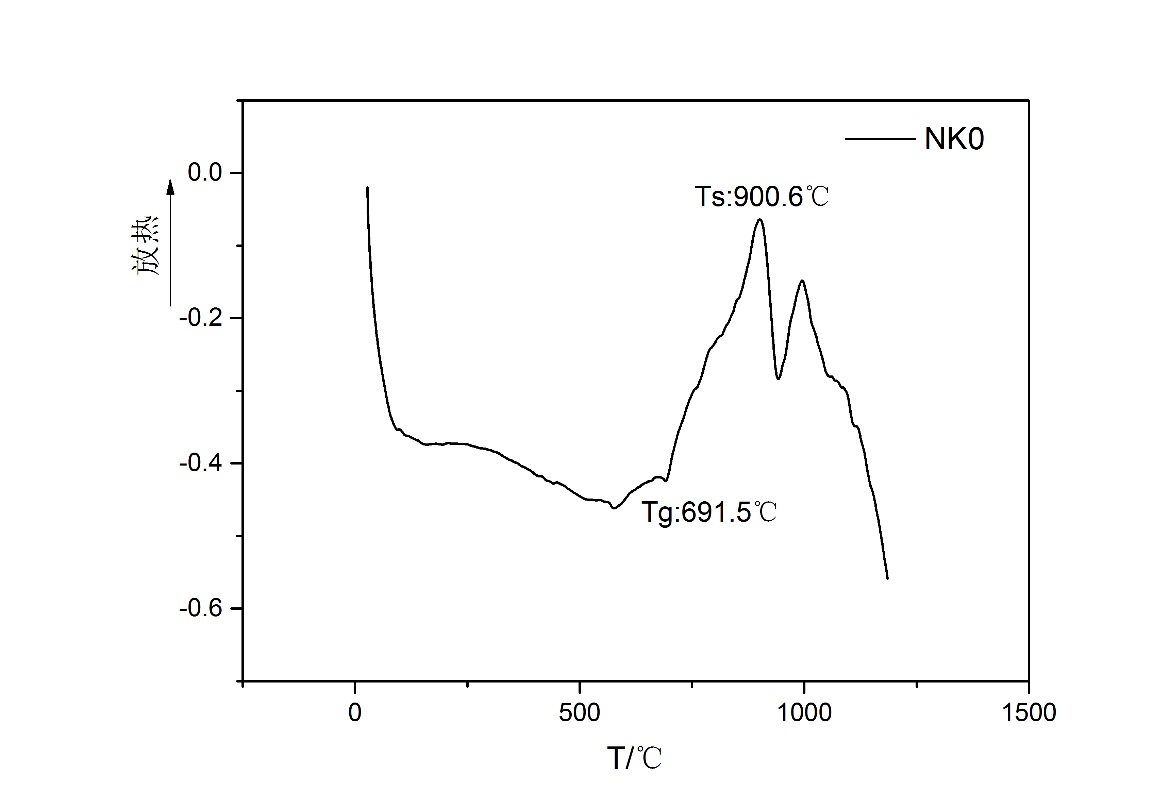
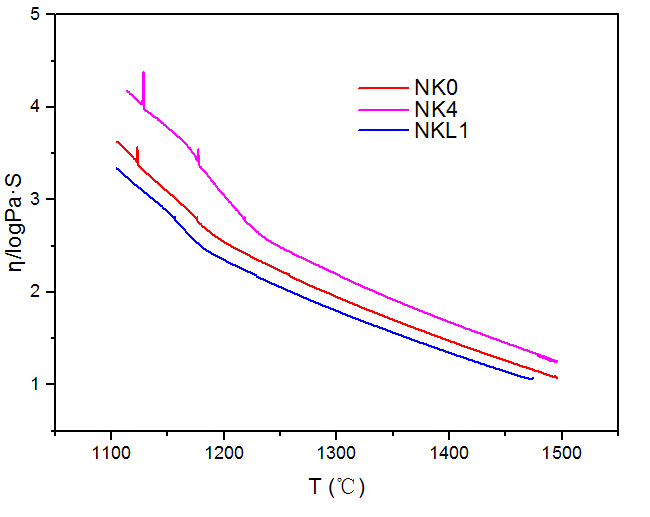
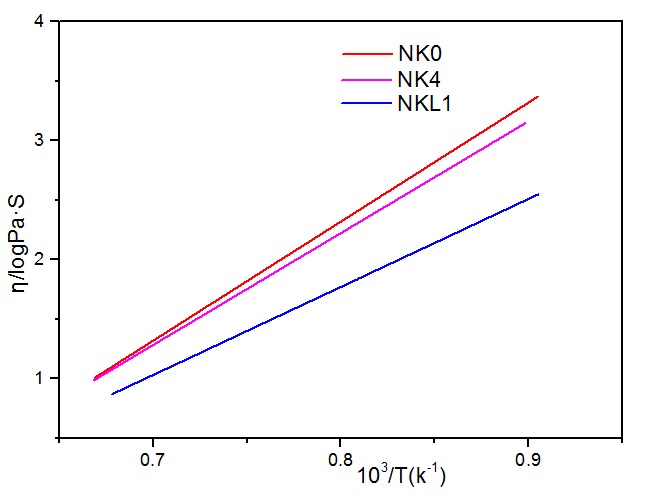
研究表明:随着NKL1中1%Li2O取代1%K2O,使得熔体粘度曲线最小,加入的正离子半径越小,降低粘度的次序越大,可以得出降低粘度的次序:Li gt;Na gt;K 。NKL1的粘滞活化能最小为182.21KJ/mol,熔化温度最低为1469.1℃。掺有K2O的NCAS玻璃在780是透明的,800℃就会失透。双掺K2O、Li2O的NCAS玻璃在730就已经失透,700℃是透明的。随着K2O逐渐从0%增加到4%时,其热膨胀系数增加。随着1%Li2O的引入,玻璃的转变温度Tg和软化温度Ts都明显的降低,并且当掺加1%的Li2O时,NKL1热膨胀系数α达到最大值98.6x10-7℃-1。NK0、NK2、NK4玻璃在650℃核化2h,700℃晶化4h,通过扫描电镜对其形貌观察,发现其均有球状晶体。随着单掺K2O的百分含量从0%逐渐增加到4%,离子钢化后的微晶玻璃表面应力逐渐降低;同时700℃晶化后的微晶玻璃通过离子交换后,玻璃表面应力最低,730℃晶化后离子交换后的表面应力较高;当引入Li2O,其表面应力呈现出减小的趋势,并且随着Li2O的百分含量从1%增加到2%,玻璃表面应力都呈现出增长的趋势。NK4在750℃时离子交换深度最大,为42.21μm;并且随着K2O从0%增加到4%,NK0、 NK1、NK2、NK4的离子交换厚度逐渐增加;随着Li2O的引入,通过对比750℃晶化的NK4、NKL1,离子交换深度从42.21μm降低至19.56μm。在K 离子分布曲线中,在近表面区域形成一个K 富集峰。随着深度增加,K 离子浓度降低;并且750℃晶化的NK4中K 富集峰最大位置为32μm,最低位置为未晶化的NK4,为12.5μm。未晶化的玻璃进行离子交换后其硬度高于晶化后再进行离子交换后的玻璃。
本文的特色:通过研究K2O、Li2O对Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(NCAS)系微晶玻璃的高温粘度、热处理制度、析晶、以及离子强化后性能的研究,降低了玻璃的高温粘度为适用于浮法生产工艺提供可能,并且降低晶化温度得到透明的析晶均匀且晶粒细小的微晶玻璃。同时通过一步法离子交换得到表面应力高,硬度大的玻璃。
关键词:NCAS微晶玻璃,热处理制度,晶化,核化,离子交换
Abstract
Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(NCAS) glass-ceramic not only possess high hardness,especially for the bending strength and impact strength. but low coefficient of thermal expansion.by means of controling crystallization process,it can make process product what is transparent, translucent, opaque.Therefore, Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(NCAS) glass-ceramic has outstanding physical and chemical properties. It is widely used in photoelectric display, electronic components and other fields, and has attracted wide attention of domestic and foreign scholars.
The paper mainly studies the influence of single-doped K2O and double-doped K2O and Li2O on microcrystalline glass crystallization and performance of NCAS. High temperature viscosity meter, differential scanning calorimetry, thermal expansion analysis, X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy were used. The influence of K2O and Li2O on high temperature viscosity, nucleation temperature, crystallization temperature and microstructure of glass were discussed differently. glass-ceramic were processed by ionic-exchange,through BTP-H,EPMA, microhardness tester. Concluding Surface stress, stress depth, ion distribution of cross section, hardness. The influence of K2O and Li2O on the crystallization and properties of K2O and Li2O were obtained by the analysis of various data.
research shows that with 1%Li2O in NKL1 replacing 1%K2O, the melt viscosity curve is the smallest. With the increased radius of positive ion, The degree of viscosity reduction is greater. The order of viscosity can be reduced: Li gt;Na gt;K .the Viscous activation energy of NKL1 is minimum,which was 182.21KJ/mol. The Lowest melting temperature was 1469.1℃.NCAS glass-ceramic was transparent which was mixed with K2O.while they will be opaque at 800℃. double-doped K2O and Li2O on microcrystalline glass crystallization will be opaque at 730℃.while they were transparent at 700℃. As K2O gradually increased from 0% to 4%, its thermal expansion coefficient increased. With the introduction of 1%Li2O, the transition temperature of glass Tg and softening temperature Ts were obviously reduced. And when adding 1% of Li2O, the thermal expansion coefficient of NKL1 is the maximized,what is 98.6x10-7℃-1.when glass-ceramic of NK0、NK2、NK4 were coring 2 hours at 650℃and crystallized 4h at 700℃, By scanning electron microscopy, it was found that there were spherical crystals. The surface stress of the microcrystalline glass after ionic toughening has gradually decreased with the percentage content of K2O in single mixing increased from 0% to 4%.While 700℃after the crystallization of microcrystalline glass through ion exchange, glass surface stress is the lowest.730℃after ion exchange in the crystallization of the surface stress is higher. When Li2O was introduced, the surface stress showed a decreasing trend, and with the percentage content of Li2O increased from 1% to 2%, the surface stress of glass showed a trend of growth. Maximum ion exchange depth is NK4,which is 42.21μm. Moreover, the ion exchange thickness of NK0, NK0, NK1, NK2 and NK4 gradually increased as K2O increased from 0% to 4%. With the introduction of Li2O, by comparing the 750 ℃ crystallization NK4, NKL1, ion-exchange depth decreased to 19.56μm from 42.21μm. In the K ion distribution curve, a K enriched peak is formed in the near surface region. As the depth increases, the K ion concentration decreases. The maximum position of the K enrichment peak in NK4 crystallized at 750 °C is 32 μm, and the lowest position is NK4, which is 12.5 μm. The hardness of uncrystallized glass after ion exchange is higher than that of glass after crystallization.
Characteristics of this article: By studying the effects of K2O and Li2O on the high temperature viscosity, heat treatment system, crystallization, and ion-strengthening properties of Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 (NCAS) glass-ceramics, the high-temperature viscosity of glass is reduced to be suitable. The production process in the float process is possible, and the crystallization temperature is lowered to obtain transparent crystallized uniform and fine crystallite glass. At the same time, the glass with high surface stress and high hardness is obtained through one-step ion exchange.
Key Words:NCAS glass-ceramic;heat-treatment;nucleation;crystallization;ion exchange
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 微晶玻璃 1
1.1.1 微晶玻璃的种类 1
1.1.2 硅氧骨架的结合程度 1
1.2 微晶玻璃的制备 2
1.2.1 整体析晶法 2
1.2.2 烧结法 2
1.2.3 溶胶-凝胶法 2
1.3 微晶玻璃的热处理制度 3
1.3.1 阶梯温度制度 3
1.3.2 等温温度制度 3
1.4 NCAS微晶玻璃的研究现状 4
1.5 微晶玻璃离子强化 5
1.6 立题依据 6
1.7 研究内容 6
第2章 实验 7
2.1.实验原料与仪器设备 7
2.2.实验过程 8
2.2.1.玻璃组分 8
2.2.2.玻璃的熔制 9
2.2.3.微晶玻璃离子强化 9
2.2.4.性能测试 9
2.3.测试及表征方法 9
2.3.1.差式扫描量热分析(DSC) 9
2.3.2.X射线衍射定性分析 10
2.3.3.电子探针(EPMA) 10
2.3.4 热膨胀性 10
2.3.5 硬度 11
2.3.6 表面应力与应力深度 11
2.3.7 扫描电镜(SEM) 12
2.3.8 高温粘度 12
第3章 K2O单掺和K2O、Li2O双掺对NCAS微晶玻璃的析晶和性能的影响 13
3.1 引言: 13
3.2 单掺K2O含量对NCAS微晶玻璃析晶和性能的影响 13
3.2.1.K2O对析晶温度的影响 13
3.2.3 K2O、Li2O对玻璃熔体粘度的影响 15
3.2.4 晶化温度对NCAS微晶玻璃热膨胀性改变 16
3.2.5.热处理制度对NCAS微晶玻璃析晶的影响 18
3.2.6.NCAS微晶玻璃的晶相形貌 18
3.3.1.双掺K2O、Li2O对析晶温度的影响 20
3.3.2双掺K2O、Li2O下NCAS微晶玻璃的外观 20
第4章 一步法离子交换强化微晶玻璃 22
4.1引言 22
4.2单步离子交换法工艺 22
4.3单步离子交换后微晶玻璃的表面应力以及应力深度 22
4.3.1 单步离子交换后微晶玻璃的表面应力 22
4.3.2 换后微晶玻璃表面应力变化趋势图 22
4.3.3交换后微晶玻璃的应力深度 23
4.3.4交换后微晶玻璃表面应力深度变化趋势图 23
4.3.5 交换后微晶玻璃硬度 24
4.3.6 第一步离子交换对K 分布状态的影响 26
第五章 结论 28
致谢 29
参考文献 30
第1章 绪论
1.1 微晶玻璃
微晶玻璃(glass-ceramic)又称玻璃陶瓷,在制备好的基础玻璃上,通过控制核化和晶化的热处理制度,制得含有大量晶相及玻璃相的多晶固体材料。
微晶玻璃具有玻璃的基本特征,也具备陶瓷的多晶特征[1]。但是微晶玻璃又与玻璃和陶瓷有很多不同:微晶玻璃的晶化是从单一均匀的玻璃相或产生相分离的区域中成核,然后晶体生长得到的。得到的是微晶体均匀分散和玻璃相组成的复合材料。然而陶瓷中的晶相有多种来源,包括固相反应产生或在组分中引入的。微晶玻璃的性能取决于基础玻璃的组成,热处理制度,晶相种类,晶粒尺寸,以及残余玻璃相性质和数量。因此微晶玻璃的可设计性相当大。微晶玻璃的热膨胀系数可以通过设计生成的晶相在很大范围内去调整;机械强度高,硬度大,并且具有良好的热稳定性和化学稳定性,电绝缘性优良,接电损耗小,介电常数稳定。因此微晶玻璃作为一种具有广泛的应用前景的全新材料。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: