Cu对MnNiIn铁磁形状记忆合金马氏体相变与磁性的影响毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:48:51
摘 要
近年来,Heusler的优异的物理性质逐渐受到科学家们的青睐,比如热电性质、半金属性等,尤其是Heusler合金的铁磁形状记忆效应。本文的研究内容就是计算Cu替Mn50Ni40In10合金时马氏体相变温度呈现不同的变化行为的原因。具体来说,本文的计算可以分为以下几个方面:
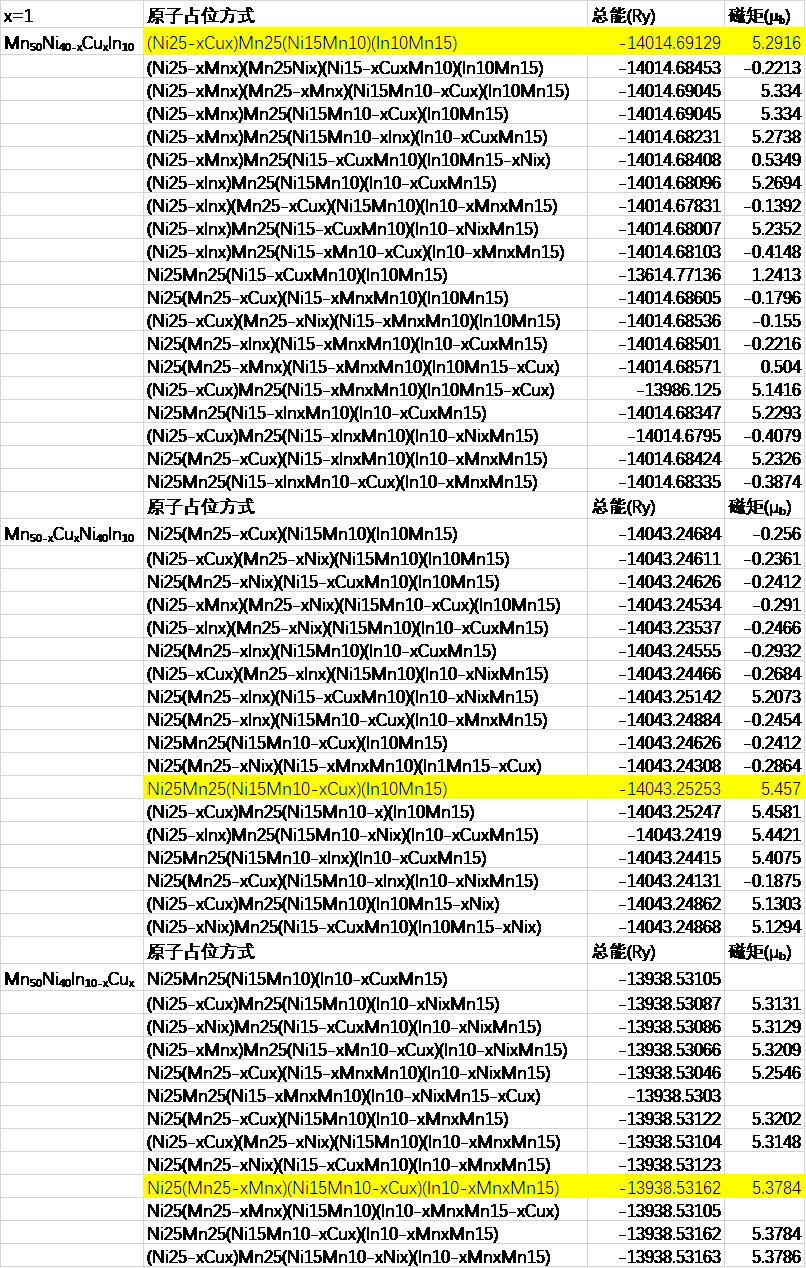
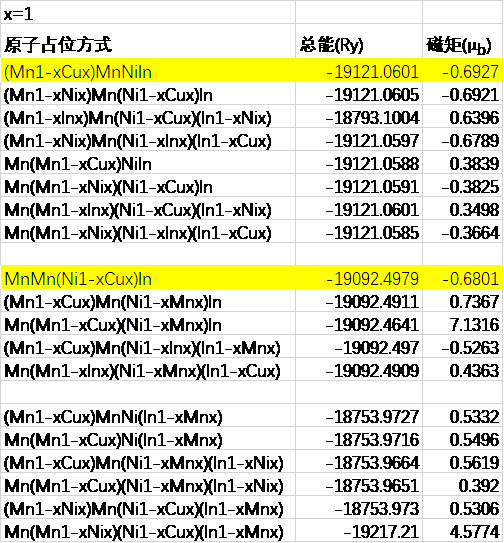
(1)第一部分首先是利用基于密度泛函理论的KKR-CPA-LDA程序包计算Cu分别替代Mn50Ni40In10合金中的Mn、Ni、In原子时的最稳定的占位方式。
(2)第二部分是通过总能计算的方法分别优化Cu掺杂Mn50Ni40In10合金中所形成三种合金体系在不同的掺杂量时的晶格常数。
(3)第三部分是计算Cu进行掺杂时合金的平均价电子数与价电子浓度随掺杂量的变化关系,尝试解释马氏体相变温度的不同变化行为。
(4)第四部分是计算Cu进行掺杂时合金的态密度随掺杂量的变化关系,深刻揭示Cu掺杂时合金的马氏体相变温度呈现不同变化行为的具体原因。
关键词:Heusler合金 铁磁形状记忆合金 电子结构 态密度
Effect of Cu on Martensitic Transformation and Magnetic Properties of MnNiIn Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy
Abstract
In recent years, Heusler's excellent physical properties have gradually been favored by scientists, such as thermoelectric properties, semi-metallic properties, etc., especially the ferromagnetic shape memory effect of Heusler alloy. The research content of this paper is to calculate the reason why the martensitic transformation temperature exhibits different behaviors when Cu is used for Mn50Ni40In10 alloy. Specifically, the calculations in this paper can be divided into the following aspects:
(1) The first part is to use the KKR-CPA-LDA package based on density functional theory to calculate the most stable occupancy mode when Cu replaces Mn, Ni and In atoms in Mn50Ni40In10 alloy.
(2) The second part is to optimize the lattice constants of the three alloy systems formed in Cu-doped Mn50Ni40In10 alloy at different doping levels by the total energy calculation method.
(3) The third part is to calculate the relationship between the average valence electron number of the alloy and the valence electron concentration with doping amount when Cu is doped, and try to explain the different change behavior of martensite transformation temperature.
(4) The fourth part is to calculate the relationship between the state density of the alloy and the doping amount when Cu is doped, and reveals the specific reasons why the martensitic transformation temperature of the alloy exhibits different behaviors during Cu doping.
Key Words: Heusler alloy Ferromagnetic shape memory alloy Electronic structure State density
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 智能材料的分类 1
1.1 铁电材料 1
1.2 磁致伸缩材料 2
1.3 形状记忆合金 2
第二章 Heusler合金的简介 4
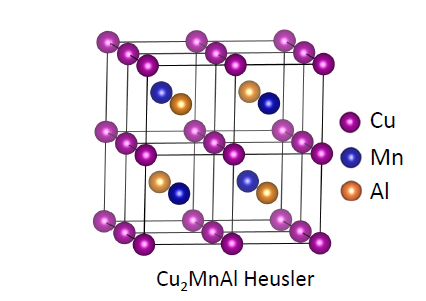
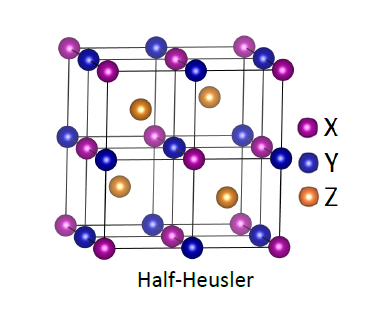
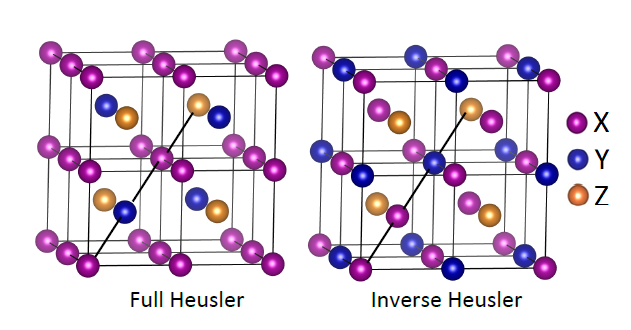
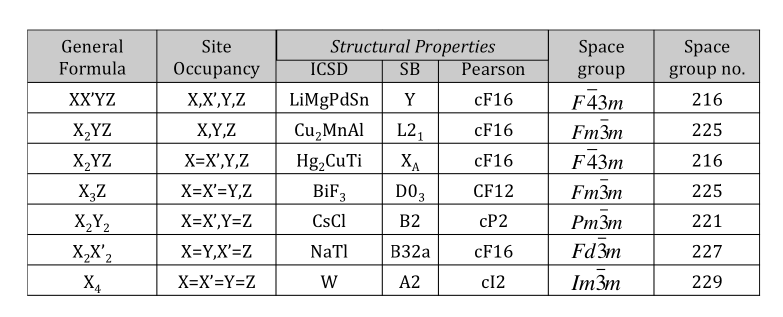
2.1 Heusler合金的晶体结构 4
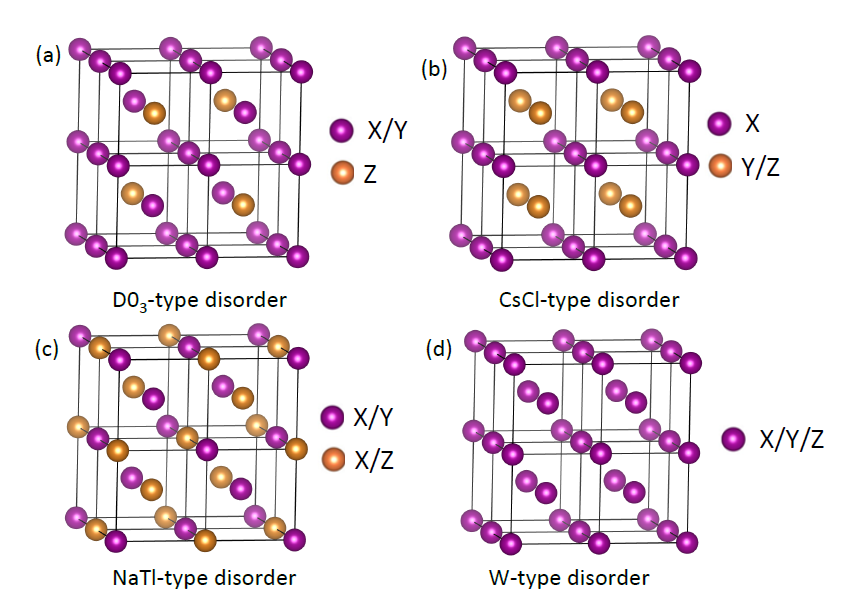
2.2 掺杂元素对Heusler合金结构的影响 7
第三章 马氏体相变和铁磁形状记忆效应 9
3.1 相变及其分类 9
3.2 马氏体相变 10
3.3 NiMnIn合金的铁磁形状记忆效应 10
3.4 影响铁磁马氏体相变温度的因素 11
3.5 NiMnIn:Cu合金中相变温度的变化 12
第四章 理论计算方法 13
4.1 密度泛函理论的简介 13
4.2 格林函数简介 14
4.3相干势近似(CPA) 14
4.4 理论计算模型 15
第五章 计算结果 16
5.1 掺入Cu原子的具体占位方式 16
5.2晶格参数的优化 19
5.3 平均价电子数与价电子浓度的计算 21
5.4 电子结构的计算与分析 23
第六章 结果与展望 29
6.1 结论 29
6.2 未来工作展望 30
参考文献 31
致 谢 33
第一章 智能材料的分类
随着21世纪科技的迅速发展,智能材料逐渐进入了人们生活之中。智能材料是一种功能材料,它们可将某种形式的输入能量转换为不同形式的输出能量。这些智能材料可以对外部刺激(例如热,电场或磁场,应力和光)的力学,电学,弹性,磁性,热或流变性质的变化做出反应。常见的输入-输出关系如表1.1所示。智能材料特点是去除外部驱动时可以恢复原始形状和特性,这使得它们适合作为驱动器和传感器。根据驱动的类型和产生响应的方式,智能材料可大致分为几类:压电,电致伸缩,磁致伸缩,电流变和磁流变,形状记忆和铁磁形状记忆等等。这一节简单介绍一些比较重要的智能材料。
表1.1 常见的输入-输出关系