三氯乙烯降解菌的筛选及降解特性的研究毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:58:14
摘 要
本文采用梯度富集的方法,在被三氯乙烯污染的土壤中筛选出了四株三氯乙烯降解菌,将四株降解菌命名为X1、X2、X3、X4。运用16S rDNA基因序列分析,对菌株进行初步鉴定。分析得到的结果显示,菌株 X1、X2及X4,是假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas sp.)。菌株X3,是无色杆菌属(Achromobacter sp.)。采用气相色谱法测定三氯乙烯浓度,确定各菌株在接种量10%,温度为30℃条件下降解三氯乙烯的能力。得出结果,菌株X1为三氯乙烯最优降解菌,降解率达到66.37%,其次为菌株X4,降解率为63.83%。对X1和X4两株菌株进行条件优化。通过单因素试验法,研究pH、温度和接种量对降解率的影响规律,最终确定了两株三氯乙烯降解菌的最优pH、最优温度以及最优接种量。其中X1菌在pH为7、温度为35℃及接种量为20%,最适条件下降解三氯乙烯的效率最高;X4菌在pH为7、温度为35℃及接种量为20%,最适条件下降解三氯乙烯的效率最高。
[ 关键词 ] :三氯乙烯降解菌 降解 分离筛选 假单胞菌
Screening of trichloroethylene degrading bacteria and their degradation characteristics
ABSTRACT
In this paper, four strains of trichloroethylene degrading bacteria were selected from the soil contaminated by trichloroethylene by means of gradient enrichment, coating and streaking. The four strains of trichloroethylene degrading bacteria were named as X1, X2, X3and X4,respectively. Moreover, in this paper, 16S rDNA gene sequence analysis will be used.Strains X1, X2 and X4 was found to belonged to pseudomonas.,and strain X3 was found to belonged to Achromobacter sp..The concentration of trichloroethylene was determined by gas chromatography, and the ability of each strain to degrade trichloroethylene at a seeding rate of 10% and a temperature of 30 ℃ was determined.strain X1 is the best biodegradable strain for trichloroethylene., with a degradation rate of. 66.37%.; followed by strain X4, and the degradation rate was 63.83%.Condition optimization of two strains of X1 and X4. The effects of pH, temperature and inoculation on degradation rate were studied by single factor experiment.The optimum pH value, temperature and inoculum of trichloroethylene were determined. The X1 strain has the highest efficiency at the pH of 7, the temperature is 35 ° C and the inoculation amount is 20%. The efficiency of degrading trichloroethylene is optimum;The X4 strain has the highest efficiency at the pH of 7, the temperature is 35 ° C and the inoculation amount is 20%. The efficiency of degrading trichloroethylene is optimum.
[Key Words] : Trichloroethylene; Degrade;Separation screening;Pseudomonas
目录
第一章 绪论
1.1. 前言
1.2. 三氯乙烯的降解
1.2.1. 现状
1.2.2. 研究意义
第二章 实验材料与方法
2.1. 实验材料与仪器
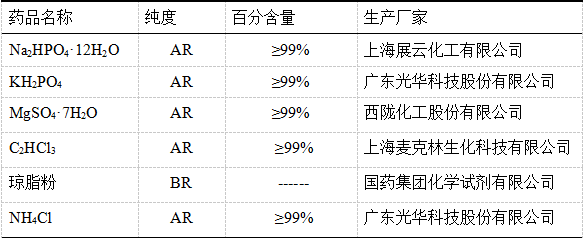
2.1.1. 实验材料
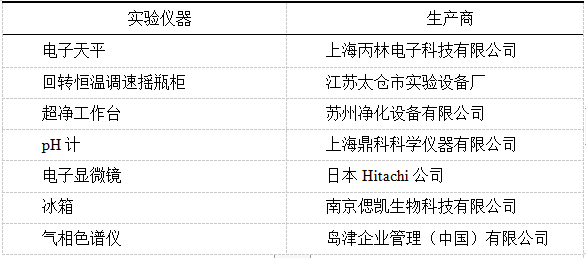
2.1.2. 实验仪器
2.2. 实验方法
2.2.1. 筛选三氯乙烯降解菌
2.2.2. 三氯乙烯检测方法
2.2.3. 三氯乙烯降解菌降解能力的验证
2.2.4. 三氯乙烯降解菌培养条件的优化
第三章 结果与讨论
3.1. 菌株的筛选
3.2. 菌株的鉴定
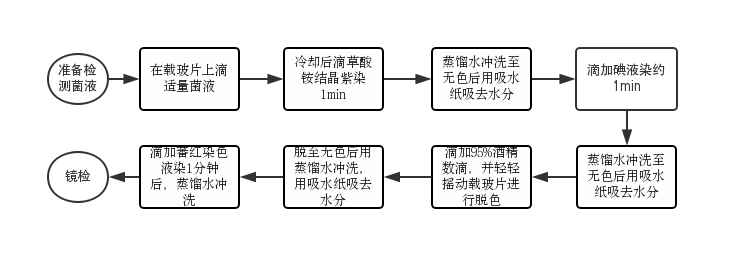
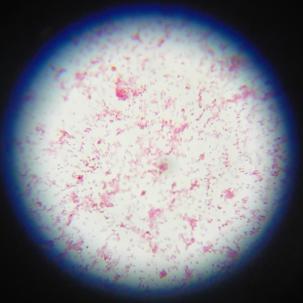
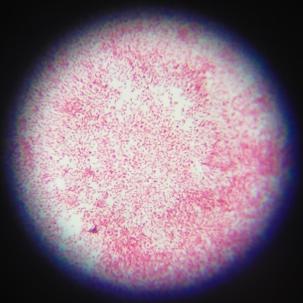
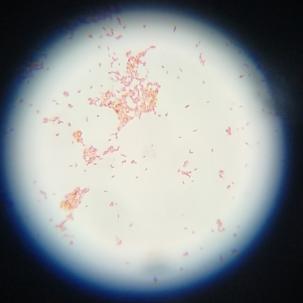
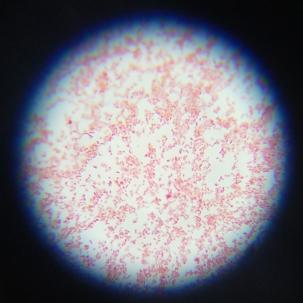
3.2.1. 革兰氏染色结果
3.2.2. 16S rDNA基因鉴定
3.3. 三氯乙烯降解菌的降解能力
3.3.1. 三氯乙烯标准曲线
3.3.2. 三氯乙烯降解能力的验证
3.4. 三氯乙烯降解菌培养条件优化
3.4.1. X1菌株降解三氯乙烯
3.4.2. X4菌株降解三氯乙烯
第四章 结论与展望
4.1. 结论
4.2. 展望
参考文献
附录
致谢
绪论
前言
三氯乙烯,是一种易挥发的有机氯代烃化合物。在现代生活中,它的许多优良的特点被广泛应用在诸多行业,特别在化工行业中,将会作为非常重要的原料。随着三氯乙烯的广泛应用的同时也产生了许多环境污染问题,由于不达标准的工业废水排放将会导致含有三氯乙烯的废弃物被大量释放到环境中。相比其他污染物而言,三氯乙烯在水体沉积物中较为普遍,并且三氯乙烯对生物的毒性作用也较强,并且具有持久性[1]。随着如今科技的进步和发展,工业废水水量加大,对处理废水的需求也会不断增加,但是,值得注意的是不合理的处理方式可能加重污染。
三氯乙烯具有较大的毒性,对于人体的中枢神经系统有麻醉作用,也会引起肝、肾、心脏及三叉神经的损害,并存在着三致(致畸致癌致突变)的危险[2-3]。我国对于三氯乙烯造成的人体危害研究也逐渐增多,在各地都有针对性的调查研究。工厂工人在长时间的工作后,会对身体造成一定程度的伤害,并且具有持久性[4-5]。三氯乙烯主要是通过皮肤及呼吸道吸入人体内,从而对人体的产生危害。因此,许多国家都已将其列入优先控制污染物黑名单,国内对使用三氯乙烯的企业也实施了严格的环保审查和环保整顿[6]。在对三氯乙烯的危害研究深入的同时,国际上各大环保组织及癌症研究组织都将三氯乙烯纳入了致癌物名单中。国内外各大医院也对三氯乙烯造成的机体损害进行了研究治疗,但目前控制病情的效果并不理想。
相关图片展示: