金属离子对金纳米团簇荧光响应性研究毕业论文
2021-12-06 20:54:02
论文总字数:22578字
摘 要
荧光成像技术是继核磁共振成像和CT扫描成像之后的第三代活体成像技术,该技术具有无痛、无创伤、无光损、高时空分辨率、安全等优点。荧光成像技术的检测灵敏度非常高,能够实现细胞水平成像,是疾病精准诊疗最具前景的方法之一。目前制约荧光成像技术活体应用的主要原因是缺乏合适的荧光探针材料,尤其是缺乏生物相容性好、量子产率高的近红外荧光探针。金纳米团簇是一种大小介于原子和量子点之间的类分子纳米材料,尺寸小于3 nm,由几个到数百个金原子构成,由于其光学和电学性质优异、生物相容性良好,金团簇在细胞成像、生物检测、药物运载等方面有着良好的应用前景。但金团簇的一个显著缺点是荧光量子产率低,这极大限制了其在生物成像和检测方面的应用。因此增大金团簇的荧光量子产率是目前急待解决的问题。本文采用半胱氨酸-精氨酸(CR)二肽作为配体,制备了水溶性的CR-AuNCs,并探究了各种金属离子对其荧光性质的影响,其研究成果如下:
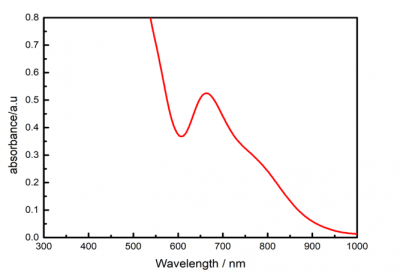
(1)本文成功制备了粒径小于3 nm的水溶性CR-AuNCs,并通过紫外可见吸收光谱、红外光谱和荧光光谱表征了其光学性质,发现其吸收峰位于665 nm处,荧光发射峰位于1128 nm附近,属于近红外II区,但荧光强度较弱,量子产率较低。
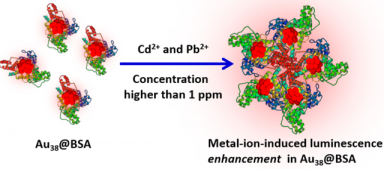
(2)为了改善金团簇的荧光量子产率,本文探索了九种金属离子(Cu2 、Pb2 、Ag 、Ba2 、Cd2 、Cr3 、Mn2 、Au3 、Zn2 )对CR-AuNCs荧光发射性能的影响,发现9种金属离子都能使CR-AuNCs的荧光发射显著增强,且除Cu2 外,其余离子对CR-AuNCs的荧光发射增强均呈剂量依赖性。
总之,本文利用金属离子诱导金团簇荧光增强的效应,不仅可以应用于金属离子的探测,还能为金属离子诱导金团簇应用于荧光成像提供部分基础数据。
关键词:CR-AuNCs、金纳米团簇、金属离子、生物成像
Abstract
Fluorescence imaging technology is the third generation of in-vivo imaging technology after MRI and CT scan imaging, which has the advantages of no pain, no trauma, no light loss, high spatial and temporal resolution, and safety and so on. The detection sensitivity of fluorescence imaging technology is very high, and it can achieve cell-level imaging. Fluorescence imaging is one of the most potential methods for accurate diagnosis and treatment of diseases. At present, the main reason for restricting the application of fluorescence imaging technology in vivo is the lack of suitable fluorescent probe materials, especially the lack of near-infrared fluorescent probes with good biocompatibility and high quantum yield. Gold nanoclusters are molecular-like nanomaterials with a size between atoms and quantum dots, composed of several to hundreds of gold atoms, their size is usually less than 3 nm. Due to their excellent optical and electrical properties and good biocompatibility, gold clusters have good application prospects in cell imaging, biological detection and drug delivery, etc. However, a significant disadvantage of gold nanoclusters is their low fluorescence quantum yield, which greatly limits their application in biological imaging and detection. Therefore, it is urgent to increase the fluorescence quantum yield of gold clusters. In this paper, water-soluble CR-AuNCs were prepared by using cysteine-arginine (CR) dipeptide as ligand, and the effects of various metal ions on their fluorescence properties were studied. The research results are as follows:
(1) In this paper, water soluble CR-AuNCs were prepared successfully with a particle size of less than 3 nm, and their optical properties were characterized by UV-visible absorption spectrum, infrared spectrum and fluorescence spectrum. The absorption peak was found at 665 nm and the fluorescence emission peak was near 1128 nm, belonging to the near infrared II region, but the fluorescence emission intensity was weak and the quantum yield was low.
(2) In order to improve the fluorescence quantum yield of gold clusters, by exploring the effects of nine metal ions (Cu2 , Pb2 , Ag , Ba2 , Cd2 , Cr3 , Mn2 , Au3 , Zn2 ) on the fluorescence emission performance of CR-AuNCs, it was found that nine metal ions could significantly enhance the fluorescence intensity of CR-AuNCs. And except copper ion, the fluorescence emission enhancement of CR-AuNCs by other ions was dose-dependent.
In short, the metal ion-induced gold cluster fluorescence emission enhancement effect can not only be applied to detection of metal ions, but also provide some basic data for metal ion-induced gold clusters to be used in fluorescence imaging.
Key words: CR-AuNCs, gold nanoclusters, metal ions, biological imaging
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
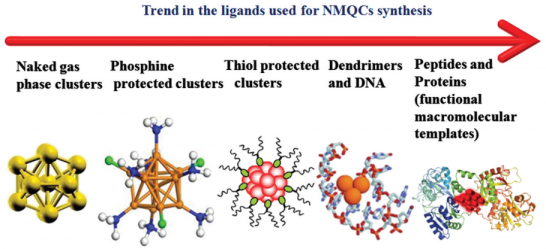
1.2 金纳米团簇的制备 2
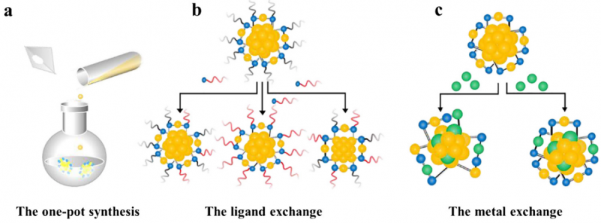
1.2.1 一锅法 4
1.2.2 配体交换法 5
1.2.3 金属原子交换法 5
1.3 金纳米团簇的性质 6
1.4 增强金纳米团簇荧光的方法 6
1.4.1 配体工程 6
1.4.2 金属掺杂 7
1.4.3 聚集诱导发光(AIE) 7
1.4.4 结晶诱导荧光增强(CIEE) 7
1.5 金纳米团簇的应用 8
1.5.1 生物成像和检测 8
1.5.2 重金属离子探测 9
1.5.3 作为催化剂 10
1.6 本论文的研究背景、内容及对环境健康等的影响 10
第2章 CR-AuNCs的制备、光学性质和粒径表征以及细胞毒性探究 12
2.1 引言 12
2.2实验部分 12
2.2.1 主要实验试剂和仪器 13
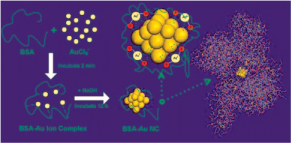
2.2.2 CR-AuNCs的合成 13
2.2.3 CR-AuNCs的表征测试 13
2.3 实验结果和讨论 14
2.3.1 紫外可见吸收光谱 14
2.3.2 傅里叶变换红外光谱 14
2.3.3 紫外-可见-近红外荧光光谱 15
2.3.4 透射电镜图 16
2.3.5 动态光散射分析 16
2.3.6 细胞毒性分析 16
2.4 本章总结 17
第3章 金属离子对CR-AuNCs的近红外荧光性质影响探究 18
3.1 前言 18
3.2 实验部分 18
3.2.1 实验试剂和仪器 18
3.2.2 实验过程 18
3.3 实验结果和讨论 18
3.3.1 紫外可见近红外荧光光谱 18
3.4 本章总结 20
第4章 结论与展望 21
4.1 结论 21
4.2 展望 21
参考文献 22
致 谢 27
第1章 绪论
1.1 引言
医学影像技术在当今临床诊断治疗中发挥着重要的作用,其发展反映着现代医学的进步。随着科学技术的进步,已经发展出了计算机X射线断层扫描(CT)和核磁共振(MRI)等成像技术,极大推动了现代医学的进步。但这两种技术也各有缺陷,CT和核磁共振虽然都具有极高的分辨率、无限的穿透深度,但CT对软组织的灵敏性较低且缺乏功能信息,MRI的缺点是灵敏性低,需要更长的采集时间和更大的成像量[[1]]。而且这两种成像技术大多检测到的是病变以后的结果。以肿瘤为例,目前医学技术能检测出来的肿瘤大小在1厘米左右,而严重恶化的肿瘤细胞往往已扩散到身体其他部位。因此,在癌症早期发现病变对于癌症治疗十分重要,这要求我们的检测技术灵敏度能达到分子细胞水平,只有这样才能充分了解病情,以制定适宜的治疗方案。
荧光成像技术是继核磁共振和CT成像后发展起来的新型成像技术,具有安全、无创、高时空分辨率等特点[[2]]。特别是近红外荧光具有较深的组织穿透能力,不易受其他物质的背景荧光干扰,对于疾病的诊断更加灵敏准确。因此发展新一代的近红外荧光成像技术对于治疗癌症、阿兹海默症等疾病具有重大意义。由于光的衰减和散射以及人体内细胞色素、血红蛋白等分子的自发荧光干扰,使得可见光区(400650 nm)和近红外I区(650900 nm)的荧光在体内成像方面用途有限。近红外II区(10001700 nm)的荧光发射,由于具有较长的发射波长,因此具有更深的组织穿透力、更高的图像对比度以及较低的光毒性和光漂白,更适合用于体内成像研究[1][[3]][[4]](图1.1)。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:22578字
相关图片展示: