千米深井煤矿地应力场特征及地压控制对策研究毕业论文
2020-02-16 23:26:50
摘 要
随着浅部煤炭资源日渐枯竭,淮南矿区正逐步向深部延伸,最大采深已接近或超过1000m。煤矿巷道进入深部开挖阶段后,地质环境会变得复杂和糟糕,地应力、水头压力以及地温梯度将会明显升高,巷道因高地应力而引发的失稳破坏比例骤增。这些因巷道埋深变化而附带的地质环境和地应力等的变化将会造成煤矿巷道开挖支护过程中的重大安全隐患,也会给国家和人民带来经济损失,给深部巷道围岩稳定与巷道安全控制提出了严峻挑战。顾桥矿水平地应力高,巷道围岩稳定控制难度高,急需开展千米深井地应力测试及地压控制对策方面的研究工作,优化巷道围岩支护方法,提高巷道支护效率。
本文通过分析该矿区巷道存在的工程特点和工程实际情况,通过查看大量和本文相关的文献资料和期刊,学习和了解相类似工程的稳定性控制并掌握有限差分程序FLAC3D的用法。针对淮南矿区顾桥矿深部煤矿软岩巷道所存在的复合地层及相应地层的工程特性,建立三种支护设计方案,然后采用有限差分程序FLAC3D建立仿真数值模型,计算出不同支护设计方案的支护效果,比较得出最优的一种方案。结合深部煤矿软岩巷道围岩支护的工业性试验,对比数值模拟结果和相应的工业性试验结果然后提出最终的支护方案。论文的主要研究内容主要如下:
(1) 淮南矿区地应力场及典型深部巷道围岩力学参数分析
依托淮南矿区典型巷道,采用现场工程地质调查、室内物理力学试验分析、经验类比等手段,调查分析巷道地质构造及水文地质条件、围岩赋存应力状态等围岩赋存条件,分析淮南矿区地应力场及典型深部巷道围岩力学特性参数,为数值仿真计算及支护设计优化提供基础依据。
(2) 深部巷道开挖卸荷破坏机理及发展模式
针对依托巷道,结合(1)中的研究结果,采用FLAC3D数值模拟方法研究深部巷道围岩开挖卸荷条件下的变形破坏机理及其随时间演化特征,分析围岩不同区域的开挖扰动应力状态及其发展规律,进一步揭示开挖后围岩破坏区域及随时间的发展特征。
(3)基于FLAC3D数值模拟地压控制支护设计优化
以典型巷道为依托,结合(2)的研究结论,在现有常用的设计方案为参照基础,提出优化支护设计方案。建立FLAC3D计算模型,研究巷道围岩在不同支护方案条件下的稳定状态,通过分析计算结果进行方案比选,确定最优支护方案。
(4)地压控制优化支护监测研究
以淮南地区顾桥矿的典型巷道为试验巷道,试验经过flac3D模拟后确定的最优支护方案。对试验煤矿深部软岩巷道的顶板、底板、两帮的变形位移量进行监测,对巷道稳定性及支护结构承载状态进行监测,将监测数据整理好后与flac3D数值模拟结果进行对比,验证支付设计是否可靠。
关键词:FLAC3D;高地应力;深部巷道;围岩支护
Abstract
With the exhaustion of shallow coal resources, huainan mining area is gradually extending to the deep, with the maximum mining depth approaching or exceeding 1000m. After the coal mine roadway enters the deep excavation stage, the geological environment will become complex and bad, the ground stress, water head pressure and geothermal gradient will increase obviously, and the proportion of instability and failure caused by high ground stress in the roadway will increase sharply. These changes of geological environment and ground stress associated with the change of roadway burial depth will cause major safety risks in the process of roadway excavation and support in coal mines, and also bring economic losses to the country and people, posing severe challenges to the stability of surrounding rock and roadway safety control in deep roadways. Due to the high horizontal ground stress in Guqiao mine and the high difficulty in the stability control of roadway surrounding rock, it is urgent to carry out the research work on the ground stress test and the ground pressure control countermeasures of a kilometer deep well, optimize the roadway surrounding rock support method and improve the roadway support efficiency.
In this paper, through the analysis of the engineering characteristics and actual engineering situation of the mine roadway, through the review of a large number of literature and journals related to this paper, learn and understand the stability control of similar projects and master the use of finite difference program FLAC3D. In view of the composite stratum existing in typical roadway in this interval and the engineering characteristics of this stratum, the finite difference program FLAC3D was used to establish the analysis model. Combined with the industrial test of roadway support, the numerical simulation results and industrial test results were analyzed, and the optimal support scheme was proposed. The main research contents of this paper are as follows:
- analysis of ground stress field and mechanical parameters of typical deep roadway surrounding rocks in Huainan mining area
Based on typical of Huainan coal mine roadway, the in-situ engineering geological investigation, indoor physical mechanics test analysis and experience analogy, investigation and analysis of roadway of geological structure and hydro-geological conditions, occurrence of surrounding rock stress state of surrounding rock occurrence conditions, analysis of ground stress field of Huainan coal mine and typical characteristics of deep roadway surrounding rock mechanics parameters, optimization of numerical simulation calculation and design of support to provide basic basis.
(2) failure mechanism and development mode of deep roadway excavation and unloading
Against relying on the roadway, in combination with (1) the research results, using FLAC3D numerical simulation study of deep roadway surrounding rock under the condition of excavation unloading deformation failure mechanism and evolution characteristics over time, the analysis of excavation disturbance in different areas of the stress state of surrounding rock and its law of development, further reveal the surrounding rock after excavation damage area and the development characteristics of over time.
(3) Design optimization of ground pressure control support based on FLAC3D numerical simulation
Based on the typical roadway and the research conclusions of (1) and (2) provided by the teacher, the optimization support design scheme is proposed on the basis of the existing common design schemes. FLAC3D calculation model was established to study the stable state of roadway surrounding rock under the conditions of different support schemes. Through the analysis and calculation results, scheme comparison was conducted to determine the optimal support scheme.
(4)Ground pressure control support monitoring
The typical roadway of Guqiao mine in Huainan area was taken as the test roadway, and the optimal support scheme was determined after flac3D simulation. The deformation and displacement of the roof, floor and two sides of the deep soft rock roadway in the test coal mine were monitored, and the stability of the roadway and the bearing state of the support structure were monitored. After the monitoring data were sorted out, the results of flac3D numerical simulation were compared to verify whether the payment design was reliable.
Key Words: FLAC3D; high ground stress; deep mine roadway; surrounding rock support
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2国内外研究现状 1
1.3本文研究内容 3
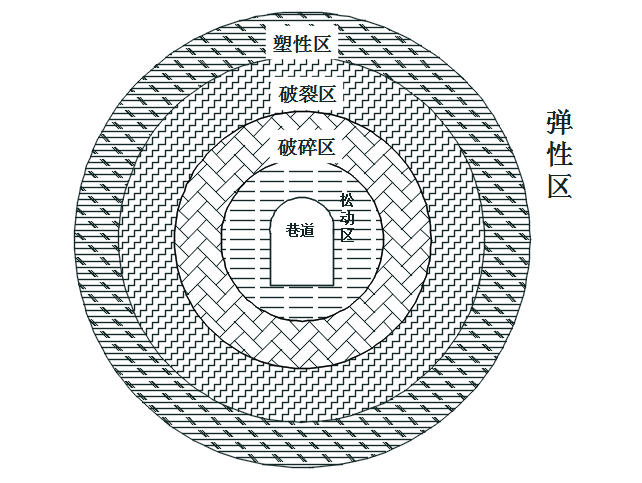
第2章 淮南矿区地应力场及深部巷道开挖破坏机理分析 4
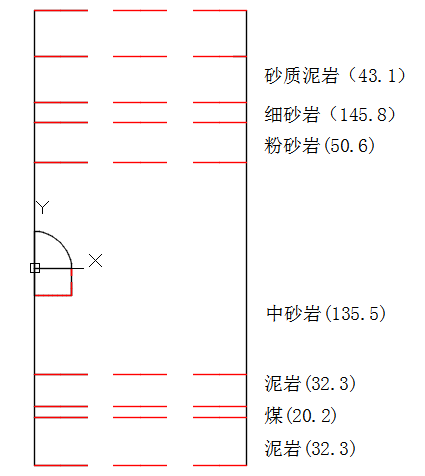
2.1淮南矿区千米深巷道赋存地质环境 4
2.1.1地质构造与工程地质条件 4
2.1.2瓦斯地质构造 4
2.1.3水文地质条件 5
2.2淮南矿区深部地应力场及其分布规律 5
2.3深部巷道开挖卸荷机理及破坏模式 6
2.3.1变形破坏机理 6
2.3.2开挖扰动状态 7
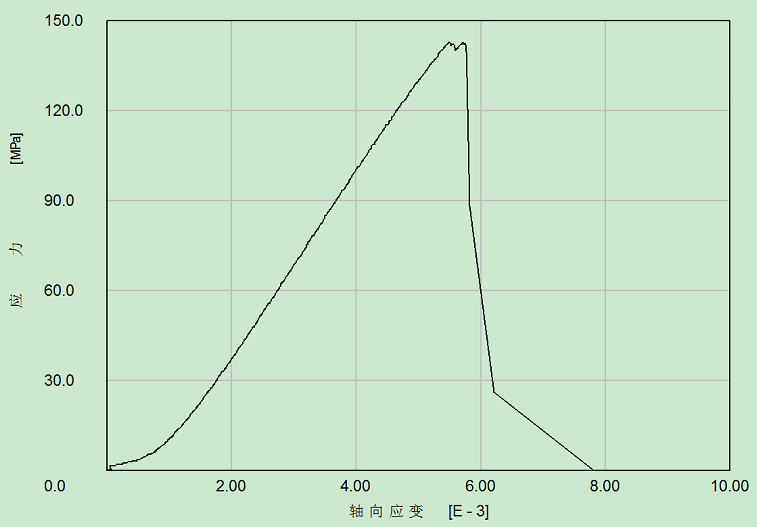
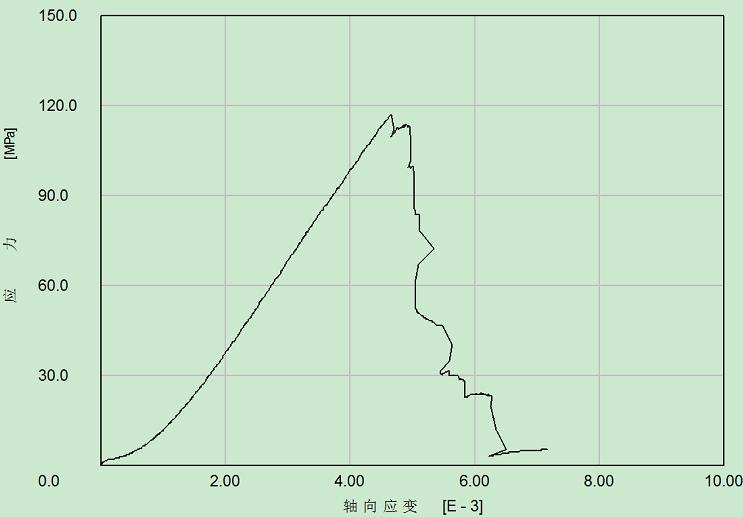
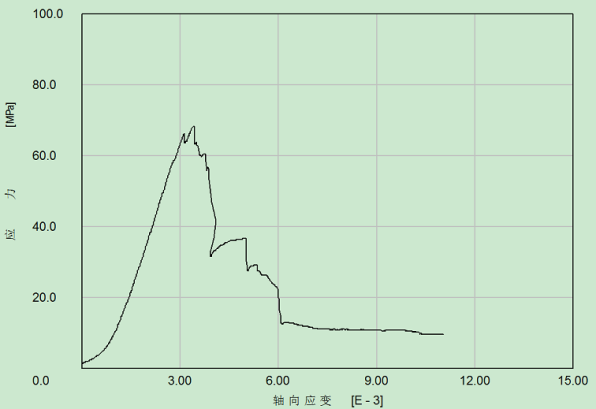
2.3.3围岩强度特征 8
2.3.4演化特征 11
第3章 深部巷道地压控制支护设计与优化 15
3.1围岩支护的基本概念 15
3.1.1巷道支护的发展 15
3.1.2巷道支护破坏的机理 15
3.1.3围岩支护的理论与原则 15
3.2巷道规格及临时支护措施 16
3.2.1巷道断面规格及支护参数 16
3.2.2临时支护措施 17
3.3.1支护方案设计思路 20
3.3.2方案一 20
3.3.3方案二 23
3.3.4方案三 26
3.3.5支护方案比选 28
第4章 巷道支护和地压控制的监测与分析 29
4.1现场监测内容与方法 29
4.2地压控制支护方案监测 31
4.3试验数据与flac3D数值模拟结果对比 33
第5章 结论与展望 34
5.1结论 34
5.2展望 34
参考文献 36
致 谢 38
第1章 绪论
1.1研究背景
随着中国能源需求的增加和中国工业对煤炭资源的长期依赖,浅部煤炭已是日渐枯竭,淮南矿区的煤炭开采已开始向深部延伸,最大采深已接近或超过1000m。进入深部开挖后的煤矿巷道,因地质环境变复杂,地应力明显升高等因素,煤矿巷道因高地应力而引发的失稳破坏比例骤增。这些因巷道埋深变化而附带的地质环境和地应力等的变化将会造成煤矿巷道开挖支护过程中的重大安全隐患,也会给国家和人民带来经济损失,给深部巷道围岩稳定与巷道安全控制提出了严峻挑战。顾桥矿水平地应力高,巷道围岩稳定控制难度高,急需开展千米深井地应力测试及地压控制对策方面的研究工作,优化巷道围岩支护方法,提高巷道支护效率。
1.2国内外研究现状
深部巷道开挖一般都是在具有高地应力的地质环境中进行,也是引发巷道失稳破坏的关键因素。准确掌握深部围岩地应力场及其开挖扰动演化特征,是地压控制和深部巷道支护设计的必要前提与步骤。因反复构造运动和沉积环境的影响,深部煤矿巷道围岩大多破碎软弱,力学强度低。目前常采用的地应力测试方法在这样的地质环境中实施极为困难,而且存在局限性和不小的测量误差。深部围岩赋存条件和应力环境与浅部明显不同,浅部巷道围岩稳定控制的理论与技术已远远不能适应深部巷道围岩稳定控制的要求,必须尽快发展深部巷道围岩稳定性分析方法、控制理论和支护技术,形成理论与技术的系统成果,然后对深部巷道开挖与支护的设计和施工进行有效指导,确保深部巷道的长期稳定和安全运行。国内外在深部地应力测量和深部地应力分布特征上以及某些特定地质条件下的深部地应力场中巷道开挖支护的研究已经是广泛而深入。如
- 煤巷深部地应力场研究
地应力的概念早在1912年首次被瑞士地质学家海姆提出,海姆先生还提出假定,认为地壳中各点上的任意方向的应力均等于单位面积上所覆岩层的重量[1]。
前苏联金尼克先生修正了海姆先生的假定,认为地壳中在任意点的垂直应力与上覆岩层的重量成正比,斜率为1,而水平应力不相等,是泊松效应的结果[1]。
我国地质学先驱李四光先生认为如果构造应力仅影响地壳上层部分区域的前提下,地应力水平方向的分量其重要性要比垂直方向的分量重要[1]。
哈斯特先生在Skandinaviska halvön所进行的地应力测量结果让其发现地壳上部所存在的地应力的最大主应力一般处处是水平的,而且地应力的垂直应力几乎处处小于水平最大主应力[1]。后来的研究也证实了哈斯特的发现。
刘泉声,刘恺德等[2]在淮南矿区进行深部地应力测量而且根据测量结果对深部地应力场进行研究。研究发现淮南矿区的深部地应力场是构造应力占绝对优势。垂直应力在最大和最小主应力之间,不过最小主应力与垂直应力相差不大。
董鹏,蔡海兵等[3]的研究发现,在宏观统计分析下淮南矿区深部地应力场总体为高地应力区,垂直应力随深度线性增长。当深度增加,测压比会相应减小,当深度处于800m-1100m的区间时,测压比接近1。
(2)深部煤矿巷道地应力控制研究
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: