车用PEM燃料电池阴极流道的排水二维数值分析毕业论文
2020-04-11 17:49:41
摘 要
随着人们对地球能源问题和环境的关注,汽车行业的传统内燃机能源装置不利于人类的长久发展而正在被逐步革新。人们寻求新的能源利用装置来作为汽车的动力源。燃料电池是一种新型理想的汽车能源装置,其具有广阔的应用前景。研究燃料电池汽车主要使用的质子交换膜燃料电池是发展燃料电池汽车产业的奠基石。
本文对质子交换膜燃料电池的阴极流道进行添加堵块的新型结构设计,通过理论基础和数学模型建立二维的阴极流道模拟模型。运用流体力学软件Fluent来进行数值计算,研究流道内堵块结构对流道排水的影响效果。根据研究结果为质子交换膜燃料电池阴极流道的设计提供建议。
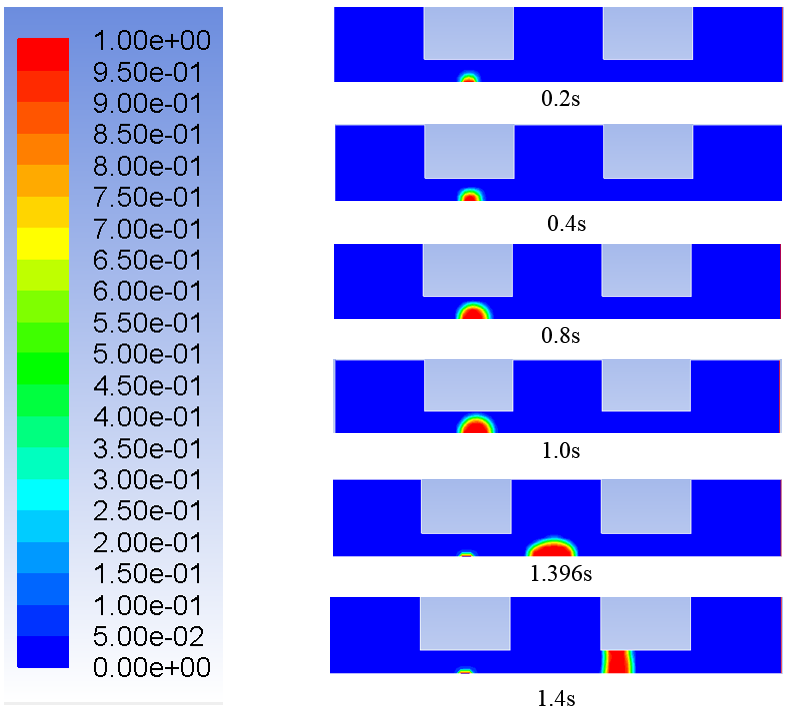
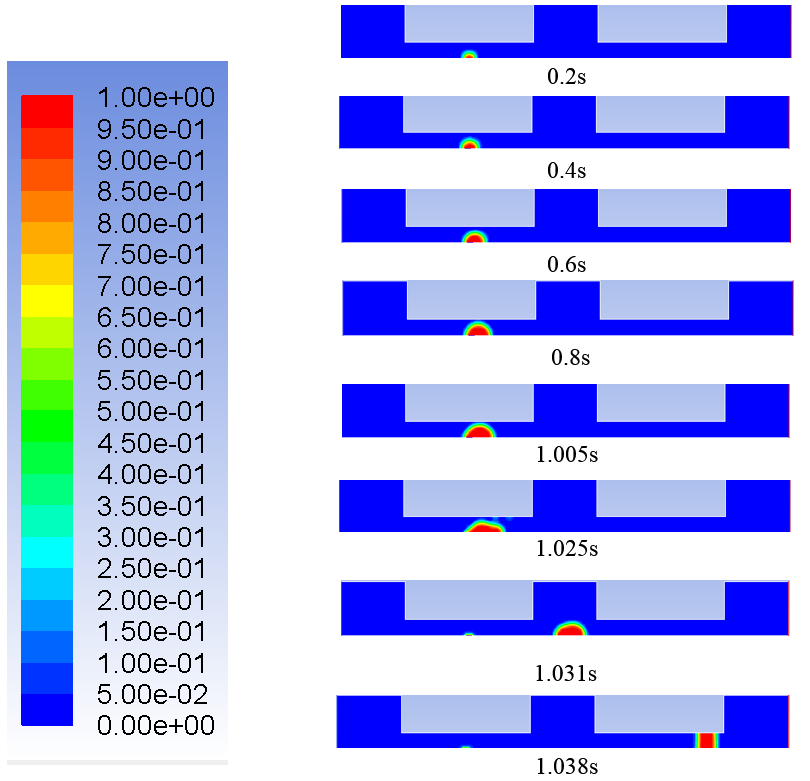
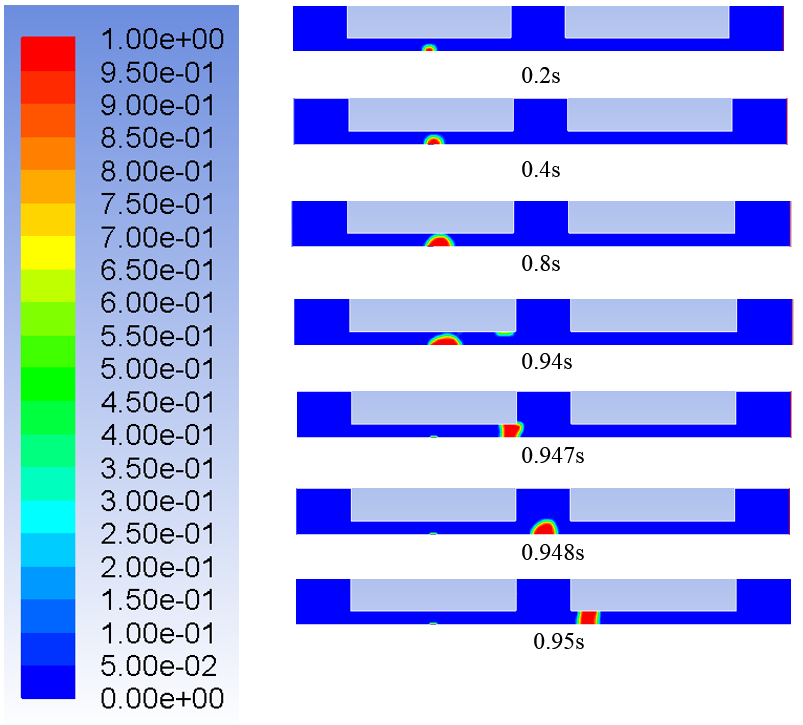
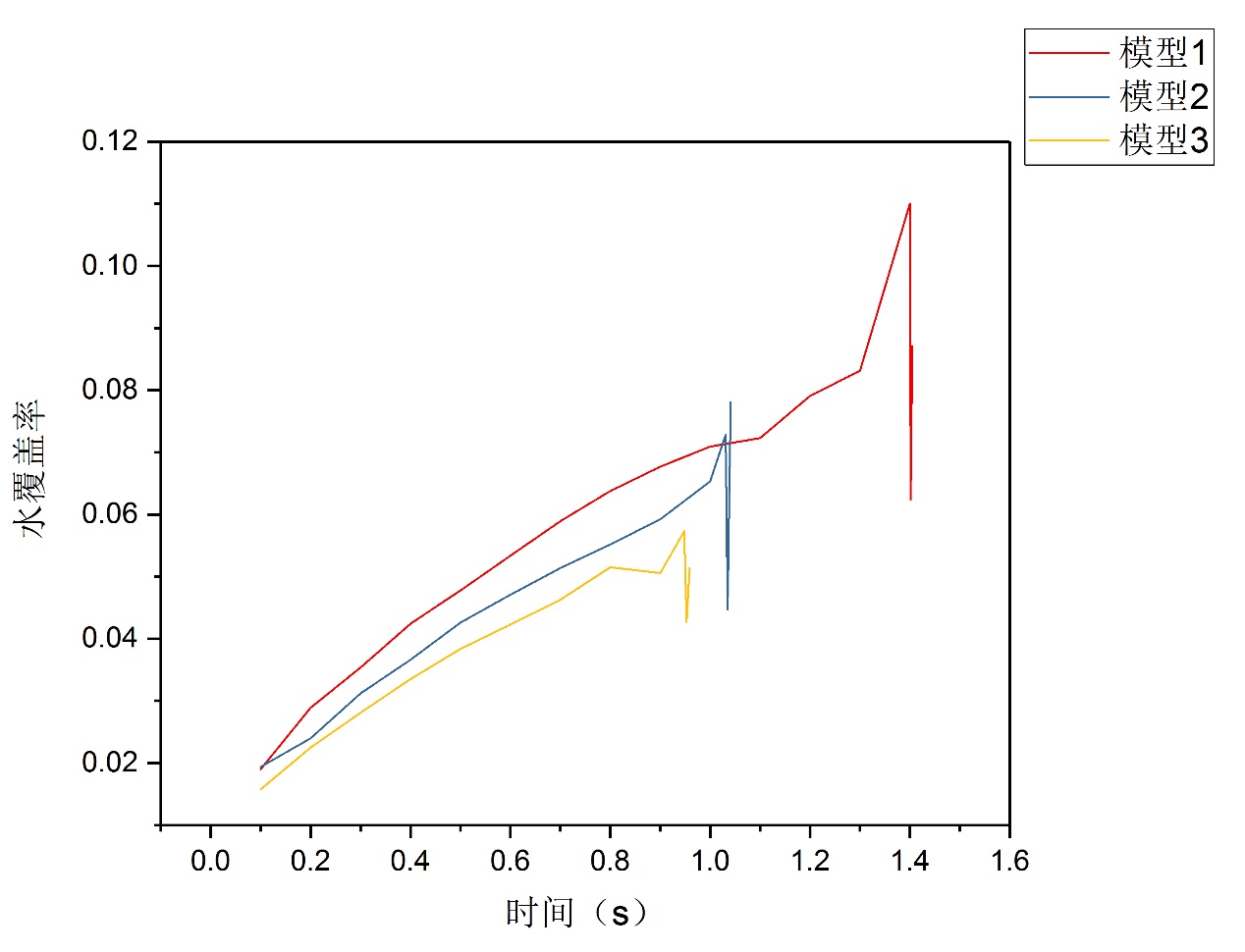
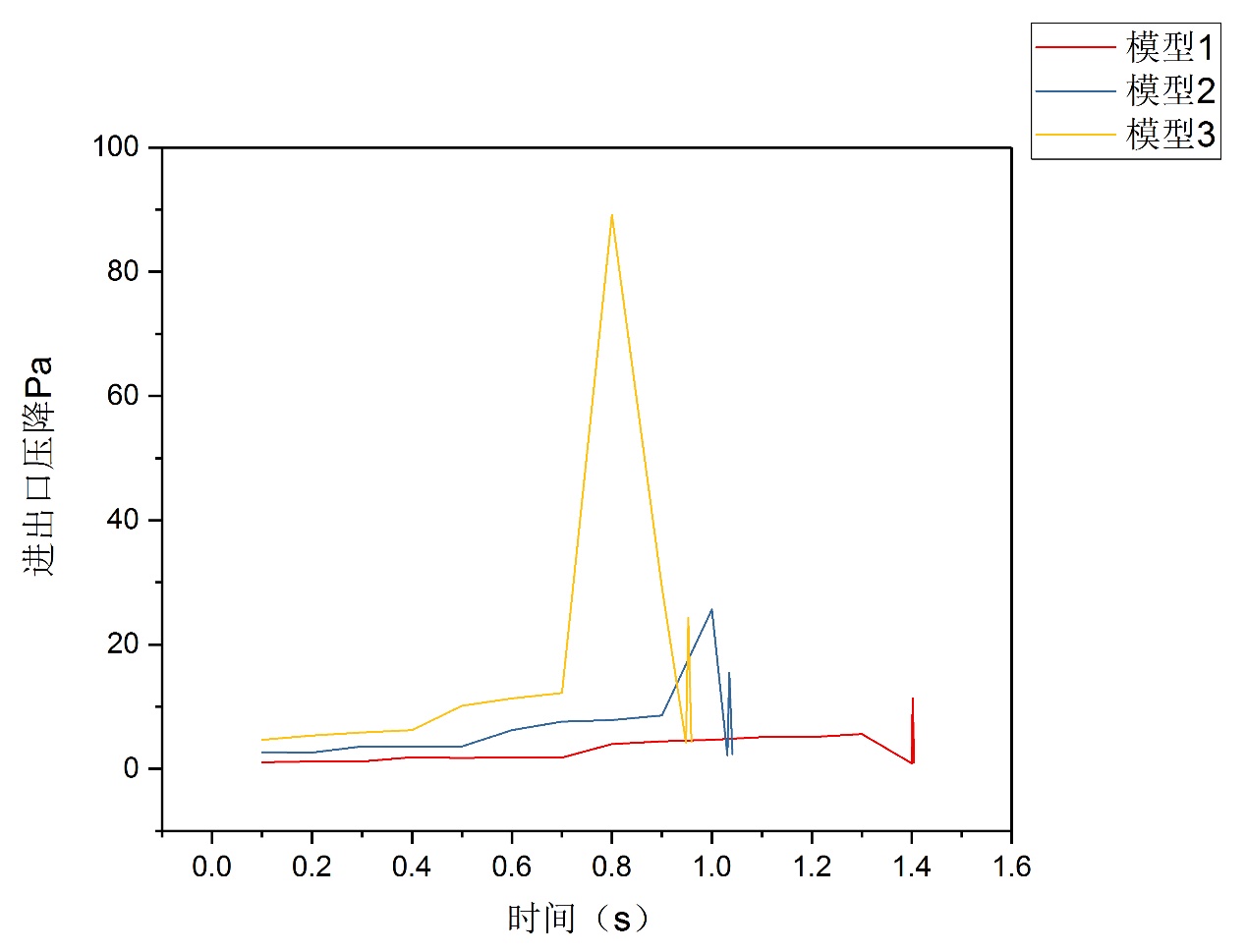
研究结果表明: (1)直流道上壁面布置的堵块会改变阴极流道的排水速率。堵块长度与堵块间隔长度比为3∶1的阴极流道排水最快,堵块长度与堵块间隔比为2∶1的阴极流道排水速率其次,堵块长度与堵块间隔长度比为1∶1的阴极流道排水速率最慢。(2)水滴在流道内的排出过程可分为水滴长大,分离,移动三个阶段。水滴的长大所历经的时间比水滴分离和移动所历经的时间长很多。(3)堵块会使水滴的形状产生变化。水滴在第一个堵块下方和堵块间隔处呈半球状,在第二个堵块下方呈水柱状。(4)水滴在堵块下方位置时与流道下壁面的附着面积会比水滴在无堵块位置时与流道下壁面的附着面积小。(5)堵块长度与堵块间隔长度比为3∶1的阴极流道的进出口压降最大,堵块长度与堵块间隔长度比为2∶1的阴极流道的进出口压降其次,堵块长度与堵块间隔长度比为1∶1的阴极流道的进出口压降最小。
本文的特色在于构建了布置堵块的新型阴极流道模型,并进行了仿真计算。在定量分析的基础上,提出了质子交换膜燃料电池阴极流道的设计优化建议。
关键词:质子交换膜燃料电池;阴极流道内堵块布置;排水
Abstract
With people's concern for the Earth's energy problems and the environment, the traditional internal combustion engine energy devices in the automotive industry are not conducive to the long-term development of human beings and are gradually being reformed. People seek new energy utilization devices as a source of power for cars. Fuel cell is a new type of ideal automotive energy device, which has a broad application prospect. The study of the proton exchange membrane fuel cells used in fuel cell vehicles is the cornerstone for the development of the fuel cell vehicle industry.
In this paper, a new structural design for the blockage of the cathode channel of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell is proposed. A theoretical model and a mathematical model are used to establish a two-dimensional cathode channel simulation model. Fluent fluid mechanics software was used for numerical calculations to study the drainage effect of the flow channel. According to the results of the study, the design of the cathode channel of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell is proposed.
The results of the study indicate that: (1) Blockages placed on the wall of the DC track will change the drainage rate of the cathode flow path. The ratio of the block length to the block interval length ratio is 3:1 and this cathode channel discharge is the fastest. The ratio of the block length to the blockage interval ratio is 2:1 and its drain rate of the cathode channel is the second. The ratio of the length of the block to the interval length of the block is 1:1 and its drain rate of the cathode channel is the slowest. (2) The discharge process of water droplets in the flow channel can be divided into three stages: water droplet growth, separation, and movement. The growth of the water droplets takes much longer than the time the water droplets separate and move. (3) Blocking block will change the shape of the water droplets. Water droplets are hemispherical below the first block and at the blockage interval, and are columnar under the second block. (4) The attachment area of the water drop to the lower wall surface of the flow channel at the lower position of the blocking block is smaller than the attachment area of the water drop to the lower wall surface of the flow channel at the non-blocking position of the water drop. (5) The pressure drop of the inlet and outlet of the cathode channel with the ratio of the length of the plugging block to the length of the plugging block is 3:1 is the largest, and the pressure drop of the inlet and outlet of the cathode channel with the plugging block length and plugging block length ratio of 2:1 is the second. The pressure drop of the inlet and outlet of the cathode channel with the ratio of the block length to the block interval length of 1:1 is the minimum.
The feature of this paper is to construct a new type of cathode flow channel model with block plugs and perform simulation calculations. Based on the quantitative analysis, the design and optimization of the cathode channel of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell are proposed.
Key words: Proton exchange membrane fuel cell; the layout of blocks in the cathode channel; drain
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
1绪论 1
1.1课题研究的背景 1
1.1.1质子交换膜燃料电池工作原理 1
1.1.2质子交换膜燃料电池国内外研究现状 3
1.2课题研究的意义 5
1.3研究的主要内容 5
2质子交换膜燃料电池的数学模型 6
2.1基本流体力学模型 6
2.1.1质量守恒方程 6
2.1.2动量守恒方程 6
2.1.3能量守恒方程 7
2.1.4组份守恒方程 7
2.2电化学反应模型 7
2.2.1电化学方程 7
2.2.2电流守恒方程 8
2.2.3反应物消耗和水生成 8
2.3气平衡模型 9
2.4水平衡模型 9
2.5热平衡模型 10
2.6 VOF两相流模型 11
2.6.1 VOF连续性方程 11
2.6.2 VOF动量方程 11
3阴极流道的排水二维数值分析 13
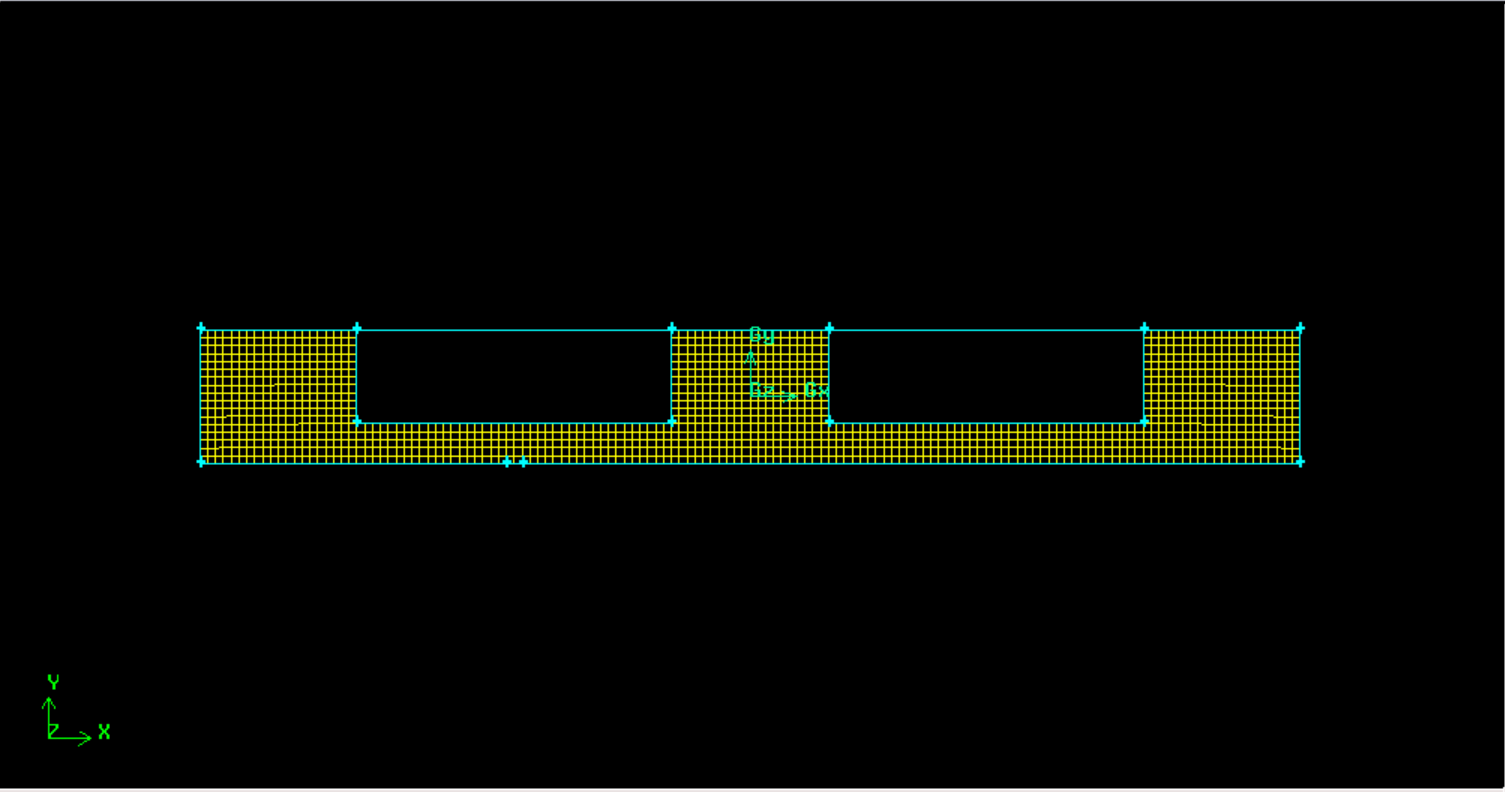
3.1模型设计方案 13
3.2模型边界条件 15
3.3结果分析 19
3.3.1流道内水滴运动分析 19
3.3.2流道排水时间分析 24
3.3.3流道下壁面水覆盖率分析 24
3.3.4流道进出口压降分析 27
4结论与建议 30
4.1主要结论 30
4.2建议 30
参考文献 31
致 谢 33
1绪论
1.1课题研究的背景
近年来,随着全球环境问题和能源问题的日益突出,汽车行业内正在进行由传统汽车向新能源汽车发展的巨大变革。传统内燃机汽车难以解决燃料问题和排放污染问题,不利于世界和人类的未来可持续发展,因此全球各国汽车产业正都致力于研究新能源汽车。在新能源汽车中,燃料电池汽车以其效率高和接近零排放的特点而受到了汽车人的重点关注和研究。欧盟、美国、日本和韩国都大量投入人才和资金进行燃料电池汽车的研究和开发,通用、奔驰、本田、丰田等公司已成功研发出燃料电池汽车。我国也将抓住全球汽车产业的新潮流和发展机遇,在燃料电池汽车方面不断加大研究力度。《中国制造2025》中节能与新能源汽车产业发展中已将燃料电池汽车列为国内未来重点发展方向之一,并分别提出了2020年以及2025年的发展目标。
今天使用的燃料电池可分为六种主要类型。它们分别是碱性燃料电池(Alkaline fuel cell,简称AFC),质子交换膜燃料电池(Proton exchange membrane fuel cell,简称PEMFC),直接甲醇燃料电池(Direct methanol fuel cell,简称DMFC),磷酸燃料电池(Phosphoric acid fuel cell,简称PAFC),熔融碳酸盐燃料电池(Molten carbonate fuel cell,简称MCFC),固体氧化物燃料电池(Solid oxide fuel cell,简称SOFC)。目前广泛配置于燃料电池汽车上的燃料电池是质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)。质子交换膜燃料电池以氢气为燃料,以空气中氧气为氧化剂,通过电化学反应产生能量。其所用的电解质为固体高聚合物膜,膜只允许质子通过而得名质子交换膜。质子交换膜燃料电池的效率比传统内燃机效率高出一两倍,因为它不具有内燃机气体燃烧的热机循环过程,热损失少使得能量转换效率高。同时,质子交换膜燃料电池工作平稳,噪声小,使用寿命长。质子交换膜燃料电池最突出的优点是它的排放产物是水,环保而无污染,这使得其成为理想的能源装置。另外质子交换膜燃料电池还可在低温下快速启动。上述特点使得PEMFC非常适合用作交通工具的动力源。对质子交换膜燃料电池的性能研究是燃料电池汽车研究的首要问题。
1.1.1质子交换膜燃料电池工作原理
质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)由于其电解质的形态,也被称为固体聚合物燃料电池。质子交换膜燃料电池的电解质为固体高分子聚合物膜,在聚合物膜中H 可以自由移动。质子交换膜的工作原理示意图如图1-1所示。
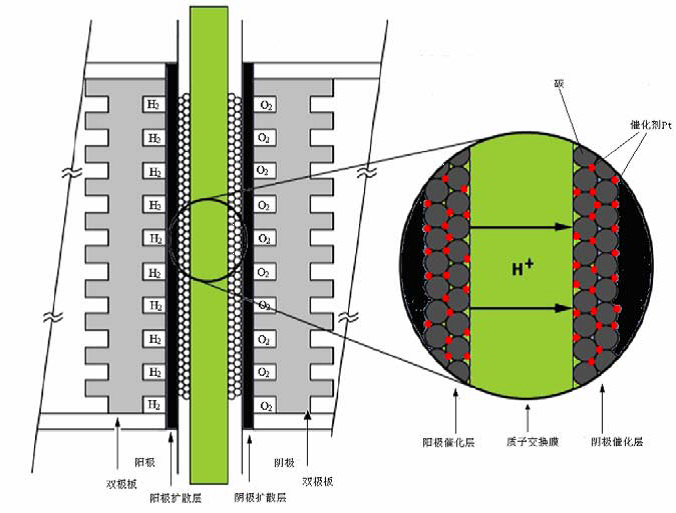
图1-1 质子交换膜燃料电池工作原理图[1]
PEMFC的基本结构主要由阳极,电解质,阴极,和外电路组成。电池的反应气体为氢气和氧气。在阳极,氢气通入流道后,通过气体扩散层扩散到催化层,在铂催化剂的作用下,降低活化能,解离成氢离子和电子。氢离子会通过质子交换膜移动向阴极流动,电子则通过外电路移动到阴极,外电路将产生电流。在阴极,空气通入流道后,通过气体扩散层扩散到催化层,空气中的氧气将与电极上的电子以及电解质移动过来的氢离子反应生成水。电化学反应式如下:
阳极:H2→2H 2e-
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: