降熔元素的添加对钛合金碳钢瞬间液相复合界面微观组织的影响毕业论文
2020-06-28 20:12:37
摘 要
钛合金/碳钢的复合在汽车制造、海洋工程中有很大的发展前景,而中间层成分的选择对两种金属的复合至关重要。本文选用铜锌合金为中间层,通过改变铜的含量,来探究了降熔元素对钛合金/碳钢瞬间液相复合界面组织和性能的影响,并通过X射线衍射、光学显微镜、显微硬度分析等手段,对界面组织和力学性能进行了检测。结果发现,在910℃的条件下,复合时间为1h,钛合金与碳钢之间加入铜锌合金中间层能够较成功的发生瞬间液相复合。随着降熔元素含量的不同,其组织和力学性能都会发生改变。中间层中降熔元素Zn含量越高,扩散区的总厚度以及分别各层的厚度都相对降低,而且碳钢侧扩散层发生了晶粒长大。随着中间层中Cu含量的增多,碳钢侧扩散层的硬度逐渐增大。以H65为中间层制得的样品的硬度分布方差较小,即硬度分布较为均匀。
关键词:瞬间液相复合 钛合金复合 力学性能 显微组织
Effect of the melting point modifiers on Transient Liquid Phase Bonding between Titanium Alloy and Carbon Steel
Abstract
Titanium alloy/carbon steel composites have great development prospects in Car manufacturer and marine engineering, and the selection of inter-layer components is crucial for the recombination of the two metals. In this paper, the copper-zinc alloy is selected as the inter-layer. And the influence of the melting point modifiers on the interfacial microstructure and properties of the instantaneous liquid phase composite of the titanium alloy/carbon steel is investigated by changing the content of copper. In addition, X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy and microhardness analysis were used to detect the interface microstructure and mechanical properties. It was found that the instantaneous liquid phase recombination can be successfully achieved by adding a copper-zinc alloy inter-layer between the titanium alloy and the carbon steel under the conditions of 910° C and a recombination time of 1 h. With the different content of the melting point modifiers, their microstructure and mechanical properties will change.The higher the melting point modifier (Zn) content in the inter-layer, the lower the total thickness of the diffusion zone and the thickness of each layer. In addition, grain growth occurred in the carbon steel side diffusion layer. With the increase of Cu content in the inter- layer, the hardness of the diffusion layer of carbon steel side gradually increases.The hardness distribution variance of samples prepared with H65 as the intermediate layer is smaller, ie, the hardness distribution is more uniform.
Key Words: TLP; Composite of titanium alloy; Mechanical properties; Microstructure
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
目录 III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 钛合金/碳钢复合材料研究现状 1
1.1.1 钛合金复合方法 1
1.1.2 钛合金/碳钢复合中的问题 1
1.2 瞬间液相复合 2
1.2.1 瞬间液相复合过程 3
1.2.2 瞬间液相复合技术研究进展 4
1.3 本课题研究的内容及意义 5
第二章 实验材料和方法 7
2.1 实验材料及设备 7
2.1.1 实验材料 7
2.1.2 实验设备 7
2.2 实验方法 8
2.3 分析及测试方法 8
2.3.1 光学显微镜观察 8
2.3.2 X射线分析 9
2.3.3 显微硬度分析 9
第三章 实验结果与分析 10
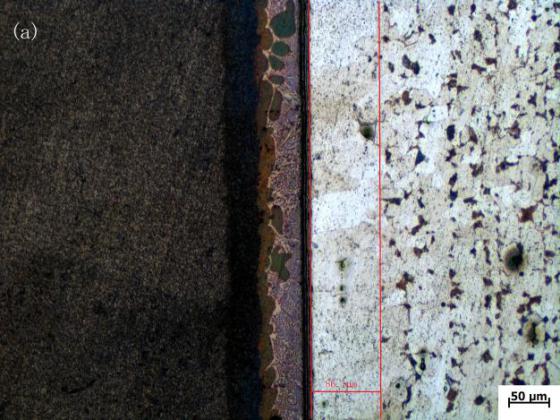
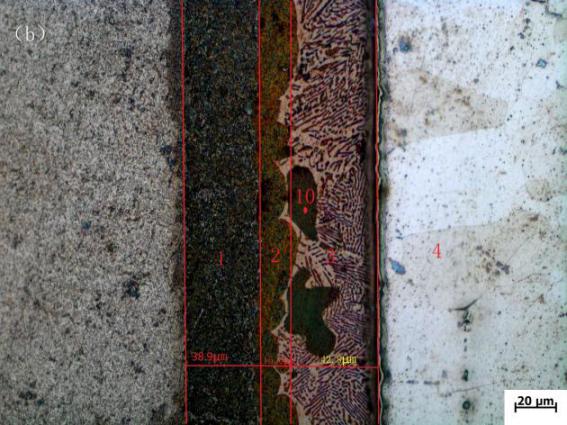
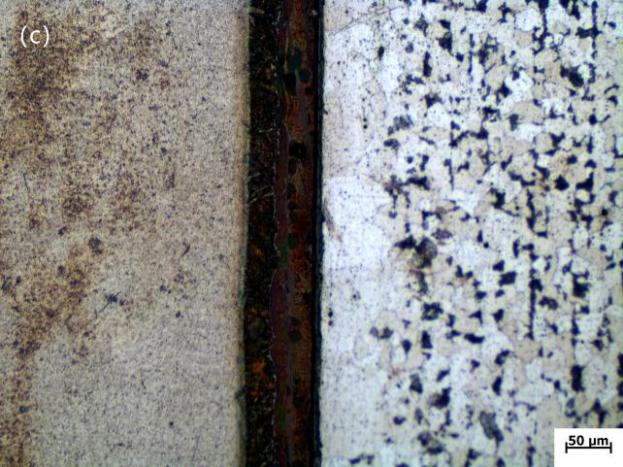
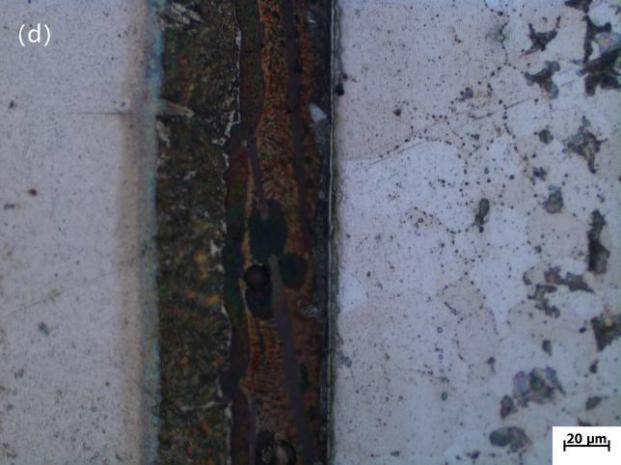
3.1 降熔元素对组织的影响 10
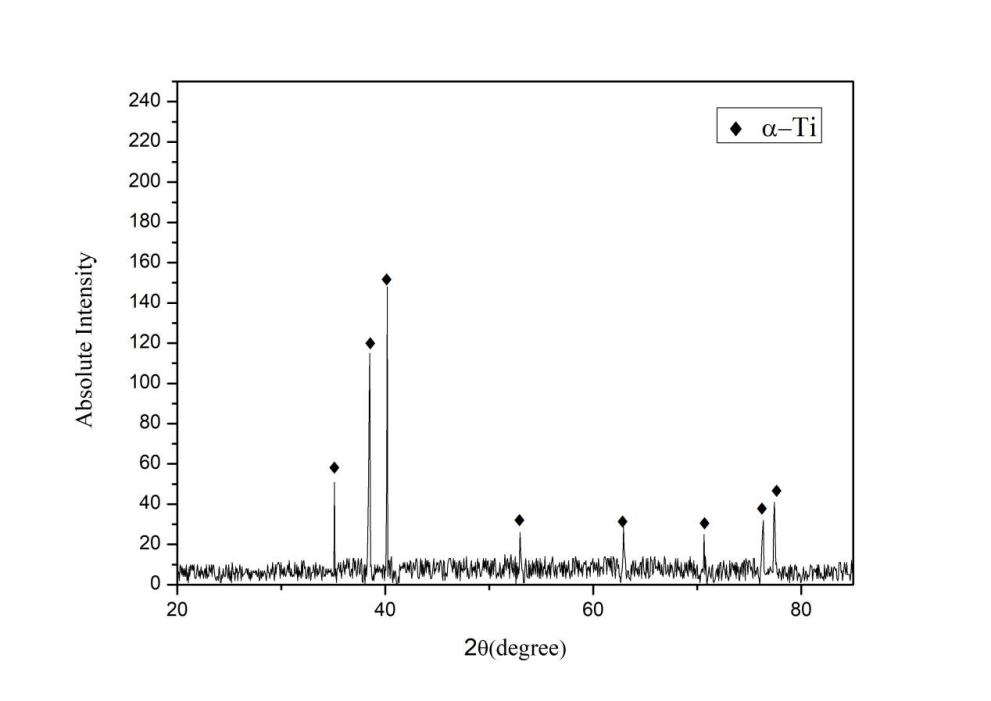
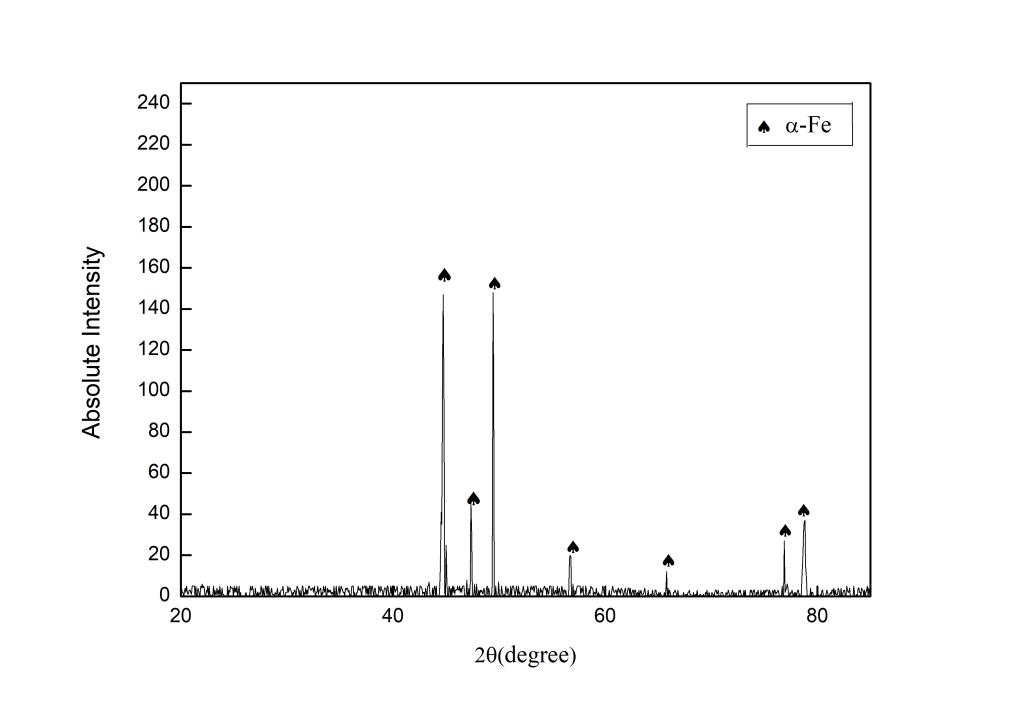
3.1.1 X射线衍射分析 10
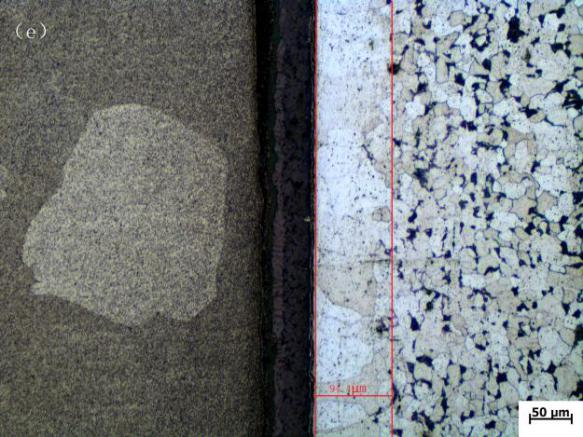
3.1.2 光学显微镜分析 11
3.1.3 降熔元素对各组织厚度的影响 13
3.1.4 降熔元素对碳钢侧扩散层晶粒度的影响 14
3.1.5 电子显微镜分析 15
3.2 降熔元素对力学性能的影响 17
第四章 结论 19
参考文献 20
致谢 22
第一章 绪论
1.1 钛合金/碳钢复合材料研究现状
1.1.1 钛合金复合方法
在近代工业发展中,钛及钛合金之所以成为了高性能结构件的首选材料,是因为其优良的耐腐蚀性能、耐高温性能、低的密度,并显现了其较大的发展潜力[1],但其性能仍不能满足由于高新技术领域的迅猛发展所带来的更多更大地需要。最近几年的时间,钛合金与其他金属的复合方面的研究逐渐发展,不断取得各种成就[2]。一般来讲,金属之间的复合分为两种,一种属于弥散强化型复合,又被称为金属基复合[3,4],应用到钛合金上即钛基复合材料,它的许多性能都优于原钛材料,它克服了原来的一些缺点,它可形成形状各一不同要求的零部件,减少了废料产生以及机械加工过程中的损耗[5];钛基复合材料能够应用于诸多情况下的恶劣条件,并可以减少钛使用量,降低成本,因此这被认为是能够拓宽钛材应用前景的一代材料[6]。除此之外,另一种金属复合的方法为层状复合[7],其属于金属连接的一种。层状金属复合材料是指利用复合方法使两种或两种以上层状金属牢固结合而制成的一种新型的复合材料。最近几年,这种技术在性能改进、成本降低等方面的研究卓有成效。
1.1.2 钛合金/碳钢复合中的问题
相关图片展示: