异步电机零频率下的磁链观测技术研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 21:43:14
摘 要
异步电机在一定场合中不能安装转速传感器,并且电机可能长时间低速运行于发电模型,电机的同步频率接近于零。传统的观测理论无法观测出电机磁链,为此需要研究零频率下的磁链观测技术。
本文主要进行了异步电机零频率下的磁链观测技术研究,选用无速度传感器条件下适用性较高的电压型观测模型,使用带补偿的低通滤波器改进模型,能够明显消除或者抑制定子磁链中的直流成分,并通过反馈补偿尽量避免交流成分的衰减。以此得到较为准确的定子磁链,再通过计算转换进而得到转子磁链的幅值和空间位置,然后通过建立转子磁链观测的电流模型作为对比,检验新型磁链观测器的准确性。
在本次研究过程中,同时建立了新型磁链观测模型的仿真和电流模型转子磁链观测器的仿真,通过对比即可看出新型磁链观测器是否具有低速下的适用性。
关键词:无速度传感器、异步电机、零频率、低速、磁链观测、电压观测模型、电流观测模型、定子磁链、转子磁链。
Research on flux observation technology of asynchronous motor at zero frequency
Abstract
The induction motor can not install speed sensor in some occasions, and the motor may run in the power generation model for a long time at low speed, and the synchronization frequency of the motor is close to zero. Traditional observation theory can not observe the flux linkage of the motor, so it is necessary to study the flux linkage observation technology at zero frequency.
In this paper, the flux observation technology of asynchronous motor at zero frequency is studied. Voltage-type observation model with high applicability without speed sensor and low-pass filter with compensation are used to improve the model. The DC component in stator flux can be eliminated or restrained obviously, and the attenuation of AC component can be avoided as far as possible by feedback compensation. The size and spatial position of the rotor flux are calculated. The accuracy of the new flux observer is verified by comparing the current model of the rotor flux observer.
In the process of this research, the new flux observer model is simulated, and the rotor flux observer of the existing model is simulated. By comparison, we can see whether the new flux observer is applicable at low speed.
Key words: No speed sensor, asynchronous motor, zero frequency, low speed, flux observation, voltage observation model, current observation model, stator flux, rotor flux.
目录
摘要 Ⅰ
Abstract Ⅱ
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2磁链观测技术的现状及发展 2
1.2.1 转子磁链观测器 2
1.2.2 定子磁链观测器 3
1.3磁链观测技术的必要性 4
1.4本文的主要研究内容和章节安排 4
第二章 异步电机数学模型及起动 6
2.1 运行方式 6
2.2 异步电机动态数学模型及结构图 6
2.2.1 静止三相坐标系中的异步电机动态数学模型 6
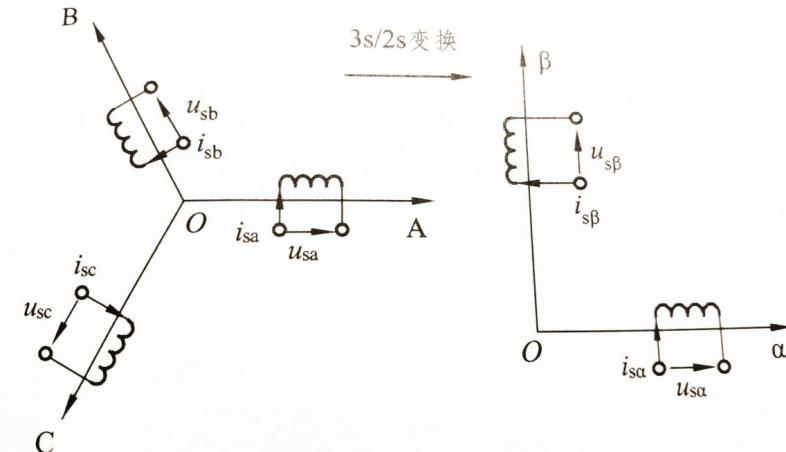
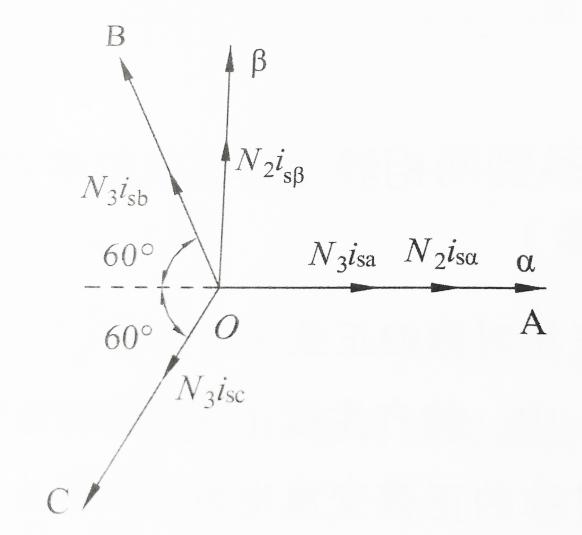
2.2.2 3s/2s变换,也称Clark变换 7
2.2.3  坐标系中的异步电机动态数学模型 8
坐标系中的异步电机动态数学模型 8
2.2.4 异步电机直接起动运行结构图 9
2.3 本章小结 9
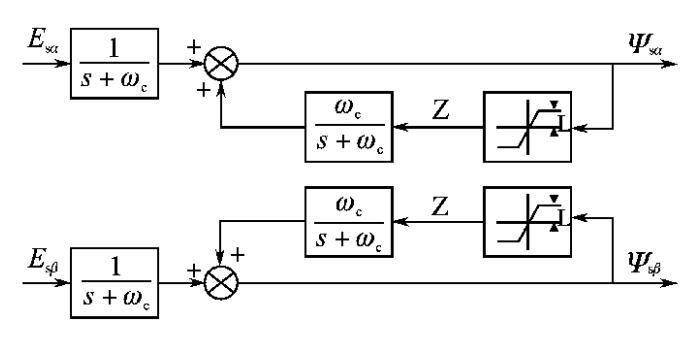
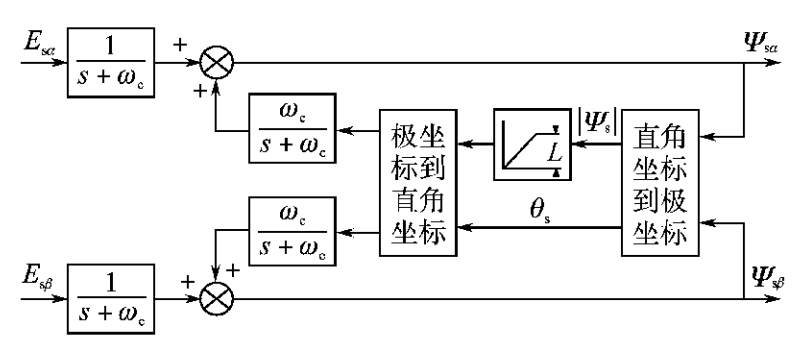
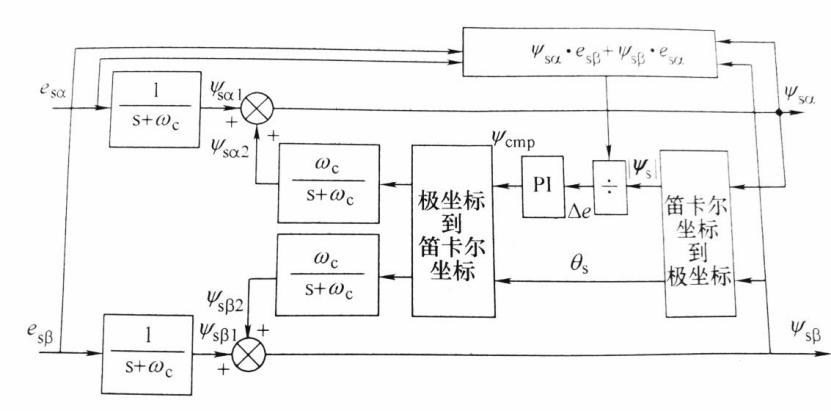
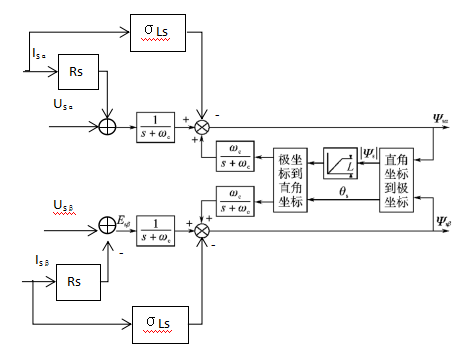
第三章 改进的电压型磁链观测器 10
3.1 普通的电压型磁链观测器 10
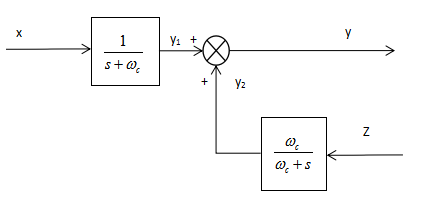
3.2 改进型积分器 11
3.2.1 低通滤波器的原理 11
3.2.2 信号补偿 12
3.3.3 三种改进型积分器 13
3.3 低通滤波器替代纯积分器的电压模型 15
3.4 电流型磁链观测器 16
3.5 本章小结 17
第四章 异步电机起动仿真图和磁链观测仿真 18
4.1异步电机起动仿真图 18
4.2 磁链观测仿真图 18
4.3 电流型磁链观测器仿真 21
4.4 本章小结 21
第五章 仿真参数设置与结果分析 22
5.1仿真参数设置 22
5.2 仿真结果及分析 22
5.2.1 异步电机起动结果及分析 22
5.2.2 磁链观测环节仿真结果及分析 24
5.2.3电流型磁链观测器的转子磁链观测仿真结果 26
5.3 本章小结 26
第六章 总结与展望 27
参考文献 28
致 谢 30
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
当今世界,能源问题已经成为一大制约经济社会发展的重要因素,而我国在能源生产和能源消耗方面都位居世界前列,在众多能源之中,电能始终位于一个非常特殊的地位,既普遍又不可或缺,而电机是电能消耗的最大户,在2004年由国家发改委颁布的《节能中长期规划》中,电机系统节能被列为十大重点节能工程之一,在2007年由科技部颁布的《国家中长期科学和技术发展规划纲要》中,“工业电机及典型泵阀关键技术研究”又被列为“十一五”国家科技支撑项目[1]。
目前我国电机年用电量十分巨大,位列世界前列。1KV以上的高压电动机由于单机容量大,是电动机用电的主要部分,比如,大功率的传动机械,大功率的风机和水泵在各自领域均占有重要地位,他们通常采用400kw~40KW,3~10KV的大功率交流电机进行拖动,采用高压大容量变频器对其进行变频调速改造后,可以直接降低该电机的用电损耗,避免不必要的耗电并有效延长电机适用寿命,对节能减排和可持续发展战略有巨大贡献[2]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: