OLED内提取光学结构的模拟计算毕业论文
2020-05-25 23:39:07
摘 要
OLED,即有机电激发光二极管,发展速度迅猛异常,已经在显示、照明等领域取得了巨大的成功。但是,一般的OLED光学结构不理想,出光率较低,一般而言光输出效率仅在20%左右。由于玻璃层与空气折射率相差较大,导致一部分的光全反射而形成波导,被困在器件之中,无法射出。就目前而言,提高光提取效率的方法大致分为一下几种:基底涂布散射层技术,通过改变光的随机轨道使得被反射的光射出;微腔共振科技,将一个由多层介质膜构成的布拉格反射镜(DBR)插入铟氧化锡层与玻璃基底之间,主要效用是影响分子的激发态,增强光之强度;还有便是在ITO层与玻璃基底之间加入纳米散射层。
本文首先介绍了OLED的发展历史、基本概况、发光原理、发展前景、OLED光学模型等内容,随后介绍FDTD软件,建造OLED模型,模拟出光实验。我们将着力探讨,在玻璃基底层与ITO阳极层之间,引入纳米散射层,通过散射、干涉、衍射等方式,将被困的光导出,从而提高OLED器件的出光效率。采用的研究手段便是利用FDTD软件进行模拟计算,建立模型。在光源波段400-700nm范围中,通过改变纳米散射层的纳米小球直径、小球间距与折射率这三个要素,研究其对出光率的影响。我们发现,纳米散射层的加入,有效提高了OLED出光效率。当纳米小球的直径越大,对出光率的增强倍数也越大,但有一个消极影响便是造成光谱偏移。小球间距越大,增强效果越弱,同时,间距对光色的影响也尤为明显。最后,纳米散射层折射率越大,出光率越高。并且在此基础上,我们试图寻求最佳结构,为优化OLED提供参考。
关键词:OLED 纳米散射层 出光率 FDTD
Simulation of internal extraction structure
in organic light emitting diodes
Abstract
OLED, namely organic light diodes, abnormal rapid pace of development, has achieved great success in the display, lighting and other fields. However, the general OLED optical structure is not ideal,a lower rate of light. The light output efficiency in general only about 20%. Since the refractive index of the glass layer and the air quite different, resulting in a portion of the optical waveguide formed by total reflection, being trapped in the device and can not be fired. For now, to strengthen light extraction efficiency of the way is generally classified as follows: a substrate coating scattering layer technology, by changing the light rail makes random reflected light is emitted; microcavity resonance technique, a multilayer dielectric film Bragg reflector (DBR) mirrors inserted between the composition of the indium tin oxide layer and the glass substrate, the main effects of the excited molecule, to enhance the intensity of light; there is between the ITO layer and the glass substrate was added nano-scattering layer.
This paper This paper shows the introduction of the OLED development history, basic profile, light-emitting principle, the development prospects, OLED optical model and other content, then introduced FDTD software, build OLED model, simulate light experiment. We will focus on discussions with the glass substrate layer amp; the ITO anode layer, the introduction of nano-scattering layer by scattering, interference, diffraction, etc., to export the trapped light, thereby improving the light efficiency of the OLED device. Research methods employed is the use of FDTD simulation software, build the model. The range of wavelength is from400-700nm, by changing the scattering layer nano-nano-ball diameter, the ball spacing and the refractive index of these three elements, study its effect on the rate of light. We found that the addition of nano-scattering layer, effectively improve the OLED light extraction efficiency. When the nano-beads larger the diameter of the light extraction efficiency enhancement multiples greater, but there is a negative impact caused by the spectral shift. The ball the greater the spacing, the reinforcing effect is weaker, while the distance between the light-colored impact is particularly evident. Finally, nano-scattering layer refractive index, the higher the rate of light,and on this basis, we try to find the best structure to provide reference for optimizing OLED.
Keywords: OLED Nano-scattering layer light-out rate FDTD
目录
摘 要 II
Abstract III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 OLED的基本结构 2
1.3 OLED的发光原理 4
1.3.1 载流子的注入 4
1.3.2 载流子的迁移 5
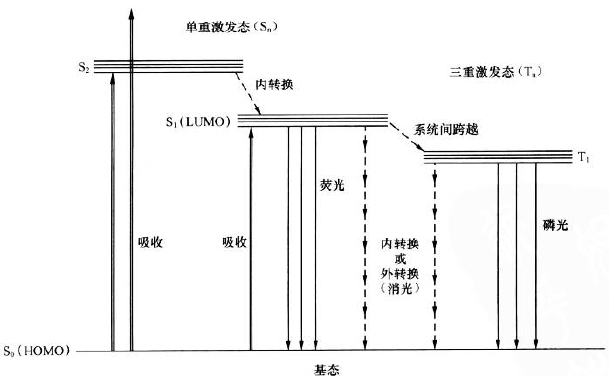
1.3.3 激子的形成 5
1.4 OLED的优点 6
1.5各层材料的选用 7
1.6 OLED发展前景 7
1.7 本论文的主要工作 8
第二章 理论基础 9
2.1 增强出光率的方法 9
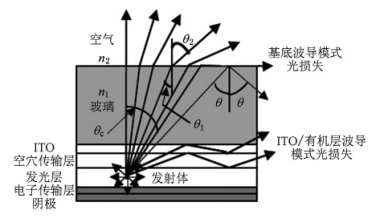
2.1.1提高基底光取出技术 9
2.1.2抑制ITO/有机层波导模式 9
2.1.3微腔共振技术 10
2.2 OLED的主要参数 10
2.2.1发光效率 10
2.2.2 光谱 11
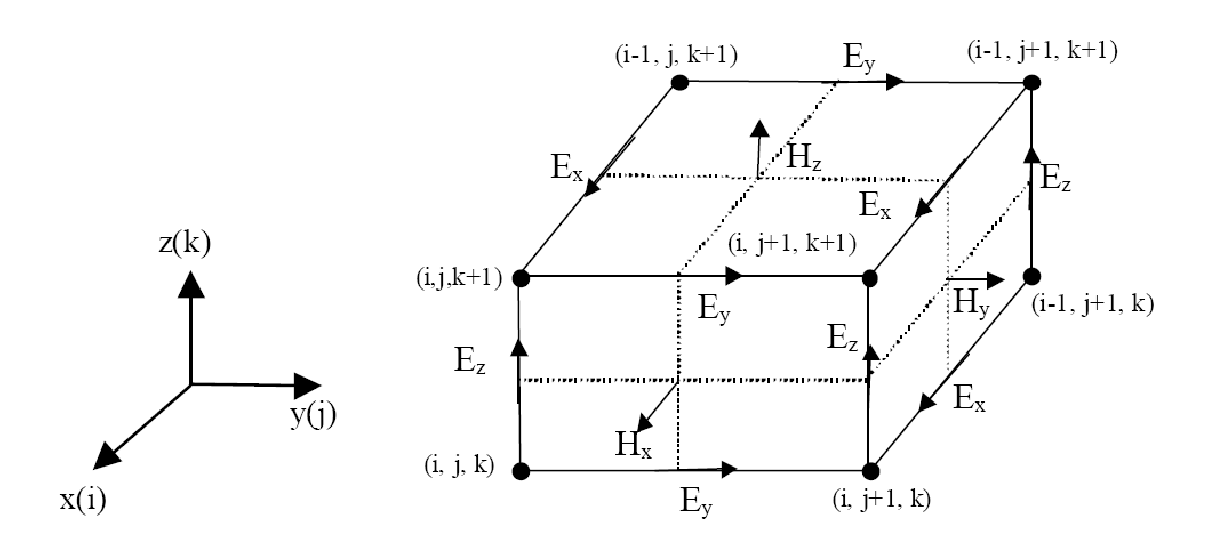
2.3 FDTD软件简介 11
2.4 FDTD模拟流程简介 12
第三章 纳米散射层对OLED出光率的影响 13
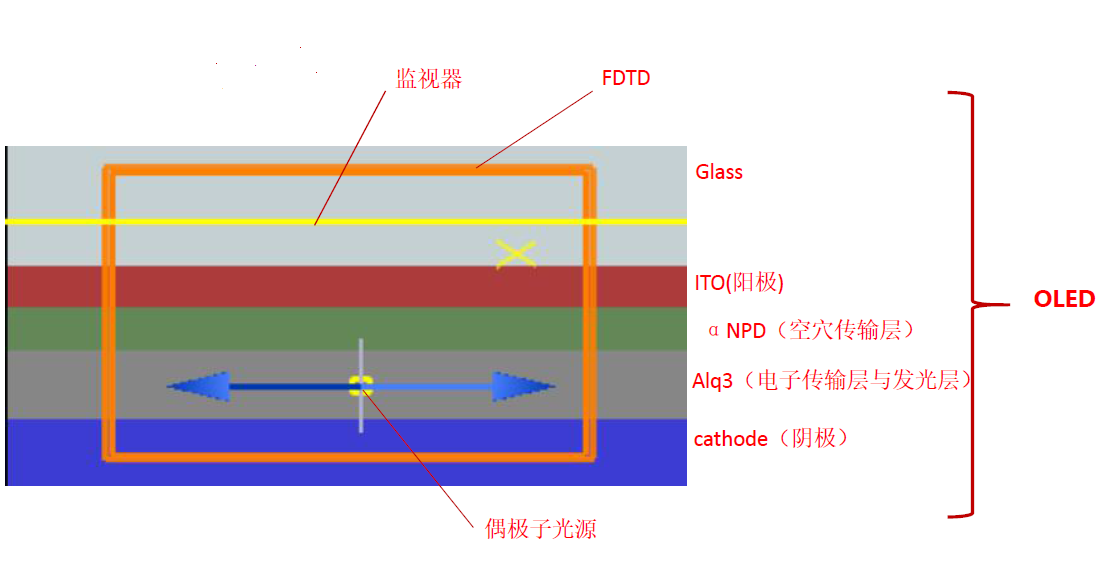
3.1 FDTD仿真模拟基本介绍 13
3.2模拟结果及分析 14
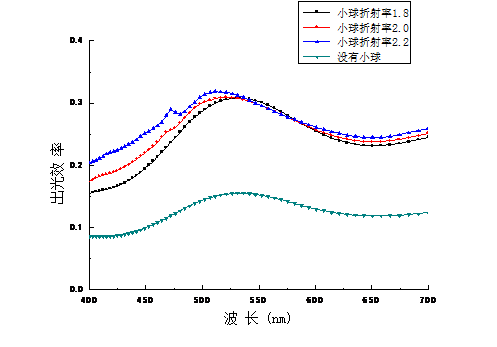
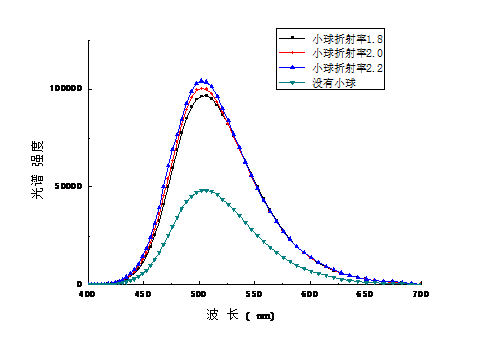
3.2.1纳米散射层折射率对OLED出光率的影响 14
3.2.2纳米散射层小球间距对OLED出光率的影响 15
3.2.3纳米散射层小球半径对OLED出光率的影响 17
3.3本章小结 18
第四章 总结与展望 20
4.1 总结 20
4.2 展望 20
参考文献 22
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
当今世界飞速向前,对能源的需要越来越大。科技持续发展的同时,地球环境亦不堪重负。在能源压力愈演愈烈的今天,缓解能源压力迫在眉睫。而解决这一问题,主要从两个方面入手,一是发展新能源;二则是节能减排。据统计,照明领域所消耗的能量大约占总能量的20%,因此提高照明效率是一个有效的方法。早先的电激发光现象由Destriau等人在20世纪30年代年发现,而在当时,无机材料是光电材料的重要组成,直至最近几年,白光LED技术,等等也都使得无机发光二极管等技术继续发展壮大。但无机材料缺点较多,例如无法制造出高分辨率的显示器,发光效率不计有机材料,可塑性较差等,这也使得人们将目光转移到了有机材料上。
有机电致发光二极管( organic light emitting diode),又称OLED,现如今以相当迅猛的速度蓬勃生长,其制造成本较低、加工性能好、较好的发光性质、超轻薄、宽阔的视角等一系列的优点[1-3],被认为是理想的并具有市场潜力的显示照明技术之一。如今,OLED显示器、照明板等应用设备已进入公众视野,巨大的应用价值使人们加速了对它的研究。电激磷光材料以及热激发延迟荧光材料的开发使得OLED的内量子效率已经能达到100%,然而由于光学结构不理想,出光率较低,严重制约了其发展与应用,因此,改善OLED光学结构,提高出光效率,已经成为世界各国的研究热点[4-5]。
OLED的发展历史大约分为以下几个阶段[6-9]:
相关图片展示: