无机低温微波烧结填缝剂的制备毕业论文
2020-07-08 21:44:13
摘 要
近年来,伴随着建筑业的发展,各类室内外面砖、地砖的使用广泛,因此瓷砖填缝剂的需求也日益增加。现有填缝剂主要可分为两类:水泥基填缝剂和反应型树脂填缝剂。但都分别有着各自缺点,如泛碱掉粉现象、粘结强度低和价格高昂等。
本课题主要从事无机低温微波烧结填缝剂的制备研究。通过对以磷铝元素为主的低熔点玻璃粉制备,调控原料组分中各组分的质量百分比,再加入少量固化剂和微波吸收介质,通过低温微波烧结方式进行制备,形成流动好、吸水量低且粘结强度高的填缝剂,研究填缝剂的力学性能与热学性能,并且使其固化时间适中,选择合适的组分比并探究填缝剂的使用寿命。
通过实验研究发现加入不同的固化剂,对填缝剂的固化时间及粘结强度均产生明显的影响,在实验中,以磷酸二氢铝作为无机粘结剂制备的填缝剂,与中性硅溶胶对比,其添加效果更为良好。在此基础上,通过更深入的研究发现,加入铁氧体微波吸收材料,大大缩短了填缝剂的固化时间,较为方便快捷,使用效果良好。
关键词: 填缝剂;固化;微波烧结
Preparation of Inorganic Low-temperature Microwave Sintering Sealat
Abstract
In recent years, along with the development of the construction industry, various kinds of indoor and outdoor bricks and floor tiles have been widely used, so the demand for tile sealants has also increased. Existing grouts can be mainly divided into two categories: cement-based grouts and reactive resin grouts. However, they all have their own shortcomings, such as the phenomenon of pan-alkali powder, low bond strength and high prices.
This topic is mainly engaged in the preparation of inorganic low temperature microwave sintering gap sealants. Preparation of low-melting-point glass powder mainly composed of phosphorus-aluminum element modulates the mass percentage of each component in the raw material component, adding a small amount of curing agent and microwave absorbing medium, and preparing through low-temperature microwave sintering to form a good flow and water absorption. The sealant with low amount and high bond strength was studied to study the mechanical properties and thermal properties of the sealant, and the curing time was moderate. The appropriate composition ratio was selected and the service life of the sealant was explored.
Through measurement and observation. By adding different curing agents, there are different influences on the curing time and bonding strength of the gap sealant. For example, the aluminum dihydrogen phosphate selected for this experiment is better than the neutral silica sol.
On this basis, through more in-depth research and discovery, adding ferrite microwave absorbing material, the sample has a short curing time, which is more convenient and faster, and the use effect is good.
Keywords: Sealant;Curing; Microwave sintering
目 录
摘要I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论1
1.1引言1
1.2低熔点玻璃体系2
1.2.1硼硅锌玻璃体系2
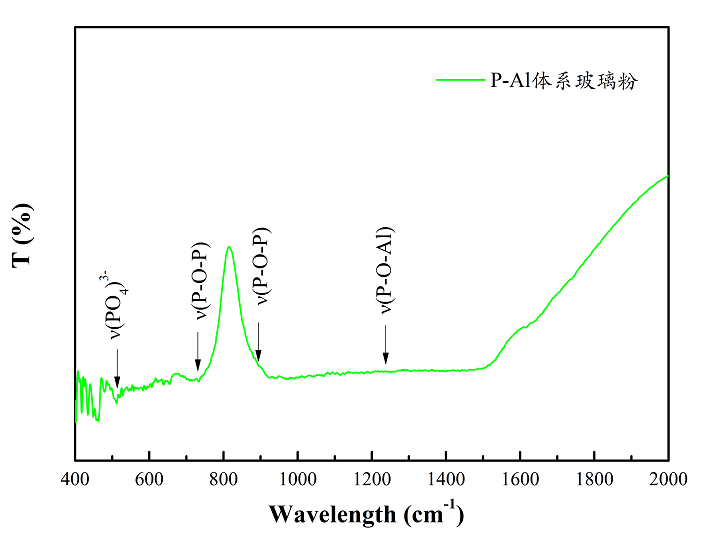
1.2.2磷铝玻璃体系3
1.2.3硼硅酸盐玻璃体系3
1.3微波烧结4
1.3.1技术原理4
1.3.2技术特点5
1.4微波吸收介质国内外研究现状5
1.5选题背景6
1.6研究目的及研究内容7
1.6.1研究目的7
1.6.2研究内容8
第二章 实验方法9
2.1实验原料及仪器9
2.1.1实验所用主要原料9
2.1.2实验所用主要仪器11
2.2实验步骤12
2.2.1配料12
2.2.2实验操作12
2.2.3材料表征15
第三章 实验数据分析18
3.1固化时间测试18
3.2吸水量测试20
3.3拉伸强度测试21
3.4抗折强度测试22
第四章 总结与展望24
4.1总结24
4.2展望24
参考文献25
致谢26
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
填缝剂是一种日常生活中常用的产品,对于各类外墙、面砖的装修,其重要性不言而喻。现有陶瓷地砖填缝剂主要可分为两类:水泥基和树脂基。在早期的发展中,白水泥往往作为填缝剂使用,但经常出现瓷砖表面泛碱现象。这是由于其中大量Ca 2 通过缝隙到达地砖的表面,然后就会与空气中的二氧化碳发生反应,生成CaCO3物质留在陶瓷地砖的表面,这就是形成泛碱的主要原因。后来又出现了勾缝剂,就所谓勾缝剂,通常就是在白水泥的基础上加了一些添加增强物质,来提高其防水防污性能,并且还能制成不同色彩,增加了美观的效果,然而以往的根本问题泛碱现象并没有得到解决,勾缝剂是较为常见的一种填缝剂。随着技术的发展,目前又出现了美缝剂,美缝剂又可分为单组份和双组份两类。单组份美缝剂呈现水性流动,使用后易坍缩,形成V字槽,缺点明显;双组份美缝剂采用固化剂 树脂的组分,其凝固后一次成型,填缝缝隙表面硬度高,防水防污性能优良。此外,使用环氧树脂 固化剂组分的美缝剂又被称为瓷缝剂,其表面硬度较之美缝剂更高,缝隙光洁如瓷质,但价格昂贵,成本较高。
因此,对比现有的填缝剂,我们发现水泥基填缝剂随着使用时间的推移,伴随着各种老化泛碱问题,影响瓷砖和面砖的美观性;而相对美观的美缝剂大多价格昂贵,并且为双组份,使用起来较为繁琐复杂,并不适合大面积使用,多用于厨卫装修。
相关图片展示: