偏心中空二氧化钛微米马达的光控运动行为研究毕业论文
2021-12-10 17:50:12
论文总字数:23943字
摘 要
由于其独特的运动行为和对微纳米物体的操控能力,微纳米马达有望为生物医学、环境治理和微纳米加工提供变革性技术。然而,现有微纳米马达往往需要多组分/多层的复杂结构和贵金属催化材料,导致其规模化制备与应用受到了严重的阻碍。因此,发展简单结构的微纳米马达,特别是具有可控运动性能的简单结构微纳米马达,对本领域的发展具有重要的意义。在前期研究中,本研究组发展了各种简单结构的TiO2光控微纳米马达,包括单层管状,双晶相球形和各向同性TiO2微米马达。然而,由于受TiO2能带结构限制,这些微纳米马达只能对紫外光波段响应,而紫外光仅占太阳光总能量的8.7%,且对生物体有着巨大的危害,这大大地限制了他们在环境治理和生物医学方面的应用。另外,这些TiO2微纳米马达仅能产生无规运动或在特定角度的紫外光照射下产生趋光性运动,运动行为相对单一。针对以上问题,本论文提出发展染料敏化的偏心中空TiO2微米马达,重点研究了光照强度、光的波长、光照方向和燃料浓度对其运动速率和方向的影响规律,揭示了其光控运动机制,不仅实现了其可见光驱动,而且发展了其光趋重性、趋光性和无规运动的多模式运动控制技术。具体如下:
(1)提出了表面各向同性而内部质量分布非对称的微纳米马达结构新设计,发展了其溶剂热简易制备技术,制备了具有偏心中空结构的TiO2微米马达,发展了其表面染料敏化方法。
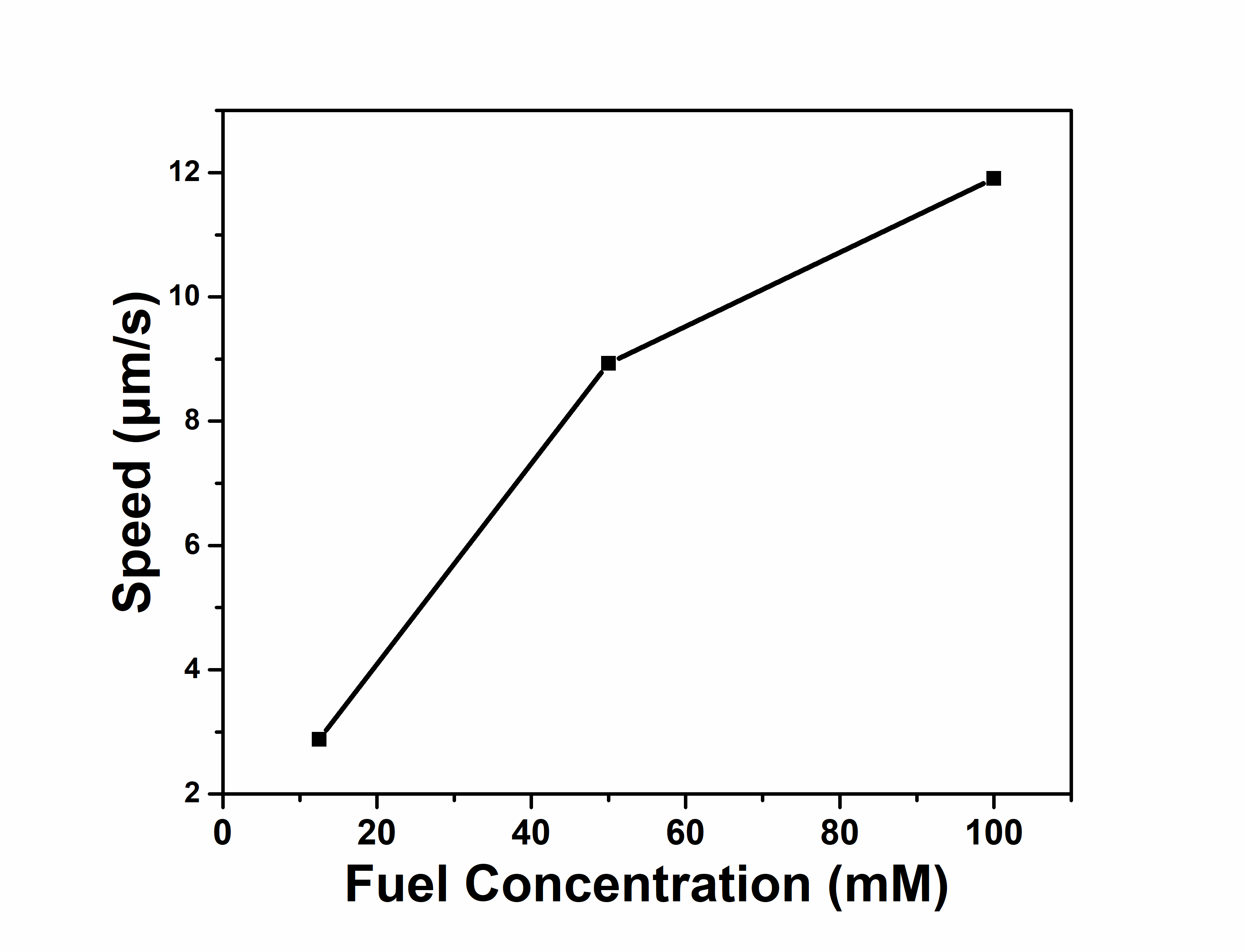
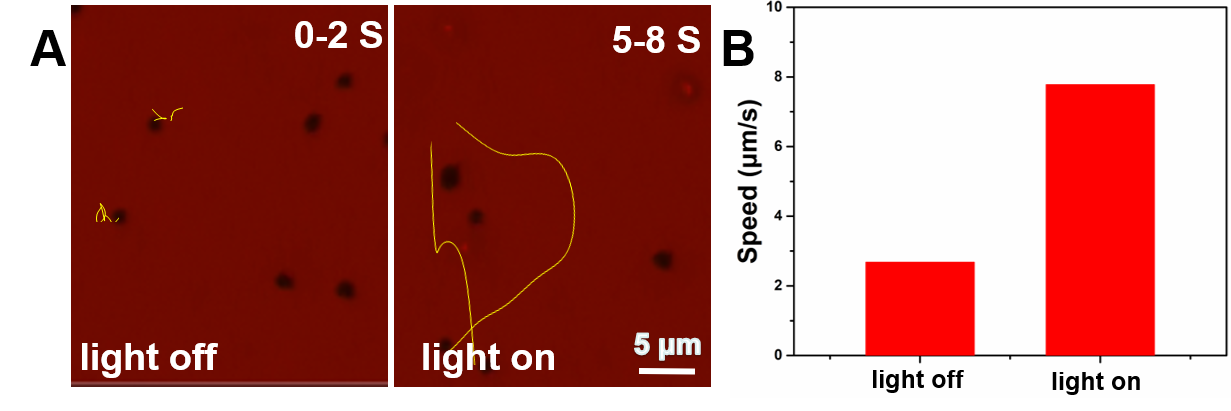
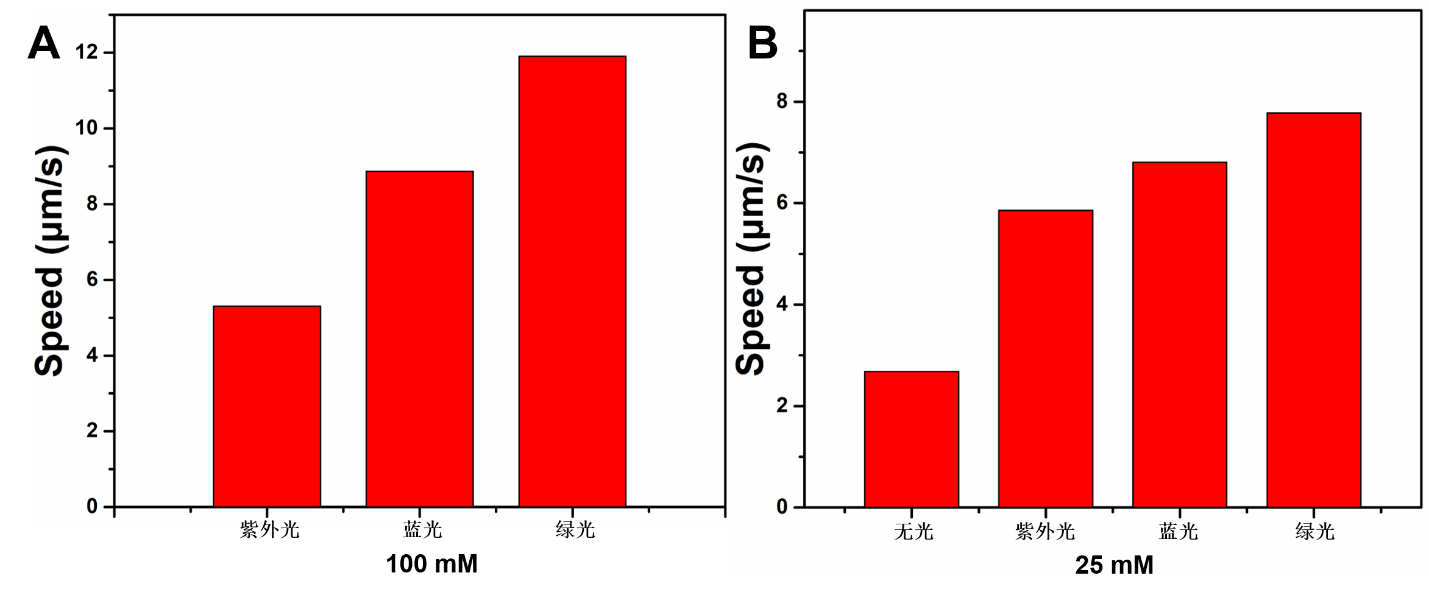
(2)利用马达表面染料N719对电子的氧化能力,扩宽微米马达的光吸收范围,实现了其在紫外到可见光范围的多波长光驱动;通过控制光强和燃料浓度可对其运动速率进行控制。
(3)发展了偏心中空TiO2微米马达在可见光下的光趋重性、趋光性和无规运动的多模式运动控制技术;由于其低密度特性,偏心中空TiO2微米马达的在竖直向上的光照条件下产生上浮运动,呈现出光趋重性运动模式,通过控制燃料浓度还可使其产生无规运动模式;而当使用斜向下的光照时,偏心中空TiO2微米马达在基板表面进行二维负趋光性运动。
本文发展的染料敏化的偏心中空TiO2微米马达不仅制备方法简单,可批量化制备,而且具有更宽的激发波长,在可见光下表现出多模式运动行为,丰富了微纳米马达的结构设计,对低成本高可控微纳米马达的发展及其在环境治理和生物医学等方面的实际应用具有重要意义。
关键词:可见光控;偏心中空;染料敏化;微纳米马达
Abstract
Micromotors are expected to provide transformative technologies for biomedicine, environmental governance and micro/nano processing because of its unique motion behavior and its ability to manipulate micro/nano objects. However, the multi-component/multilayer structures and the noble metal catalytic materials are often required for the existing micromotors, which seriously hinders their large-scale preparation and application. Therefore, the development of micromotors with simple structure and controllable motion performance, is of great significance to the development of this field. In the preliminary study, our team developed various optically controlled TiO2 micromotors with simple structures, including single-layer tubular, bicrystal spherical and isotropic TiO2 micromotors. However, due to the limitation of TiO2 energy band structure, these micromotors can only respond to the ultraviolet light, which accounts for only 8.7% of the total solar energy and has great harm to the organisms. Its greatly limits their application in environmental governance and biomedical. In addition, these TiO2 micromotors can only generate random motion or phototactic motion under the irradiation of ultraviolet light at a specific angle, and the motion behavior is relatively simple. To solve above problems, this paper put forward the development of the eccentricity of the dye sensitized TiO2 hollow micromotors. Our study focuses on the wavelength of light intensity, light, light direction and fuel concentration on the influence law of its movement speed and direction and we reveals the light-control movement mechanism. Our work not only realize the optical drive but also the development of sex of its light weight, phototaxis and random movement of multimodal motion control technology. The details are as follows:
(1) A new design of micromotor structure with surface isotropy and internal mass distribution asymmetry, and its simple preparation technology of solvothermal was developed. We prepared the TiO2 micronmotor with eccentric hollow structure, and we studied its surface dye sensitization method.
(2) With the oxidizing ability of the dye N719 on the motor surface, the light absorption range of the micronmotor was broadened. And the multi-wavelength optical drive in the range of ultraviolet to visible light was realized. By controlling the light intensity and the fuel concentration, the motion rate can be controlled.
(3) Developed the multi-mode motions control technology for the light gravitation, phototaxis and random motion of the off-center hollow TiO2 micromotor in visible light. Due to its low density characteristics, the off-center hollow TiO2 micromotor floats upward under the vertical and upward illumination conditions, presenting a light-oriented motion mode. By controlling the fuel concentration, it can also generate random motion mode. When oblique downward illumination was used, the off-center hollow TiO2 micromotor carried out two-dimensional negative phototaxis on the substrate surface.
In this paper, the eccentricity dye sensitized TiO2 hollow micromotor preparation method is simple, not only can mass preparation, and has a wider excitation wavelength. In visible light to show the pattern more exercise behavior, enrich the structure design of micromotor. Has a great significant in develop low cost and high controllable micromotors in environmental management and the practical application of biological medicine.
Keywords:Visible-light control; Eccentric hollow structures; Dye sensitization; Micromotors
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1微纳米马达 1
1.2微纳米马达的驱动机理分类 1
1.2.1自驱动微纳米马达 2
1.2.2外场驱动型微纳米马达 3
1.3研究目的与研究内容 6
第2章 可见光响应偏心中空TiO2微米马达的运动行为研究 8
2.1引言 8
2.2实验部分 8
2.2.1实验试剂与试验设备 8
2.2.2实验过程 8
2.2.3样品的测试与表征 9
2.3实验结果与讨论 10
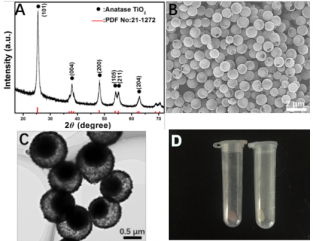
2.3.1偏心中空TiO2微纳米马达的表征 10
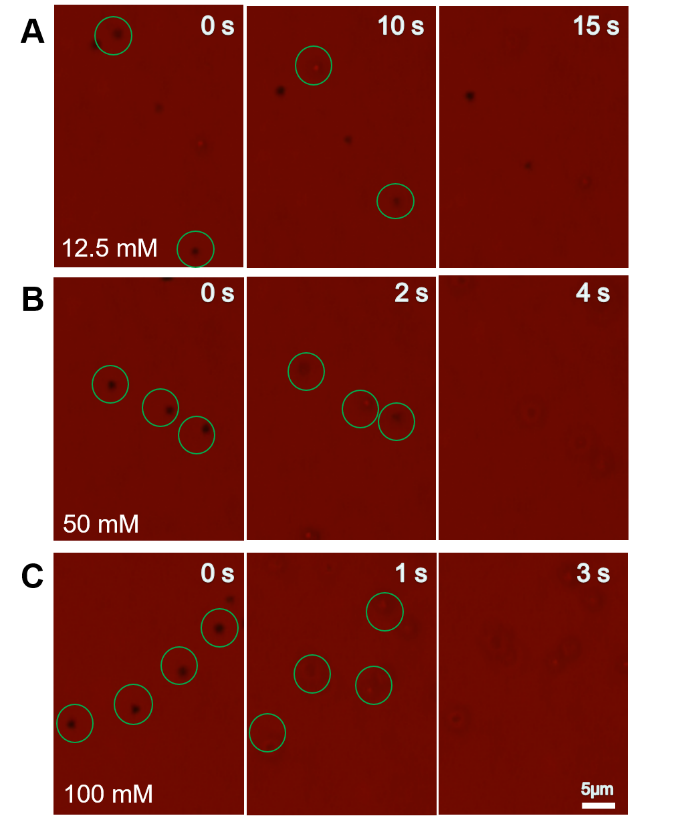
2.3.2偏心中空TiO2微米马达在直光照下的运动行为研究 11
2.4运动原理分析 18
第3章 总结 20
参考文献 21
致 谢 24
第1章 绪论
1.1微纳米马达
微纳米马达作为一种能将环境中存在的其他形式的能量转换为自身动能的微纳米粒子或器件,因其在液体环境中具有特殊的运动特性与功能,近年来发展迅速,在生物医学、环境治理和微纳米工程等领域有着巨大的应用前景[1-8]。2002年,Whiteside课题组提出了化学驱动的微纳米马达,自此微纳米马达的概念走入人们的视野。直至目前,研究者们致力于使微纳米马达获取更快的运动速度、更高的可控性、更低的制备成本、更环保的燃料以及生物相容的能量来源。在研究者们的精心设计下,通过对结构和材料的不断改进,已经制备出了具有各种各样结构的微纳米马达。其中,构造多组分不对称性是设计微纳米马达的常用方法,例如Janus微球(Au/TiO2、SiO2/TiO2等)[9]、双金属棒(Pt/Au等)[10]、多金属线(Pt/Ni/Au等)[11]、多层管(PANI/Pt等)等。除此之外,还有单组分微纳米马达,例如单质银(Ag)、氧化锰(MnO2)、各向同性TiO2、罐装MnFe2O4、双晶相TiO2等[2, 12-14]。
而从驱动方式上来讲,微纳米马达可以分为两类,一类为自驱动型微纳米马达(以自然界或合成燃料为能量来源),另一类为外场驱动的微纳米马达,包括光、磁、电、超声等物理外场。其中,光驱动微纳米马达由于其具有高时空精度、实时可控、可远程操作、无线操控等优点,受到了研究者们广泛的研究与关注。而由于光具有广泛的波长和频率,其对不同的微纳米马达体系具有不用的作用与影响,具体会引起光热、光催化反应、光致变色等现象,从而控制微纳米马达的行为。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:23943字
相关图片展示: