中空纤维膜反应器的甲烷氧化反硝化研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 21:43:46
摘 要
目前,硝酸盐污染是全球水体恶化的重要原因之一,已严重影响到人们的健康与生活,亟待解决。甲烷作为温室气体之一,可引起严重的温室效应。甲烷厌氧氧化反硝化(denitrifying anaerobic methane oxidation,DAMO)即在厌氧环境下,同步实现甲烷厌氧氧化和反硝化反应,在处理污水脱氮和控制温室气体排放工艺中具有广阔的应用前景。本文以骆马湖、佛手湖、东海中水样为原始接种源,人工模拟硝酸盐污染水体,构建中空纤维生物膜和厌氧血清瓶富集反应器,培养富集甲烷氧化反硝化菌群,测定水样中硝酸盐氮、亚硝酸盐氮浓度,确定甲烷厌氧氧化反硝化效果。实验结果表明,骆马湖富集的甲烷厌氧氧化反硝化微生物的反硝化效果最好,硝酸氮去除率达到80.75%,中空纤维膜生物膜反应器可缩短微生物富集时间,但活性依旧较低。总结了实验过程中存在的问题,提出微生物测序是下一步研究方向,并对以后关于DAMO的发展方向做出了展望,如优化反应器设计、对功能微生物影响因素进行研究,采用电化学方法加快反硝化速率等。
关键词:甲烷 厌氧氧化反硝化 微生物 DAMO 硝酸盐氮 富集
Enrichment of denitrifying methane anaerobic oxidation microorganisms
Abstract
At present, nitrate pollution is an important cause of the deterioration of global water bodies, which has seriously affected people's health and life and needs to be resolved. As one of the greenhouse gases, methane can cause a serious greenhouse effect. Denitrifying anaerobic methane oxidation (DAMO) is a simultaneous realization of methane anaerobic oxidation and NO3-/NO2-denitrification in an anaerobic environment. It has broad application prospects in the process of treating wastewater denitrification and controlling greenhouse gas emissions. In this paper, the water samples from Luoma Lake, Fossil Lake and East China Sea in Zhoushan were used as research objects to artificially simulate nitrate-contaminated water bodies. Hollow fiber biofilm and anaerobic serum bottle reactors were constructed for different inoculum and culture medium substrates to culture and enrich methane oxidation. The denitrifying bacteria group measures the concentration of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in the water sample to determine the anaerobic oxidation and denitrification effect of methane. The data showed that the anaerobic oxidation and denitrification effect of methane in Loma Lake was the best, and the nitrogen nitrate removal rate reached 80.75%. The hollow fiber membrane biofilm reactor can shorten the microbial enrichment time, but the activity is still low. The problems in the experiment process are summarized. It is proposed that the PCR amplification and sequencing of microbial genes is the next research direction, and the future development direction of DAMO is prospected. For example, the design of the reactor is optimized, the research on the factors affecting the functional microorganisms and use the electrochemical method.
Key Words: Methane ; anaerobic oxidation denitrification ; microorganism ; DAMO ; nitrate nitrogen ; enrichment
目录
摘要 - I -
Abstract - II -
第一章 绪论 - 1 -
1.1研究背景 - 1 -
1.1.1地表地下水污染问题 - 1 -
1.1.2硝酸盐污染危害 - 1 -
1.1.3国内外研究现状 - 1 -
1.1.4生物反硝化 - 2 -
1.1.5甲烷氧化反硝化 - 2 -
1.1.6 好氧甲烷反硝化机理 - 4 -
1.1.7 厌氧甲烷反硝化机理 - 4 -
1.2课题研究内容 - 5 -
1.3研究目的、意义及技术路线 - 6 -
1.3.1研究目的 - 6 -
1.3.2研究意义 - 6 -
1.3.3技术路线 - 6 -
第二章 实验材料与方法 - 8 -
2.1实验装置 - 8 -
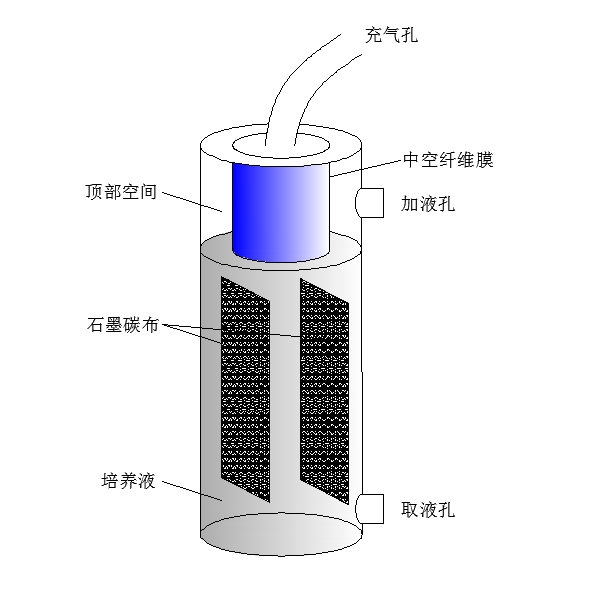
2.1.1中空纤维生物膜反应器 - 8 -
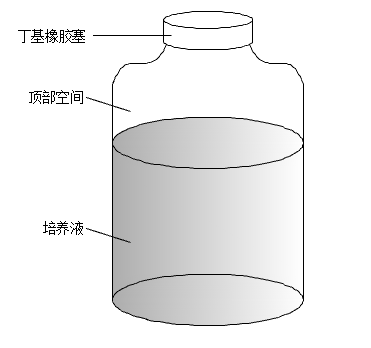
2.1.2厌氧血清瓶反应器 - 10 -
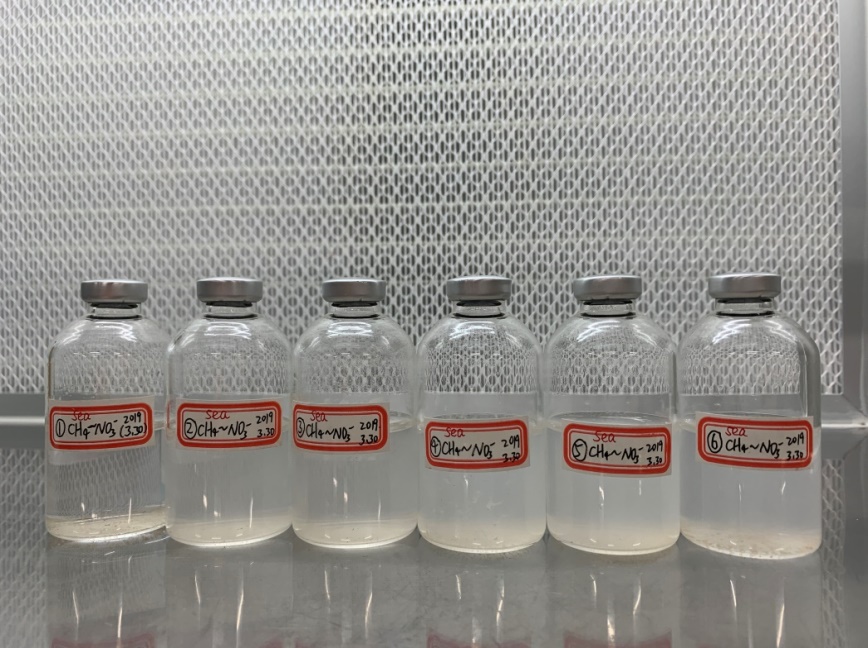
2.2水样采集 - 11 -
2.2.1骆马湖 - 11 -
2.2.2佛手湖 - 12 -
2.2.3东海 - 12 -
2.3微生物富集方法与水样检测方法 - 13 -
2.3.1微生物富集方法 - 13 -
2.3.2水样检测方法 - 15 -
2.3.3DAMO效果评定方案 - 18 -
第三章 实验结果与讨论 - 19 -
3.1骆马湖水样中甲烷厌氧氧化反硝化微生物的富集 - 19 -
3.1.1硝酸根浓度变化规律 - 19 -
3.1.2亚硝酸根浓度变化规律 - 20 -
3.1.2 eqp含量变化规律 - 21 -
3.2佛手湖水样中甲烷厌氧氧化反硝化微生物的富集 - 22 -
3.2.1硝酸根浓度变化规律 - 22 -
3.2.2亚硝酸根浓度变化规律 - 23 -
3.2.2 eqp含量变化规律 - 23 -
3.3东海水样中甲烷厌氧氧化反硝化微生物的富集 - 24 -
3.3.1硝酸根浓度变化规律 - 24 -
3.3.2亚硝酸根浓度变化规律 - 27 -
3.3.3 eqp含量变化规律 - 29 -
3.4本章小结 - 30 -
第四章 结论与展望 - 32 -
4.1结论与存在问题 - 32 -
4.1.1结论 - 32 -
4.1.2存在问题 - 33 -
4.2展望 - 33 -
参考文献 - 35 -
致谢 - 39 -
第一章 绪论
1.1研究背景
1.1.1地表地下水污染问题
水是生命之源。随着人类的发展,目前地球上的水资源正遭受着不同程度的污染,尤其是作为人们重要的饮用水来源,地表水和地下水的污染日趋严重。监测结果显示,地表水和地下水中的硝酸盐浓度正在逐年增加,硝酸盐污染已成为许多水体恶化的重要原因[1]。自然环境中存在一定含量的氮,在整个自然水体的循环作用下,经过硝化、反硝化及氨化等一系列反应,最终转化为硝酸盐的形式。少量的硝酸盐是植物必需的营养物质之一,但过多的硝酸盐含量便会造成严重的水体污染。不同来源的氮通过各种方式进入到不同的水体中。硝酸氮的来源主要有自然因素和人为因素。自然因素主要有大气干沉降、降水等现象,造成的硝酸盐污染程度很小;人为因素主要有农业径流、氮基化肥、动物粪便、垃圾填埋和工业污水等现象,是造成硝酸盐污染的主要来源[2]。
1.1.2硝酸盐污染危害
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: