微晶玻璃的表面析晶毕业论文
2021-11-26 23:33:59
论文总字数:25672字
摘 要
微晶玻璃有很多优异的性能,基于LAS系透明微晶玻璃的研究,为了通过利用整体晶化制备出符合要求的微晶玻璃,应该先了解微晶玻璃析晶形式,分析表面析晶的机理,从而得到最佳的热处理制度,为制备兼顾透光性和抗弯强度的微晶玻璃提供理论基础。
本论文整理归纳大量文献,通过对比XRD衍射图谱、SEM显微照片、DTA曲线,保持微晶玻璃的组分不变,进行讨论。论文利用DTA曲线、XRD衍射图谱和一些实验数据确定了最佳热处理制度;总结归纳出热处理制度对力学性能和透光性的影响;利用图示介绍两种不同的表面析晶机理,并对比异同;分析核化温度、晶核剂和升温速率对表面析晶的影响。
研究结果表明:最佳晶化温度820℃;最佳核化温度通过对比不同预核化温度对应的析晶峰面积确定,一般高于转变温度点30-50℃;核化时间2h;保温时间根据XRD的强度确定。对于力学性能的来说最佳的热处理制度是核化温度580℃,热处理时间2h,晶化温度选为析晶峰温度。晶化温度对透光率的影响明显,是主要的研究因素,另外的因素影响甚微。超过某一晶化温度,β-石英会转变为β-锂辉石固溶体,导致透光性下降。表面析晶是垂直于表面生长;不同点在于边角、缺陷更早发生析晶;表面析晶不利于透光性能。核化温度高于最佳核化温度有助于减弱表面析晶;已知2%Cr2O3晶核剂有利于整体析晶,8% TiO2晶核剂有利于表面析晶;采用较低的升温速率有利于减轻表面析晶。
本文的特色:本文为综述性论文,通过整理归纳文献,研究了制备工艺对LAS系微晶玻璃的表面析晶、显微结构、热处理制度的影响,寻找最佳的热处理制度以期尽可能减少热处理时间和降低晶化温度,从而达到降低能耗、节能减排的目的,为制备高性能透明微晶玻璃提供理论支持。
关键词:微晶玻璃,表面析晶,热处理制度,透光性。
Abstract
The properties of glass-ceramics are determined by the types of crystal phases, the size and quantity of grains, and the properties and quantity of residual glass phases. Based on the study of transparent glass-ceramics of LAS system, in order to achieve the bulk crystallization of glass to produce glass-ceramics, the surface crystallization phenomenon of glass-ceramics of LAS system and its crystallization process must be analyzed first. For mechanical properties and light transmittance, the heat treatment system can be optimized to provide foundation for the preparation of glass-ceramics.
In this paper, a large number of literatures are summarized and discussed by comparing the XRD diffraction patterns, SEM micrographs and DTA curves, on condition that keep the composition of glass-ceramics unchanged. The optimal heat treatment system is determined by analyzing DTA curves, XRD diffraction patterns and some experimental data, including nucleation temperature, nucleation time, crystallization temperature and crystallization time. This paper researchs the influence of heat treatment on flexure strength and light transmittance. Two different mechanisms of surface crystallization are introduced by means of diagrams, and compare the similarities and differences. The effects of nucleation temperature, nucleating agent and heating rate on surface crystallization were analyzed.
The results show that :820℃ is the optimum crystallization temperature. The optimal nucleation temperature is determined by comparing the crystallization peak area corresponding to different pre-nucleation temperatures, which is generally higher than Tg 30-50 ℃.Optimal nucleation time is 2h;The crystallization holding time is determined according to the XRD strength. The heat treatment system conducive to mechanical properties is nucleation temperature 600℃, nucleation time 2h, crystallization temperature selected as the crystallization peak temperature, crystallization time 2h.The effect on the light transmittance is mainly caused by the crystallization temperature and the light transmittance decrease when wo-quartz is changed into wo-lithium pyroxene solid solution. Surface crystallization is vertical to the surface growth; the difference lies in that the side ,the corner and the defect crystallize earlier; surface crystallization is not conducive to light transmittance. The nucleation temperature should be higher than the optimal nucleation temperature, which could weaken the surface crystallization. The smaller the particle size, the less the influence of surface crystallization. It is known that 2% Cr2O3 nucleating agent is beneficial to bulk crystallization, and 8% TiO2 is conducive to surface. The lower heating rate is helpful to reduce the surface crystallization.
Characteristics of this article: this article is a review , through referring to the relevant literatures, the influence of the preparation process on the heat treatment , surface crystallization and microstructure of LAS series glass-ceramics was studied. The optimal heat treatment system was sought to reduce the heat time and lower the crystallization temperature as much as possible. In this way, it can decrease energy consumption, save energy and reduce emissions, then provide theoretical support for the production of high-performance transparent glass-ceramics.
Key words: glass-ceramics , surface crystalline , heat treatment , light transmittance.
目录
第1章 引言 1
1.1前言 1
1.2微晶玻璃简介 1
1.2.1分类 1
1.2.2性能及应用 1
1.2.3组分及结构 2
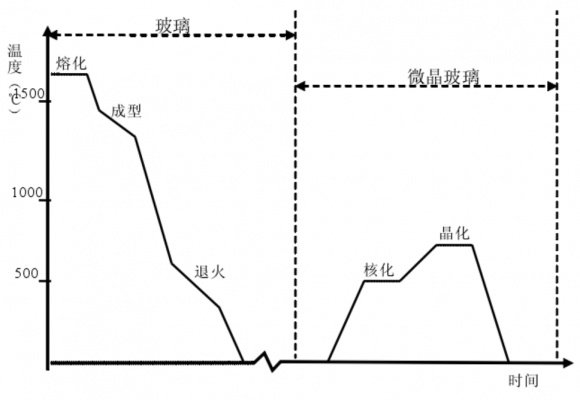
1.2.4.工艺制度 2
1.2.5热处理制度 3
1.3析晶原理 3
1.4.透光性机理 3
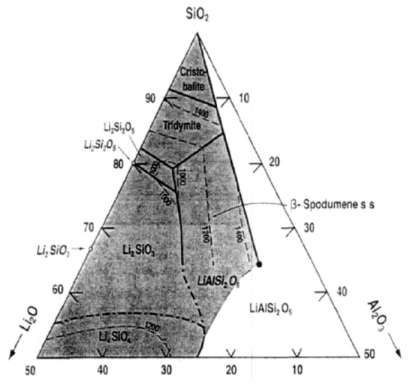
1.5 LAS系透明微晶玻璃研究现状 4
1.6 研究目的和意义 4
第2章 实验过程及研究方法 6
2.1实验原料与化学组分 6
2.1.1实验原料 6
2.1.2微晶玻璃的化学组分 6
2.2实验方法 7
2.2.1玻璃热处理制度的确定 8
2.2.2析晶动力学分析 8
2.2.3 X射线衍射物相分析 8
2.2.4 表面形貌观测 8
2.2.5 透光率的测定 8
2.2.6 力学性能测试 9
2.3 实验仪器 9
第3章 表面析晶机理的研究 10
3.1 前言 10
3.2析晶活化能的确定 10
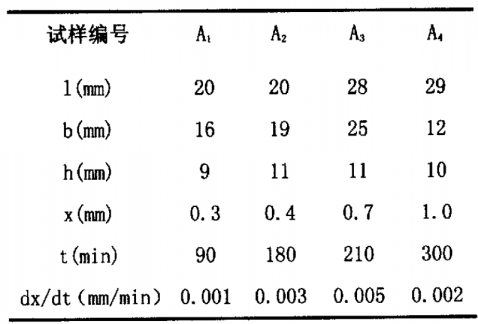
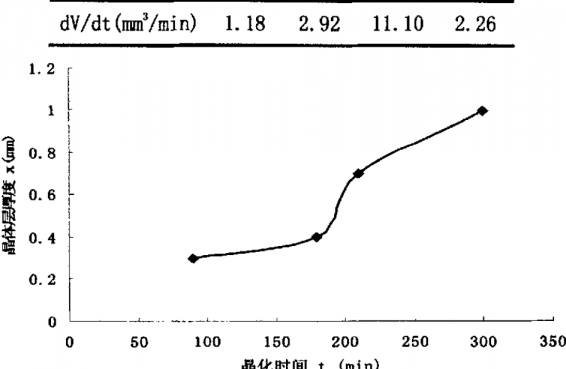
3.3析晶速率的确定 10
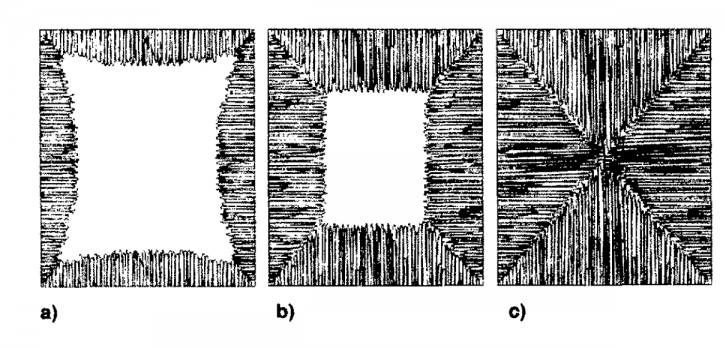
3.4表面析晶机理 11
3.5 表面析晶的影响因素 13
3.5.1核化温度对析晶的影响 13
3.5.2晶核剂的影响 13
3.5.3 升温速率的影响 15
3.6 晶化指数 16
第4章 LAS系透明微晶玻璃热处理制度的优化 17
4.1前言 17
4.2 DTA 曲线和梯温炉 17
4.3 最佳核化温度确定 18
4.4 最佳晶化温度和时间确定 19
4.5 热处理对LAS系透明微晶玻璃性能的影响 20
4.5.1 热处理对微晶玻璃力学性能的影响 21
4.5.2 晶化温度对微晶玻璃可见光透过率的影响 23
第5章 结论 27
参考文献 28
致谢 31
附录A 32
第1章 引言
1.1前言
微晶玻璃(又称玻璃陶瓷)的定义是加入晶核剂的基础玻璃,在一定成分范围内,通过可控制晶化而制得的一类既含微晶相又含玻璃相、二者均匀分布的新型材料。微晶玻璃具有玻璃和陶瓷的双重特性,但又不同于玻璃和陶瓷[1]。
微晶玻璃产品在使用时有很多很好的性质,生产中其性能主要受晶相和玻璃相的比例影响,结构上的区别又取决于原始玻璃的成份及制备工艺。热处理制度是制备过程中最重要的因素,影响微晶体和玻璃体的比例、晶粒个数等,在某个温度下可以保持一定的晶相,改变温度也有可能改变晶相,而晶相的改变往往使得微晶玻璃产品的使用性能发生改变。微晶玻璃的析晶方式有从整体、内部析晶和表面析晶之分。考虑到微晶玻璃表面析晶往往很难得到优良力学性能的细晶显微结构,为了利用整体晶化生产出符合要求的微晶玻璃,应该先对LAS系统微晶玻璃的表面析晶现象及其析晶机理有清晰的认识。
1.2微晶玻璃简介
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:25672字
相关图片展示: