激光选区熔化制备钛合金过程中熔覆道有限元模拟毕业论文
2021-11-27 22:35:46
论文总字数:21594字
摘 要
TC4钛合金自问世以来便凭借着优秀的机械性能,良好的耐腐蚀性,较宽的温度应用范围,良好的生物相容性等优点被广泛应用在军事、医疗等领域。但由于钛和钛合金材料具有导热性差、韧性低、硬度高以及在高温下会形成氧化硬层包覆着零构件等特点,使得一些具有复杂结构的零构件及整体结构件由传统制造工艺制造很难符合设计要求。激光选区熔化(Selective Laser Melting,SLM)技术利用增材制造的思想,层层堆积便可制造出精密复杂零构件。但SLM技术在生产中容易产生球化、裂纹空洞等内部缺陷,故对SLM技术成形中的激光传播进行研究有很大意义。
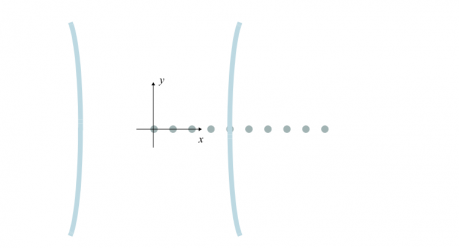
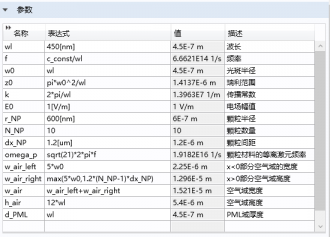
本文对激光选区熔化制备钛合金过程中的单个熔覆道进行有限元模拟,利用模拟软件COMSOL Multiphysics中的波动光学模块将激光光束在TC4钛合金颗粒中的传播进行了数值模拟,着重分析了TC4钛合金颗粒尺寸与间距的对激光光路的影响。
本次模拟得到结论如下:
(1)光束的偏振方向为铺粉方向(z轴)时,光束与TC4颗粒阵列之间的相互作用很强,TC4颗粒阵列反射和边缘衍射的效应很明显。在保持TC4颗粒间距与TC4颗粒半径比例不变的情况下,随着TC4颗粒半径的减小,被激光束照射的TC4颗粒数量逐渐增加,入射光束和TC4颗粒阵列反射光束形成的驻波逐渐融合交织在一起,最终形成了一个大的驻波,同时由于TC4颗粒阵列反射和边缘衍射,TC4颗粒阵列对激光光束的阻碍也愈加明显。
(2)光束的偏振方向为TC4颗粒阵列方向(x轴)时,TC4颗粒阵列对激光光束的阻碍不明显。在保持TC4颗粒大小不变的情况下,随着TC4颗粒间距的减小,TC4颗粒间的偶极耦合愈发强烈。
关键词: TC4钛合金;选区激光熔化;有限元分析法;表面等离激元
Abstract
TC4 titanium alloy has been widely used in military, medical and other fields because of its excellent mechanical properties, good corrosion resistance, wide temperature application range and good biocompatibility. However, due to the poor thermal conductivity, low toughness, high hardness of titanium and titanium alloy materials, as well as the formation of oxide hard layer covering the components under high temperature, it is difficult for some components with complex structure and integral structural parts to meet the design requirements by traditional manufacturing process. The selective laser melting (SLM) technology makes use of the idea of additive manufacturing, which can make precise and complex components by stacking layers. However, SLM technology is easy to produce spheroidization, crack cavity and other internal defects in production, so it is of great significance to study the laser propagation in SLM technology forming.In this paper, the finite element simulation of a single cladding channel in the process of laser selective melting of titanium alloy is carried out. The propagation of laser beam in TC4 alloy particles is simulated by using the wave optics module of the simulation software COMSOL multiphysics. The influence of the size and spacing of TC4 alloy particles on the laser optical path is analyzed.
The simulation results are as follows:
(1) When the polarization direction of the beam is the direction of powder spreading (Z-axis), the interaction between the beam and TC4 particle array is very strong, and the effect of reflection and edge diffraction of TC4 particle array is very obvious. With the decrease of TC4 particle radius, the number of TC4 particles irradiated by laser beam increases gradually, and the standing wave formed by incident beam and reflected beam of TC4 particle array gradually merges and interweaves, finally forming a large standing wave. At the same time, due to the reflection and edge diffraction of TC4 particle array, TC4 particle array excites The obstruction of light beam is more and more obvious.
(2) When the polarization direction of the beam is in the direction of TC4 particle array (x-axis), the obstruction of TC4 particle array to the laser beam is not obvious. With the decrease of the distance between TC4 particles, the dipole coupling between TC4 particles becomes stronger.
Key Words:TC4 titanium alloy; selective laser melting; finite element analysis; surface plasmon
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 TC4钛合金 1
1.3增材制造技术 3
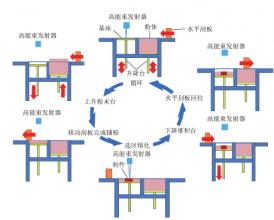
1.4激光选区熔化技术 5
1.4.1 SLM的技术原理 5
1.4.2 SLM的优势 6
1.4.3 SLM的劣势 7
1.5 有限元分析 9
1.5.1有限元分析方法的介绍 9
1.5.2有限元分析方法的特点 9
1.5.3有限元分析方法的步骤 10
1.5.4有限元分析方法网格划分的应用原则 10
第2章 实验过程 11
2.1建立模型 11
2.1.1模型定义 11
2.1.2 建模过程 12
第 3 章 实验结果与分析 18
3.1模拟计算 18
3.1.1计算电场沿面外z方向偏振的解 18
3.1.2计算电场沿面内x方向偏振的解 20
3.1.3绘制电场和激光束的背景场x分量的线图 25
第 4 章 结论与展望 30
致谢 31
参考文献 32
第1章 绪论
1.1引言
近年来,由于钛合金种类不断增加,性能不断进步,加工方法也越来越先进,钛及钛合金的发展十分迅猛,其使用量大约以每年8%的速度不断增长。20世纪60年代,钛及钛合金在军事领域应用大幅度上升,特别是在战斗机、运输机等军机中的使用量迅速增加到总生产量的20%~25%。先进钛合金比强度高、可在大幅度减轻结构重量的前提下,保证结构的强度,提高安全性,并且可以增加飞机携带弹药及其他物资的质量,已成为现代飞机和发动机不可缺少的结构材料之一。在医学领域中钛及钛合金也越来越受到重视,由于人的身体不会对钛及钛合金产生很大的排异性,人的体液系统也很难对钛及钛合金进行腐蚀,故被一致认为是外科植入体的首选金属材料,用于医疗领域中的牙科、骨科植入物和辅助器械等生产原料[1]。然而钛和钛合金材料具有导热性差、韧性低、硬度高以及在600℃以上会形成氧化硬层包覆着零构件等特点,使得一些具有复杂结构的零构件及整体结构件在铸造及后续加工中很难处理。随着结构设计软件的进步,人们的设计水平也在逐渐进步,越来越多的异形结构被人们开发出来,传统的减材制造成形工艺已无法满足异形结构的制造要求。
20世纪90年代以来,随着信息技术革命的不断进行,计算机技术飞速发展并广泛应用于各个领域,计算机辅助设计与制造技术(CAD/CAM)在材料加工、机械制造行业快速普及,将零件利用软件进行分割并逐层累积制造的增材制造理念变成了现实,为解决这一难题提供了契机。激光选区熔化技术(Selective Laser Melting,SLM)是增材制造技术的一种,相比于其他增材制造技术SLM具有精度高,机械性能好等优点。然而SLM成形过程中伴随复杂的物理化学冶金等过程,容易产生球化、孔洞、裂纹等内部缺陷,严重影响零构件的机械性能。Khairallah S A等人利用高保真度模拟的方法,对飞溅引起的缺陷形成机制进行了研究[2],本文受到该模拟实验的启发,利用有限元软件对激光选区熔化中的单个熔覆道进行模拟,希望能够通过研究结果对实际生产进行指导。
1.2 TC4钛合金
钛元素在18世纪90年代首先被英国科学家发现。自钛元素被发现至今,由于其优秀的性质,国内外专家学者对其进行了大量的研究,开发出大量的钛合金种类,并将其广泛应用于各个行业。纯净的Ti具有银灰色的金属光泽,原子序数为22,核外电子排布式为1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 4s2,相对原子质量为 47.90,位于元素周期表的第三周期第四副族。Ti有两种同素异构体,其中α-Ti为密排六方晶格结构,β-Ti为体心立方晶格结构。常见的α相稳定元素有 Al、O、N 等,其中Al最重要,它可降低Ti合金的熔点并提高β转变温度,增大β稳定元素在α相中的溶解度;β相稳定元素有V、Mo、H、Si等[3]。其中V可在β-Ti中无限固溶,在α-Ti中有限互溶。V在Ti合金中的固溶强化作用显著,能同时提高Ti合金的强度且保持较好的塑性,能提高Ti合金的热稳定性[4]。故很多Ti合金主要成分中都可以看到V的身影。
TC4钛合金的中同时添加了Al和V,是一种具有α β双相结构的钛合金,同时拥有α相高强度、β相低弹性模量的特点。Ti-6A1-4V在1954年由美国水城兵工厂研制成功,问世后,凭借其出色的机械加工性能受到了许多研究学者和生产企业的追捧,其使用量占到了钛合金总使用量的75%~85%,成为众多钛合金中当之无愧王牌合金[5]。表1.1列举了TC4钛合金的主要成分,表1.2 为TC4钛合金主要性能参数。图1.1为TC4粉末的微观形貌图[6]。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:21594字
相关图片展示: