基于色素分离的皮损区域分割实现毕业论文
2020-04-12 16:00:37
摘 要
血色素(Hemoglobin)与黑色素(Melanin),作为人体皮肤中含量最多且最重要的两种色素,其浓度大小直接影响着皮肤的健康。色素分离可以从皮肤图像中将血色素和黑色素的浓度提取出来,得到独立色素的浓度分布,进而生成独立色素图像。这对于色素性皮肤病的诊治具有很大的作用。皮损分割,即从周围正常皮肤中检测出皮肤病变区域,是皮肤镜图像计算机辅助分析中的核心步骤。近年来,基于皮肤色素浓度分布的皮损分割算法因其复杂度低、无需学习和预处理等优点逐渐受到学者的广泛关注,现有的色素分离算法仅能检测出由独立黑色素或血色素浓度紊乱导致的简单皮损区域,如雀斑、红斑等,且极易受到光源的干扰,使得色素浓度估计结果不够鲁棒和准确,从而最终影响到分割算法的性能。本文基于色素分离对皮肤镜图像的皮损区域分割进行了分析与研究,论文的主要研究工作如下:
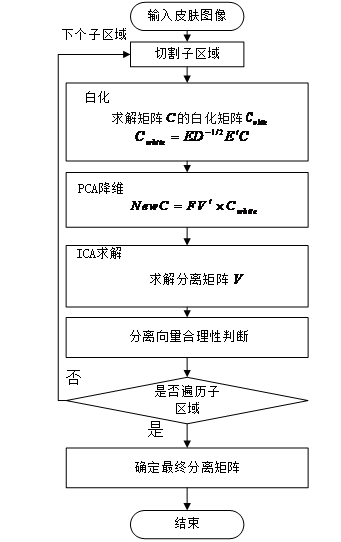
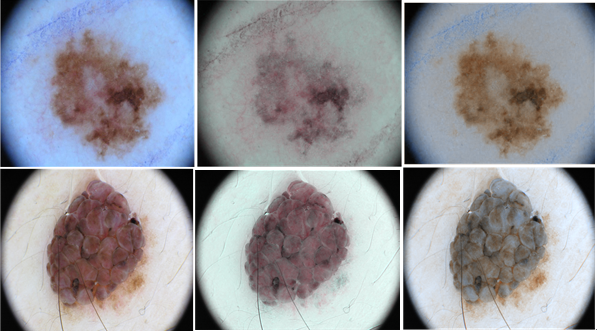
(1)实现一种基于单张皮肤图像的色素分离算法。该算法可以有效实现对皮肤图像的色素浓度估计。首先,建立皮肤图像像素与色素浓度之间的关系模型。然后,使用独立成分分析方法(ICA)计算出色素分离矩阵。最后,在此基础上根据合适的分离矩阵完成对色素浓度的估计,并可以通过对色素浓度的改变,使得独立色素紊乱造成的皮损区域更加清晰可见。
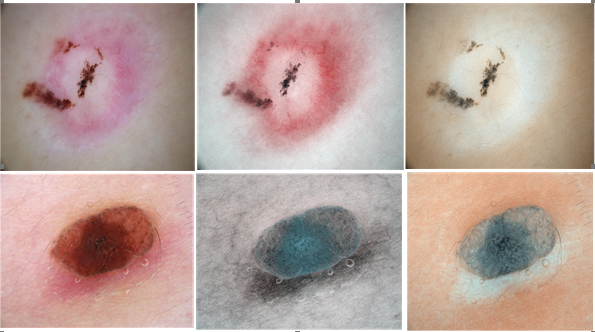
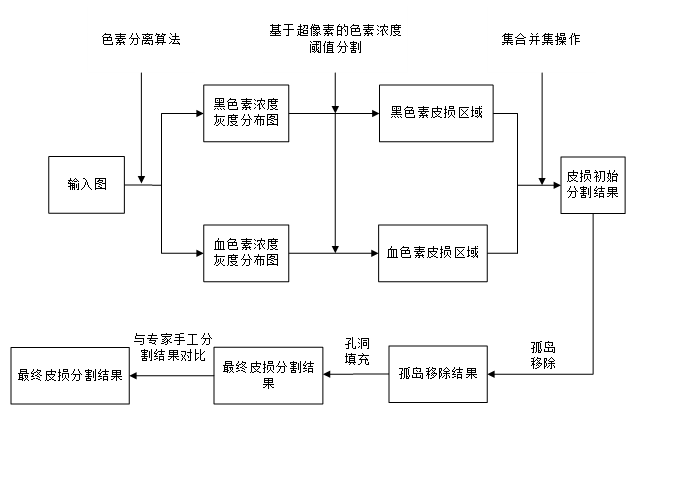
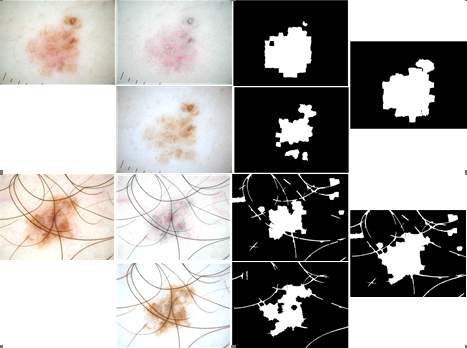
(2)实现一种基于色素浓度分布的皮肤镜图像皮损分割算法。首先,在前一算法的基础上对皮肤镜图像进行色素分离,得到血色素和黑色素的独立浓度分布图。然后,结合大津阈值法和基于色素浓度均值和标准差的阈值分割方法,检测出独立色素浓度分布对应的黑色素皮损区域和血色素皮损区域。对这两者皮损区域通过集合并集操作进行融合,得到更加完整的皮损区域。最后对皮损区域进行后处理,以最终获得更准确的皮损分割结果。经过实验对比分析,验证了本算法的准确性和鲁棒性。
关键词:皮肤镜图像,黑色素,血色素,色素分离,皮损分割
Abstract
Hemoglobin and Melanin, which are the two most abundant and most important pigments in human skin, directly affect the health of the skin. Pigment separation can extract the concentration of hemoglobin and melanin from the skin image to obtain the concentration distribution of the independent pigment, and then generate the independent pigment image. This has a great effect on the diagnosis and treatment of pigmented skin diseases. Lesion segmentation, the detection of skin lesions from the surrounding normal skin, is a core step in computer-assisted analysis of dermoscopy images. In recent years, the skin lesion segmentation algorithm based on skin pigment distribution has received widespread attention from scholars due to its low complexity, no learning and pretreatment, and the existing pigment separation algorithm can only detect the disorder of independent melanin or hemoglobin concentration. The resulting areas of simple skin lesions, such as freckles, erythema, etc., are highly susceptible to light source interference, making the estimation results of pigments less robust and accurate, and ultimately affecting the performance of the segmentation algorithm. This paper analyzes and studies the skin lesion segmentation of dermoscopy images based on pigment separation. The main research work of the thesis is as follows:
(1) Implement a pigment separation algorithm based on a single skin image. The algorithm can effectively achieve the pigment concentration estimation of skin images. First, a model for the relationship between skin image pixels and pigment is established. Then using Independent Component Analysis (ICA) calculates a pigment separation matrix. Finally, on this basis, the concentration of the pigment is estimated based on the appropriate separation matrix, and the lesion area caused by the disorder of the independent pigment can be clearly seen through the change of the pigment concentration.
(2) Implement a skin lesion image segmentation algorithm based on pigment concentration distribution. First, pigmentation is performed on dermoscopy images based on the previous algorithm to obtain independent concentration profiles of hemoglobin and melanin. Then, in combination with the Otsu threshold method and a threshold segmentation method based on the mean and standard deviation of the pigment concentration, the melanin lesion area and the hemoglobin lesion area corresponding to the independent pigment concentration distribution are detected. The skin lesion areas of the two are merged by a set union operation to obtain a more complete skin lesion area. Finally, the skin lesion area is post-treated to obtain a more accurate skin lesion segmentation result. After experimental comparison and analysis, the accuracy and robustness of the algorithm are verified.
Key Words:Dermoscopy images, melanin, hemoglobin, pigment separation, skin lesion segmentation
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 2
1.3 主要涉及内容 3
1.4 本文结构 3
第2章 皮肤图像色素分离的设计与实现 4
2.1 皮肤结构及光学属性 4
2.2 皮肤图像建模 8
2.3 独立成分分析 11
2.4 皮肤图像色素浓度估计 15
第3章 皮肤镜图像皮损区域分割 21
3.1 结合色素分离的皮损区域分割算法 21
3.2 皮损区域分割后处理 26
3.3 算法效果分析 27
第4章 总结与展望 30
参考文献 31
致谢 33
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景及意义
在计算机视觉、化妆品和皮肤医学等许多领域都涉及对人体皮肤的研究。与针对生物皮肤的研究相比,基于数字皮肤图像的研究更加安全和方便,并且便于量化分析和存储。与一般的数字图像处理不同, 了解皮肤组织的结构及其光学属性是进行皮肤图像研究的理论基础。
人体皮肤是多层结构的。皮肤结构和色素含量的轻微变化会产生视觉上明显的变化。目前各种色斑和皮肤炎症的发病率在不断上升,且皮肤疾病的种类繁多,成因各异。常见的色斑有:黄褐斑、雀斑、黑子、色素痣、黑素瘤、白癜风等,色斑不仅仅影响人的外观,某些色斑疾病还严重影响人的健康,如恶性黑素瘤等色素瘤。如何准确定位皮肤上种类各异的色斑,从而进行定量辅助诊断,成为研究的热门问题。
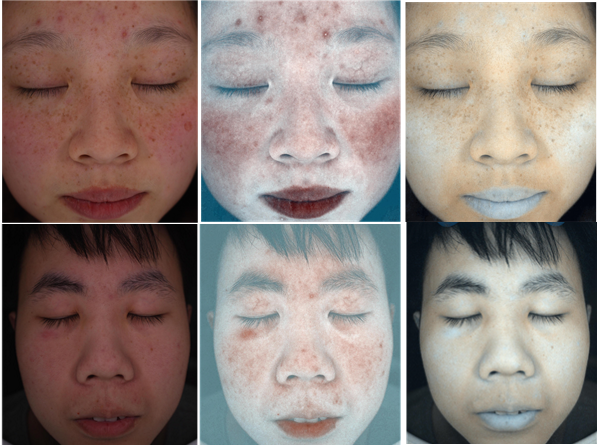
作为人体皮肤中最丰富、也是最重要的两种色素,黑色素(Melanin)和血色素(Hemoglobin)决定了皮肤的主色调,改变这两种色素的含量将直接导致肤色的变化。由调查数据显示,色素性皮肤病通常是由于黑色素浓度紊乱造成的,若早期没有及时诊治,将可能导致病症变异,进而恶化成皮肤癌。如果能直接从图像中把这两种色素的分布提取出来,其与正常皮肤的浓度差能一定程度上区分皮损区域和正常区域。因此这两种色素的分离成为皮肤研究者关注的重点。
从周围正常皮肤中分离出皮肤病变区域,是皮肤镜图像计算机辅助诊断技术的关键一步,其分割结果的精确度将影响接下来的每个处理过程,并最终影响皮损分类结果的准确性。然而对皮损区域的精确分割通常是非常困难的,主要存在以下几个分析难点[1][2]:
- 皮损区域和正常皮肤背景的颜色对比度较低;
- 皮损外观的形态差异较大,很难选择合适统一的分割方法;
- 皮损边界模糊或不规则;
- 皮损区域内的颜色特征差距很大;
- 图像中存在诸如皱纹、毛发、皮肤浸泡液产生的气泡、非均匀照明等,严重影响了分割结果的准确性。
上述难点给皮肤镜图像的皮损区域分割带来了很大的困难。目前,科研人员已提出了许多不同的监督或是半监督的皮损分割算法,主要包括基于阈值、边缘、动态聚类、区域融合以及神经网络的算法等[3][4]。但是这些算法通常需要在分割前进行图像预处理,包括黑框、毛发和阴影移除等[5],才能检测出较准确的皮损区域。同时这些算法的复杂度偏高、执行效率偏低且皮损检测结果的精确度也有待改善。
1.2 国内外研究现状
由于血色素和黑色素是决定皮肤颜色的主要色素组成,与计算黑色素和血色素浓度有关的色素分离研究得以迅速发展,其研究方法可主要分为以下两类:
- 基于反射率等其他光学属性的硬件测量
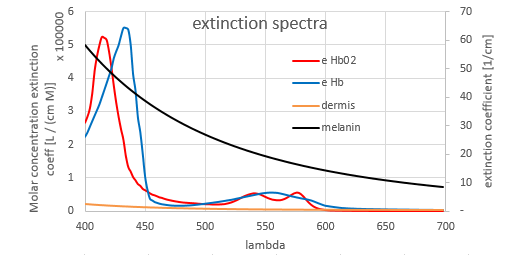
Dawson等[6]基于光在皮肤各层会发生均匀传播、散射、折射等光学性质的假设,并结合其他相关理论对皮肤反射率、吸收率进行测量分析,建立了色素浓度和皮肤反射率之间的关系。
- 基于皮肤图像的估计
Tsumura等[8]使用独立成分分析(Independent Component Analysis,ICA)成功从皮肤图像中提取出了血色素与黑色素浓度,并得到了独立的色素浓度分布图,展现了独立色度在脸部皮肤的分布。同时通过改变各自色素浓度的大小,还合成了不同的皮肤肤色。但由于算法不够完善,独立的色素浓度分布图会出现马赛克现象。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: