三氧化钨光纤光栅氢气传感的性能研究毕业论文
2021-11-26 23:32:03
论文总字数:28424字
摘 要
针对当前光纤氢气传感中的氢敏材料敏感性及稳定性不足以商业化的问题,本文通过广泛调研文献,结合实验室现有条件,提出用溶胶凝胶法制备介孔Pt/WO3颗粒以及用真空蒸镀法和磁控溅射法制备WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt复合薄膜作为气敏材料的方案,随后对两种材料进行表征观察其形貌结构并测试其氢敏性能,主要研究及结果如下:
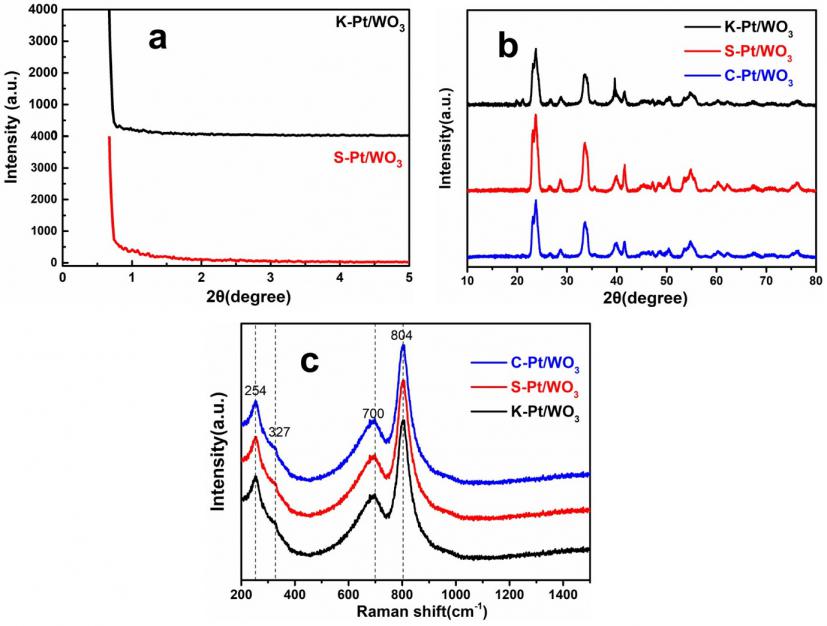
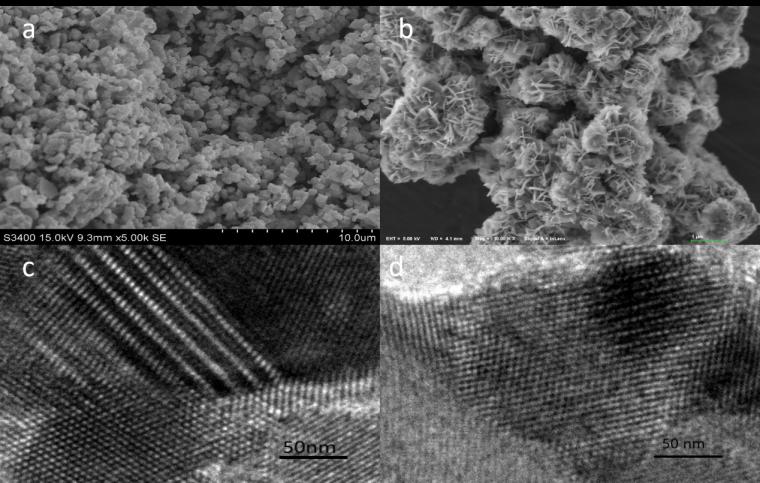
(1)采用水热法合成了两种不同的介孔二氧化硅模板SBA-15和KIT-6,并采用硬模板法和烧结法制备介孔Pt/WO3材料。对其进行XRD、SEM和TEM等表征发现以SBA-15制得的材料催化剂团聚现象更为严重。进行氢敏性能测试后发现,以KIT-6为模板制得的传感器灵敏度最高,氢气响应范围为100-40000ppm。
(2)采用真空蒸镀法及磁控溅射法在光纤端面镀WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt复合薄膜,EDS、XPS及SEM分析显示Pd和Pt均匀分布在WO3表面。随后我们对其灵敏度进行测试,结果显示基于复合薄膜的传感器在50-4000ppm范围内能多次快速响应且保持稳定,恢复后能回到初始状态。接着探究了到达传感探头光功率大小对氢敏性能的影响,结果表明适当的增加光功率可以提高探头的灵敏度和稳定性,当光功率为5mW时,传感探头的综合性能最佳。最后,本实验对探头结构进行了优化,探讨了光加热结构对整个传感系统性能的影响,对照实验结果表明光加热结构有利于维持传感器在复杂环境中的稳定性能。
本文的特色有以下两点:
(1)本文将催化剂Pt纳米颗粒填充在介孔WO3材料中,比起直接分散附着于WO3材料上,该方法减少了催化剂团聚失效现象,有利于氢敏材料与氢气反应。
(2)本文提出了一种光加热结构,保证传感探头区域的温度相对恒定,提高传感系统在复杂环境中的稳定性。
关键词:光纤氢气传感器;介孔Pt/WO3;磁控溅射;WO3薄膜;光加热
Abstract
The sensitivity and stability of hydrogen-sensitive materials are not enough for commercialization in optical fiber hydrogen sensing currently. In this paper, it is proposed to prepare mesoporous Pt/WO3 particles by sol-gel method and to prepare WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt composite films by vacuum evaporation and magnetron sputtering as gas-sensing materials through extensive literature research combining with existing conditions in laboratory. Then the two materials are characterized for morphology and tested for hydrogen-sensitive performance. The main research and results are as follows:
(1) First two different mesoporous silica templates SBA-15 and KIT-6 are synthesized by hydrothermal method and then mesoporous Pt/WO3 are prepared by hard template method and sintering. It is showed in XRD, SEM and TEM that there is more agglomeration of the catalyst prepared by SBA-15. Through the hydrogen sensitivity test, it is found that the sensors templated with KIT-6 perform best in hydrogen sensitivity and response in the hydrogen concentration range from 100ppm to 40000ppm.
(2) WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt composite film is deposited on the end face of the fiber using vacuum evaporation and magnetron sputtering. It is showed that Pd and Pt were evenly distributed on the WO3 surface by EDS, XPS and SEM analysis. Then the sensitivity test suggests that in the range of 50-4000ppm the sensor can respond quickly and remain stable for many times. What’s more, it can return to the initial state after use. Next, we probe into the influence of the light-heating power to the performance. The results show that an appropriate increase in power can improve the sensitivity and stability and 5mW is the power for the sensors’ best comprehensive performance. Finally, this experiment discusses the effect of the light-heating structure on the sensing system. The comparison shows that the structure is beneficial to keep stable in complex environment.
The features of this paper are as follows:
(1) In this paper, Pt nanoparticles, the catalyst, are filled in mesoporous WO3. Compared with the direct dispersion on the surface of WO3, it reduces the catalyst agglomeration which is conducive to the reaction of WO3 with hydrogen.
(2) This paper proposes a light-heating structure to ensure that the temperature of the sensor probe area is relatively constant and improve the stability of the sensor system in complex environment.
Key Words:Fiber optic hydrogen sensor; the mesoporous Pt/WO3; Magnetron sputtering; WO3 thin films; Light-heating
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 光纤光栅氢气传感器简介 1
1.1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.1.2 光纤光栅氢气传感器研究进展 1
1.2 氢气敏感材料简介 2
1.2.1 氢气敏感材料分类 2
1.2.2 光纤氢气传感器氢敏材料研究现状 3
1.3本文的研究内容及思路 4
第2章 三氧化钨光纤光栅传感器机理 6
2.1三氧化钨与氢气反应机理 6
2.1.1三氧化钨材料简介 6
2.1.2三氧化钨与氢气反应机理 6
2.2 光纤光栅氢气传感系统简介 7
2.2.1 基于WO3热效应的传感系统 7
2.2.2 基于WO3气致变色效应的传感系统 7
2.3 本章小结 9
第3章 基于介孔Pt/WO3热效应的光纤传感器性能研究 10
3.1 介孔Pt/WO3的制备 10
3.1.1 实验仪器及实验材料 10
3.1.2 溶胶凝胶法合成介孔Pt/WO3 10
3.2 介孔Pt/WO3的氢敏性能分析 11
3.2.1 介孔Pt/WO3的材料表征 11
3.3 基于介孔Pt/WO3热效应的光纤氢气传感器的性能测试 13
3.3.1 制备传感探头 13
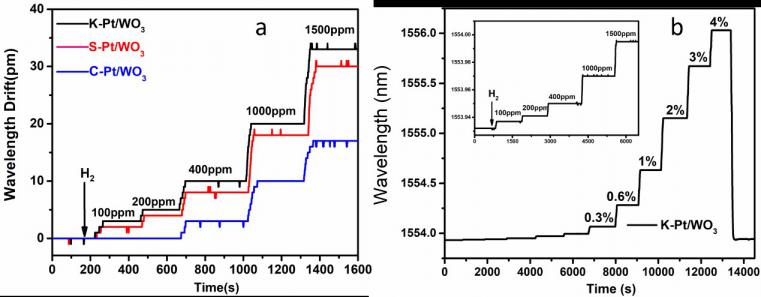
3.3.2 基于介孔Pt/WO3的光纤氢气传感器灵敏度测试 13
3.4 本章小结 14
第4章 基于WO3气致变色效应的光纤传感器性能研究 16
4.1 WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt复合薄膜的制备 16
4.1.1 实验仪器及实验材料 16
4.1.2 物理气相法合成复合薄膜 16
4.2 复合薄膜的氢敏性能分析 17
4.2.1 复合薄膜的材料表征 17
4.3 基于复合薄膜的光纤氢气传感器性能研究 18
4.3.1 基于WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt复合薄膜的传感器的重复性测试 18
4.3.2 基于WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt复合薄膜的传感器光功率性能测试 19
4.3.3 基于WO3-Pd2Pt-Pt复合薄膜的传感器稳定性测试 20
4.4 本章小结 21
第5章 总结与展望 22
5.1 本文主要内容及创新点 22
5.2 后续工作展望 23
参考文献 24
附录A 26
致 谢 27
第1章 绪论
1.1光纤光栅氢气传感器简介
1.1.1研究背景及意义
世界上已知的最轻的气体是氢气,它的密度小且储量大,燃烧效率高且产物为水,是一种理想的清洁高能燃料。目前氢气广泛应用于航空航天、食品化工、燃料电池等领域。然而氢气是一种无色无嗅、易燃易爆的危险气体,使用过程中的泄露不易察觉,在空气中的爆炸极限为4.0%-74.2%(体积浓度)。目前已发生多起与氢气泄露相关的大型事故,其中最广为人知的是2011年日本福岛核电厂爆炸事故。核电厂通常会将反应堆置于安全壳内,并对内部氢气浓度进行控制和监测,防止氢气泄露引起爆炸。但当地发生地震海啸后,所有仪器因为停电而无法使用,其中就包括燃烧控制系统。该系统平时用于控制氢气浓度,但停止工作后又未及时通风降低安全壳内氢气浓度导致氢气泄露进入厂房引起爆炸,最终导致大量放射性物质泄露,对人类安全造成重大威胁[1]。由此可见,研发安全稳定、高灵敏度的氢气传感器极为重要。
氢气传感器主要分为电化学型、半导体型、热电型和光纤型[2]。其中电化学型[3]、半导体型[4]、热电型[5]等氢气传感器使用的都是电信号,极容易在工作过程中产生电火花,从而引发爆炸,仍存在使用风险。而光纤型传感器通过弱光信号和敏感材料监测空气中氢气含量变化,具有本质防爆的优点,十分适用于易爆环境。
1.1.2光纤光栅氢气传感器研究进展
光纤的主要成分为二氧化硅,十分耐酸,不易腐蚀,且成本低廉,有利于商业化应用。光信号在光纤中传输,当光纤受到拉伸或者弯曲等外界作用后,光信号的传输也会受到影响,基于此科研人员研发出了不同类型的光纤型氢气传感器包括干涉仪型、消逝场型、微镜型及光纤布拉格光栅型。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:28424字
相关图片展示: