Mo、Fe掺入对CeSnWOxTiO2脱硝性能的影响毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:47:06
摘 要
NOx是大气主要污染物之一,严重危害着人类的身体健康。我国内河船舶众多,船舶柴油机NOx排放基本处于无控制状态,每年NOx排放总量高达100万吨,且连年快速增长,因此船舶尾气的治理不容忽视。目前国内外均无专用船用脱硝催化剂,且使用最多的是V2O5(WO3)/TiO2体系,V2O5为高剧毒物质,且废弃钒钛催化剂已被国家环保部列入危废。因此研发一种环境友好型船用脱硝催化剂迫在眉睫。
本论文是基于课题组前期自主研发的CeSnWOx/TiO2新型稀土基脱硝催化剂体系,进一步探讨离子掺入对其脱硝活性及抗水硫性能的影响。本论文采用不同金属离子Mo6 和Fe3 掺杂,以载体质量为基准,对CeSnWOx/TiO2催化剂进行(记为xMo-CeSnWOx/TiO2,x=1%,2%,3%,4%;yFe-CeSnWOx/TiO2,y=0.1%,0.3%,0.5%,1%,1.5%,2%)改性、优化,并对改性后的体系进行各项性能测试,以期拓宽其活性温度窗口,提高抗水硫中毒能力。初步通过XRD等表征对比分析了不同离子改性后催化剂组成、结构与脱硝活性温度窗口的变化规律。主要研究结果如下:
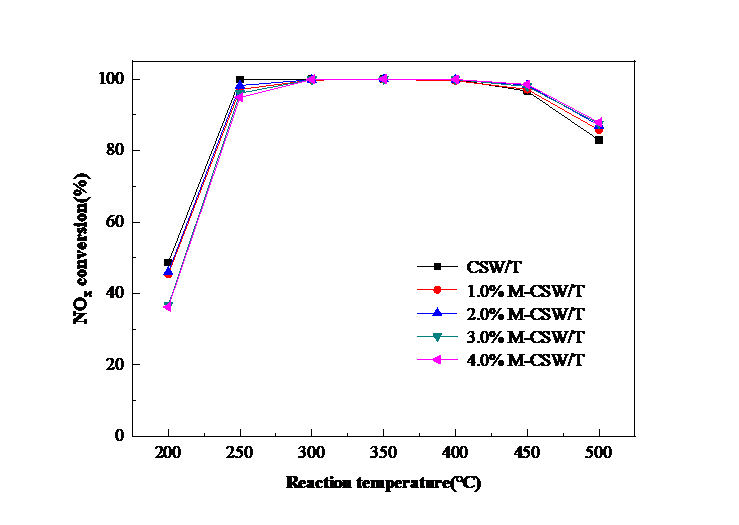
① 对Mo-CeSnWOx/TiO2系催化剂进行脱硝及抗水硫中毒性能测试发现,随着Mo掺量增加,催化剂的脱硝活性在高温区间(400-500 °C)有所提升,且当掺量为4%时,催化剂脱硝效率提升约5%;另外,Mo掺入对催化剂抗水硫中毒能力无明显提升作用。
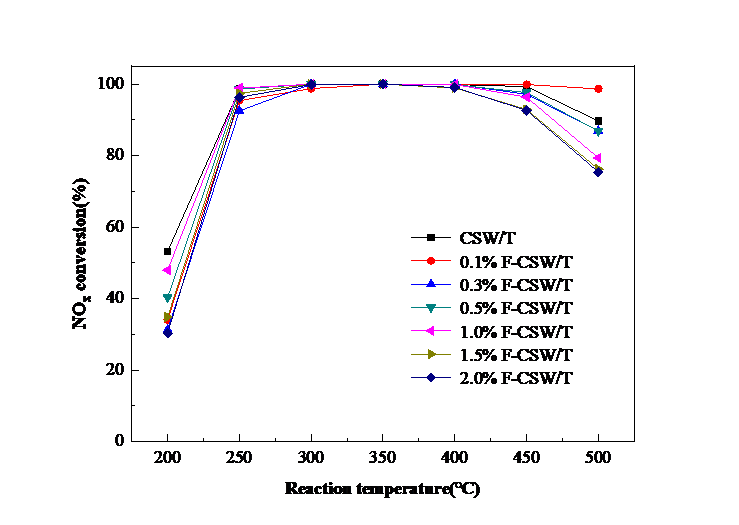
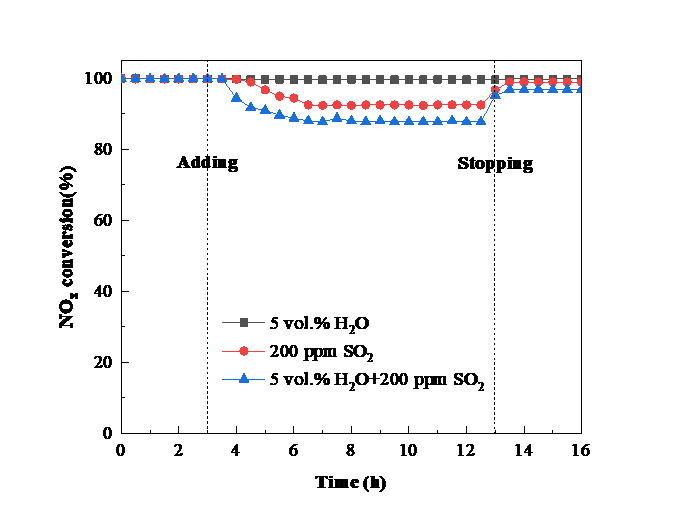
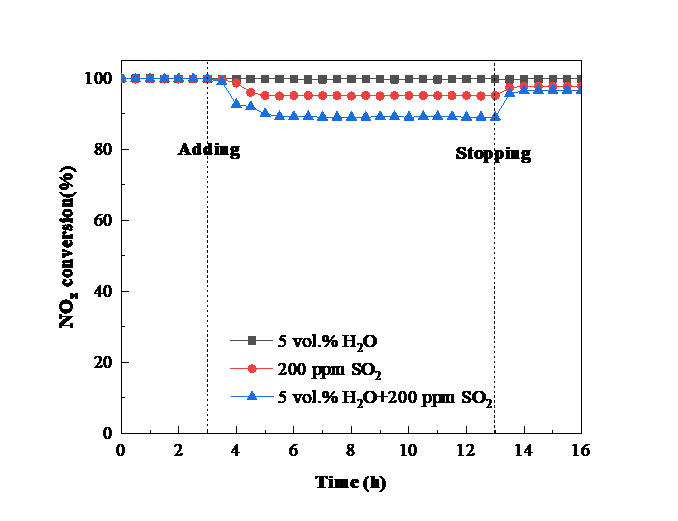
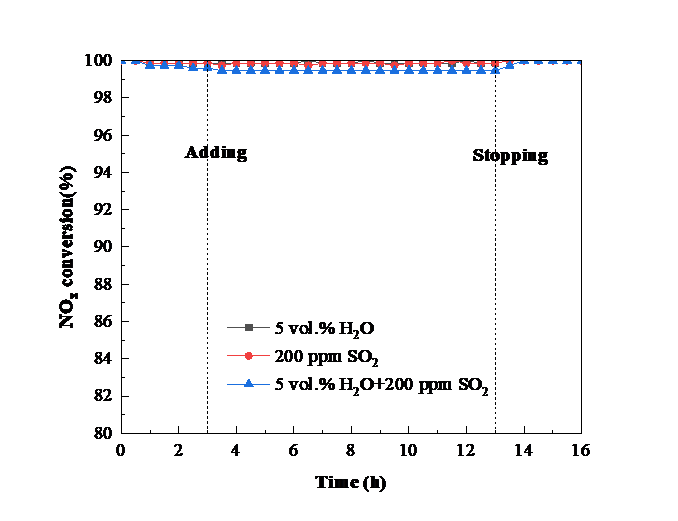
② 对Fe-CeSnWOx/TiO2系催化剂进行脱硝及抗水硫中毒性能测试发现,当Fe掺量为0.1%时,催化剂脱硝效率在高温段(400-500 °C)提升了15%左右,效率达约98%,拓宽了催化剂活性温度窗口(即300-500 °C);当Fe掺量大于0.1%时,催化剂活性呈下降趋势。另外,0.1% Fe掺入极大提高了催化剂抗水硫中毒能力,300 °C条件下,通入200 ppm SO2、5 vol.% H2O 10 h后,催化剂脱硝活性从最初的99.87% 略微下降到99.4%,停止通水硫后,经过适当加热吹扫活性可完全恢复。综上,微量Fe掺入可以极大提高催化剂的脱硝活性及抗水硫中毒能力。
关键词:NH3-SCR 氮氧化物(NOx) SCR催化剂 抗水硫中毒
Effect of Mo、Fe on catalytic performance of CeSnWOx /TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx
Abstract
Nitrogen oxides are one of the pollutants and are extremely detrimental to human health. There are many inland rivers in China, and the NOx emissions of marine diesel engines are basically in an uncontrolled state. The total annual NOx emissions are as high as 1 million tons, and the rapid growth year after year, so the treatment of ship exhausting can not be ignored. At present, there is no special catalyst for marine use in the globe, and the most used is V2O5(WO3)/TiO2 system. V2O5 is a highly toxic substance, and the waste vanadium-titanium catalyst has been listed as hazardous waste by the Ministry of Environmental Protection. For the reason that, it is extremely pressing to develop an environmentally friendly marine denitration catalyst.
This paper is based on the CeSnWOx/TiO2 new rare earth-based denitration catalyst system independently researched and developed by our research group. The influence of ion doping on its catalytic activity and the resistance to water and sulfur is further studied. In this paper, different metal ions Mo6 and Fe3 are doped, and the CeSnWOx/TiO2 catalyst is based on the carrier mass (denoted as xMo-CeSnWOx/TiO2, x=1%, 2%, 3%, 4%; yFe-CeSnWOx /TiO2, y=0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, 2%) modified, optimized, and tested various properties of the modified system, in order to broaden its active temperature window and improve the resistance to water and sulfur. The changes of catalyst component, structure and performance temperature range were analyzed by XRD etc. The main research results are as follows:
① The denitration and resistance to water and sulfur examination of Mo-CeSnWOx/TiO2 catalysts reflected that with the increase of Mo content, the activity increased in the high temperature range (400-500 °C), and when the dosage was at 4%, the activity increased by about 5%; in addition, the incorporation of Mo did not significantly improve the ability of the catalyst to resist water and sulfur poisoning.
② Fe-CeSnWOx/TiO2 system was examined for performance and the resistance to water and sulfur. When the Fe content was 0.1%, the catalytic activity of the catalyst increases by about 15% in the high temperature range (400-500 °C), about 98% which broadens the catalyst activity temperature window (300-500 °C); when the Fe content was more than 0.1%, the catalyst activity showed a downward trend. In addition, 0.1% Fe incorporation greatly improved the resistance to water and sulfur. After 300 °C, 200 ppm SO2, 5 vol.% H2O for 10 h, the catalytic performance dropped slightly from the initial 98.77% to 99.4%, after stopping adding water and sulfur, the activity can be completely recovered by proper heating and purging. In summary, tiny Fe incorporation can dramatically enhance the activity and the resistance to water and sulfur.
Key Words: NH3-SCR; nitrogen oxides(NOx); SCR catalyst; resistance to water and sulfur
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 选择性催化还原法 2
1.3 NH3-SCR催化剂 3
1.3.1 贵金属催化剂 3
1.3.2 分子筛催化剂 4
1.3.3 金属氧化物催化剂 5
1.4 研究目的和内容 6
1.4.1 研究目的 6
1.4.2 研究内容 7
第二章 实验方法 8
2.1 实验原料 8
2.2 实验设备 8
2.3 NH3-SCR实验系统 9
2.4 催化剂的表征 9
2.4.1 X射线衍射(XRD)分析 9
第三章 结果与讨论 10
3.1 催化剂的制备 10
3.2 催化剂的性能评价 11
3.2.1 Mo掺量对CSW/T催化剂脱硝效率的影响 11
3.2.2 Fe掺量对CSW/T催化剂脱硝效率的影响 11
3.2.3 CSW/T抗水硫中毒能力研究 12
3.2.4 4% M-CSW/T抗水硫中毒能力研究 13
3.2.5 0.1% F-CSW/T抗水硫中毒能力研究 14
3.3 催化剂的表征 15
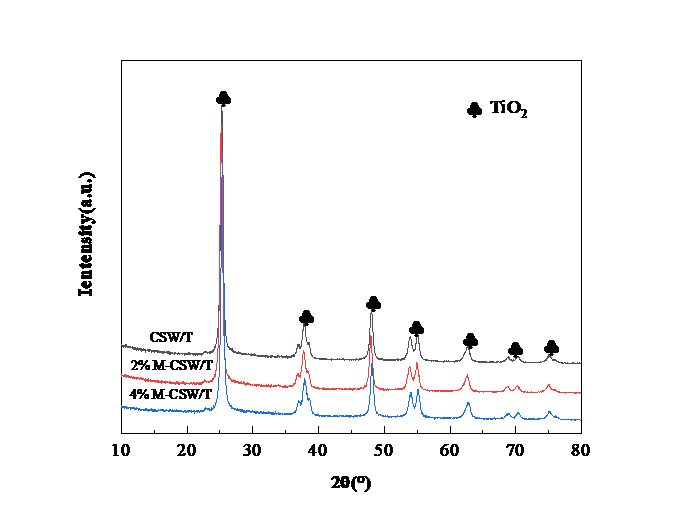
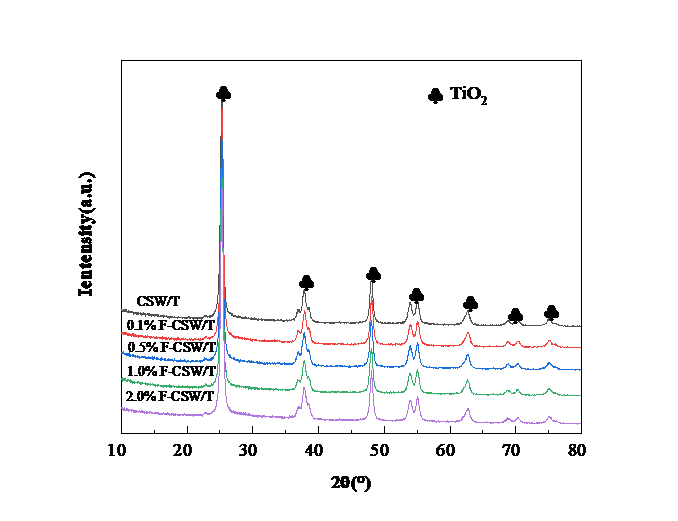
3.3.1 XRD分析 15
第四章 结论与展望 17
4.1 结论 17
4.2 展望 17
参考文献 19
本科期间所获科研成果 23
致 谢 24
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
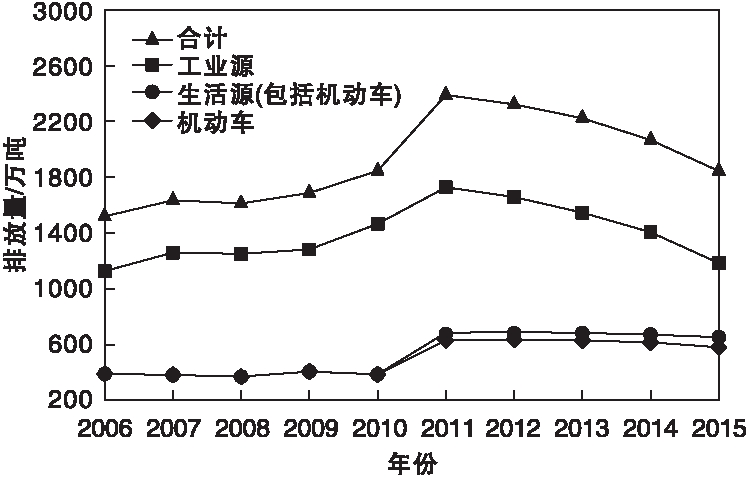
氮氧化物(NOx)不仅是大气主要污染物之一,而且是酸雨和光化学烟雾的前驱体,对于生态系统和人体健康造成严重威胁,NOx若进入人体中可与血红蛋白相结合,降低红细胞输送氧气的能力,引起组织缺氧[1]。船用柴油机尾气主要包括NOx(95%以上为NO)、一氧化碳(CO)、二氧化硫(SO2)等,其中NOx的处理是难点。根据《环境统计年报》近几年的数据统计表明(如图1-1所示),虽然2011-2015年全国NOx排放量总体呈下降趋势,但其总量依然很大[2]。在NOx的众多排放源中,由船舶柴油机排放的NOx占全世界排放总量的14-15%,在特定区域可能更高[3]。因此,船舶方向NOx的尾气处理成为大众关注的焦点问题,国际海事组织(IMO)及缔约国共同制定了船舶废弃排放标准的《73/78防污染公约》(MARPOL 公约)附则VI及修订部分,其中Tier III阶段对船用柴油机NOx的处理提出了更加严格的标准和要求。
相关图片展示: