绿色复合纳米材料在光催化中的应用研究毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:46:50
摘 要
碳量子点(CQDs)是一种低毒性、环境友好的纳米材料,它不仅光学性质优异,来源丰富,而且还有生物相容性好的特点。自2004年被发现以来,被广泛应用于生物探针、光电器械、光催化等领域,其制备方法也有很多种,其中溶液的水热法既制备简单、耗能少,且制备来源主要来自大自然中的简单有机物,遵从绿色化学的原则,因此经常被用来合成CQDs。其次,掺杂、复合等方法可增强其光学性质,扩大他的应用范围。
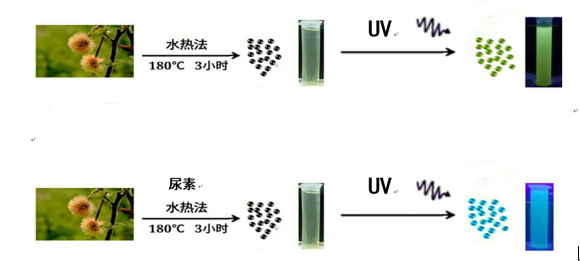
本文采用一步水热法以天然植物梧桐絮为碳源、尿素为氮源,制备了一种荧光性能良好的氮掺杂碳量子点(N-CQDs),形状为圆球状,大小约为 6-9 nm。N-CQDs的荧光强度随着N元素的掺杂量、溶液pH值、反应温度以及反应时间的改变而改变。当N掺杂量为9.61wt%、反应3h、温度为180℃、溶液pH为7时,N-CQDs的荧光性能更好。将它与金属化合物碱式碳酸铋(Bi2O2CO3)复合,形成了一种具有高效催化活性的可见光催化剂,在模拟太阳光辐照下,可高效催化降解甲基橙(MO)。照射2h时,其降解率达到95.5%,照射4h后,降解率高达97.6%。与纯的Bi2O2CO3相比,降解率得到大幅度提升,这主要是因为N-CQDs / Bi2O2CO3中的N-CQDs的应用增强了光的捕集能力、促进了电荷转移、提高了氧气分子的激活能力。N-CQDs / Bi2O2CO3催化剂化学性质稳定,且可重复利用,该研究表明N-CQDs / Bi2O2CO3复合物在水中有机污染的治理方面具有一定的发展潜力。
关键词:碳量子点 碱式碳酸铋 光催化 甲基橙 降解
Green nanocomposite in the application of photocatalysis research
ABSTRACT
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) is a kind of low toxicity, environmental friendly nanomaterials, it has excellent optical properties, and good biocompatibility, wide raw material sources, and many other advantages. Since their discovery in 2004, they have been widely used in biomarkers, bioimaging, optoelectronic devices, photocatalysis, etc. The preparation methods of CQDs are various. Due to the hydrothermal method is simple in preparation, low in energy consumption, and the preparation source mainly comes from simple organic matter in nature, which follows the principle of green chemistry, it is often used for synthesizing CQDs. Secondly, doping, recombination and other methods can enhance its optical properties and expand its application range.
In this paper, a one-step hydrothermal method was used to prepare a nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot (N-CQDs) with good water solubility and good fluorescence performance. The shape was spherical and the size was obtained as about 6-9 nm. When the N doping amount was 9.61 wt%, the hydrothermal temperature was 180 ° C, the solution pH was 7, and the reaction time was 3 h, the fluorescence performance of N-CQDs was the best. It was combined with the bismuth subcarbonate (Bi2O2CO3) to form a catalyst with high catalytic activity, which can degrade methyl orange (MO) efficiently under visible light, and was chemically stable and recyclable. Among them, N-CQDs/Bi2O2CO3-2 exhibited the highest degradation efficiency. After 2 hours ,the degradation rate reached 95.5%. After 4 hours of irradiation, the degradation rate was as high as 97.6%. Compared with pure Bi2O2CO3, the degradation rate was greatly improved, mainly because the N-CQDs in the composite enhanced the light trapping ability, promoted the charge transfer rate, and improved the activation ability of oxygen molecules. The current research proved that N-CQDs could be applied to the modification of semiconductors, which was an effective method to improve the photocatalytic efficiency. At the same time, experiments showed that this N-CQDs / Bi2O2CO3 composite had great prospects for the treatment of organic pollution in water.
Keywords: carbon quantum dots; basic cesium carbonate; photocatalysis; methyl orange; degradation.
目录
摘 要…………………………………………………………………………………I
ABSTRACT………………………………………………………………………….. II
目录………………………………………………………………………………….. IV
第一章 绪论………………………………………………………………………….. 1
1.1碳量子点简介 1
1.2. 碳量子点的制备方法 1
1.2.1 水热法 2
1.2.2 微波辅助加热法 3
1.2.3 溶液化学合成法 3
1.3. 碳量子点在光催化中的应用 4
1.4. 研究意义及工作内容 5
第二章 实验部分…………………………………………………………………….. 6
2.1 实验药品 6
2.2 实验仪器 6
2.3 材料的制备 7
2.3.1 CQDs与N-CQDs的制备 7
2.3.2 N-CQDs/Bi2O2CO3的制备 8
2.4 材料的表征 8
2.5荧光量子产率的测定 8
2.6 光催化实验 8
第三章 结果与讨论………………………………………………………………… 10
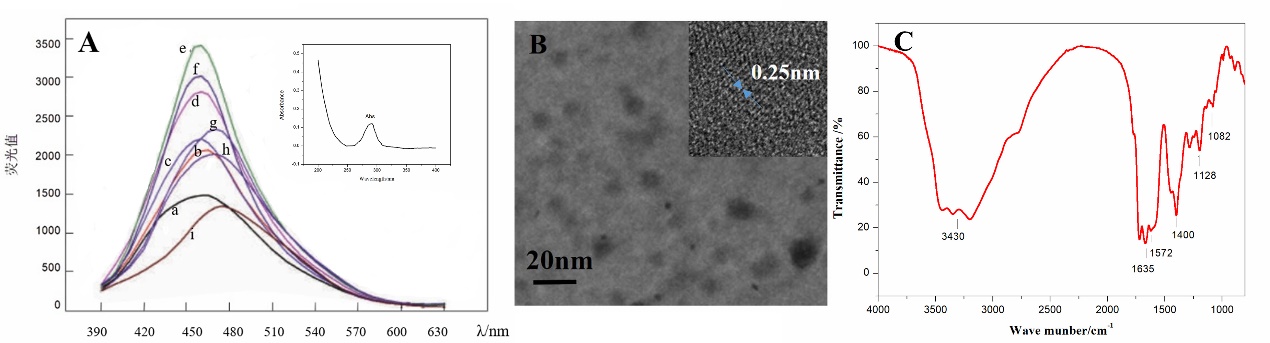
3.1 N-CQDs的形貌以及光学特性 10
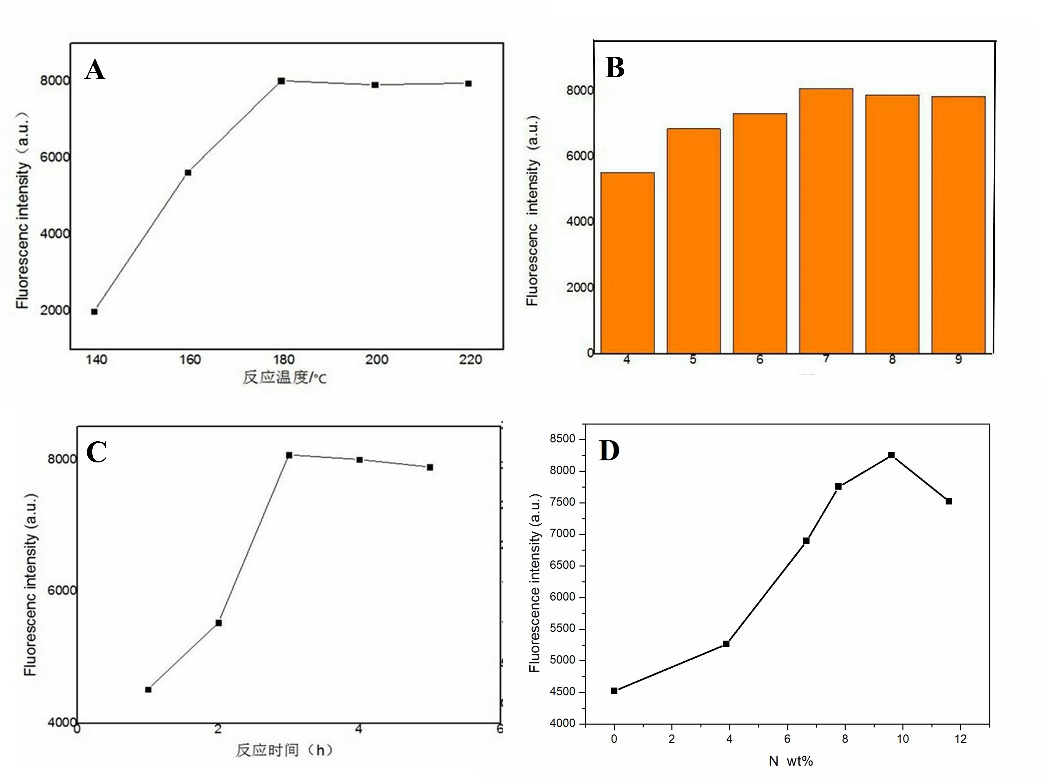
3.2 水热温度、反应时间、溶液pH以及N元素掺杂量对N-CQDs荧光性能的 影响 11
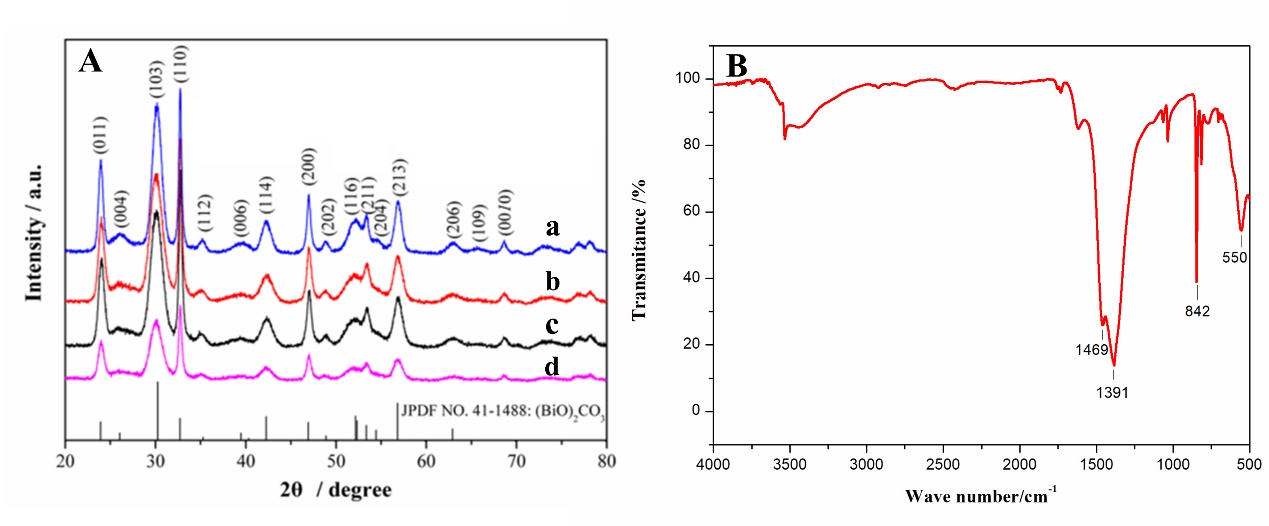
3.3 Bi2O2CO3形貌表征 12
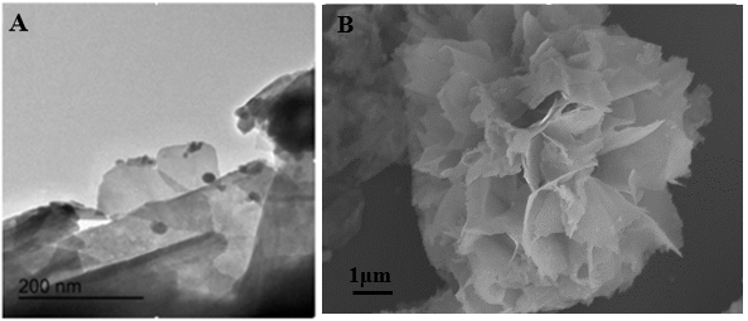
3.4 N-CQDs/ Bi2O2CO3的形貌表征 13
3.5 Bi2O2CO3和N-CQDs/ Bi2O2CO3的光谱表征 14
3.6 N-CQDs/ Bi2O2CO3的光催化降解实验 15
3.6.1 光催化条件的优化 16
3.6.2 催化剂的重复性实验 17
3.7 催化机理的探究 17
第四章 展望与结论………………………………………………………………… 18
4.1 结论 18
4.2 展望与改进建议 18
致谢 18
研究成果 20
参考文献 21
第一章 绪论
1.1碳量子点简介
生命进化的研究表明碳是有机体的内在重要成分,因此碳基化学材料成为科学领域的主导[1]。随着科学的发展,大量的研究提供了关于不同形式碳的存在的知识。在2004年,研究人员意外地发现了名为碳点(CQDs)的先进碳材料[2]。但是CQDs化学的实际时代从2006年开始的,Sun等人[3]进行了一项革命性的研究,其采用烧蚀加热的方法制得一种具有高强度强荧光的纳米粒子,并正式将其命名为CQDs。
CQDs是尺寸小于10nm的纳米颗粒,主要由作为核的sp2杂化共轭碳和有机官能团的壳组成(例如,N-H,C = O,-OH,-COOH,C-N, C-O)或聚合物聚集体。到目前为止,已经使用不同的碳源和方法来合成CQDs,并且所得到的CQDs的结构也非常不同。此外, CQDs通常通过附着小的有机分子或聚合物或通过将杂原子(例如氧,氮,硫,磷,硼,硒和氟)引入CQDs的表面,赋予CQDs具有广泛的功能。它不仅仅拥有传统制备金属纳米半导体的优异光学特性,并且对细胞及生物无毒害性、不会造成环境污染,经常作为在活体内外药物传导、荧光追踪标记、生物细胞成像的介质[4]。除此之外,由于CQDs表面基团丰富,易于功能化(复合、掺杂等)、耐光漂白和来源丰富,可以大规模制备,在活体内外药物传导、生物细胞成像、有机污染物处理、荧光追踪标记、环境有害金属离子探针、光解水制氢及光电器件和生物传感器等方面,存在极为重要的应用潜力价值,引起了科研工作者广泛关往[5-6]。
1.2.碳量子点的合成方法
随着对CQDs研究的不断深入,CQDs的制备方法层出不同,一般可分为两大类,如图1-1所示。第一类是自上而下的合成方法,它主要是指将大分子的材料不断进行切割,分散成尺寸更小的碳量子点,主要包括溶液化学、热分解、微波辅助加热法等。第二类自下而上的方法是指将小分子的碳材料不断合成来得到碳量子点,主要包括电化学氧化还原、一步水热法等。这两种过程各有其优缺点,但由于自下而上的方法步骤过于复杂,对仪器要求高,其应用较少[7]。
相关图片展示: