氮化硼无机填料聚苯乙烯三元复合材料的制备与性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-25 19:41:14
摘 要
随着微电子集成技术和微封装技术的发展,电子设备趋于小型化、轻质化、高性能化,传统的导热材料已无法满足人们的需求。而高分子材料由于其成本低、易成型、力学性能优异,再辅以导热填料,导热高分子材料已广泛应用到电子电器领域。聚苯乙烯具有易成型加工、价廉、电绝缘等优点,广泛用于轻工市场,是制造光学化学仪器零件各种仪表外壳等良好的原材料。倘若对聚苯乙烯进行改性,将氮化硼与聚苯乙烯进行溶液-熔融共混得到具有高导热、高绝缘性同时保持原有的良好的可加工性能的复合材料,这将为微电子领域导热材料提供一种可行的方案。
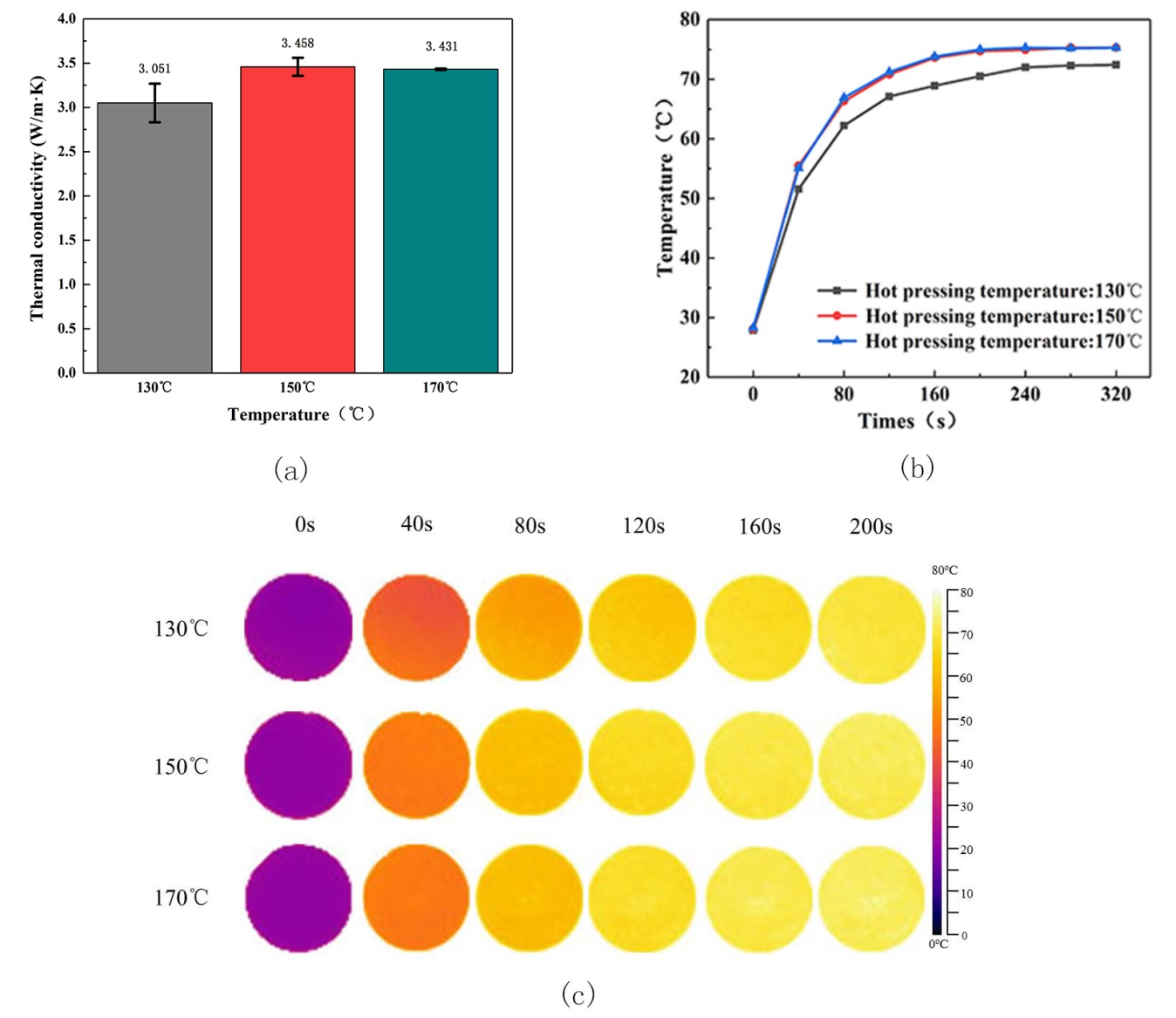
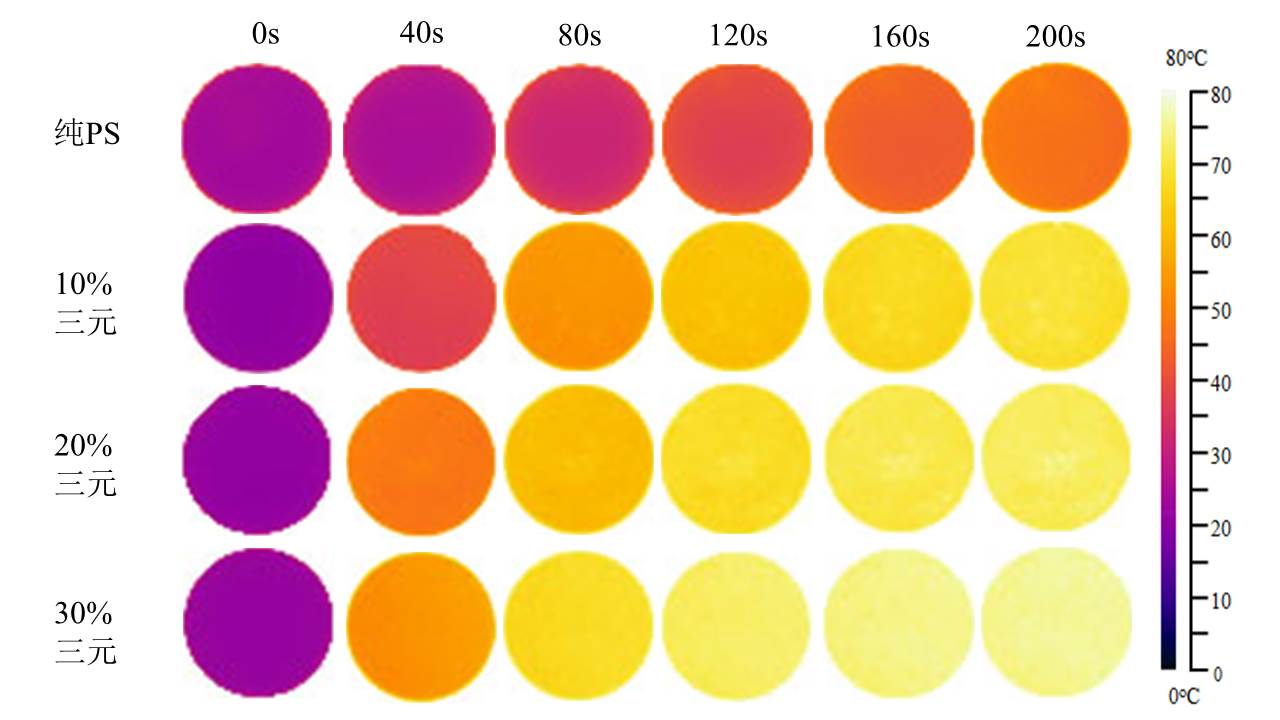
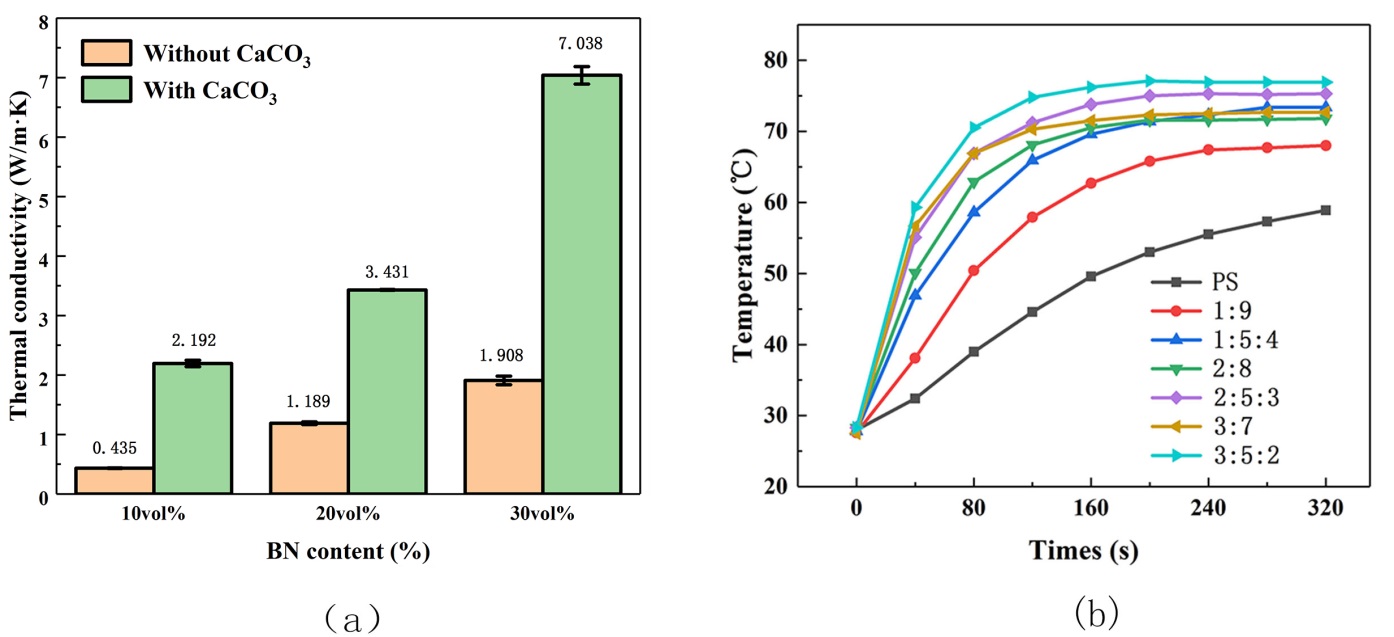
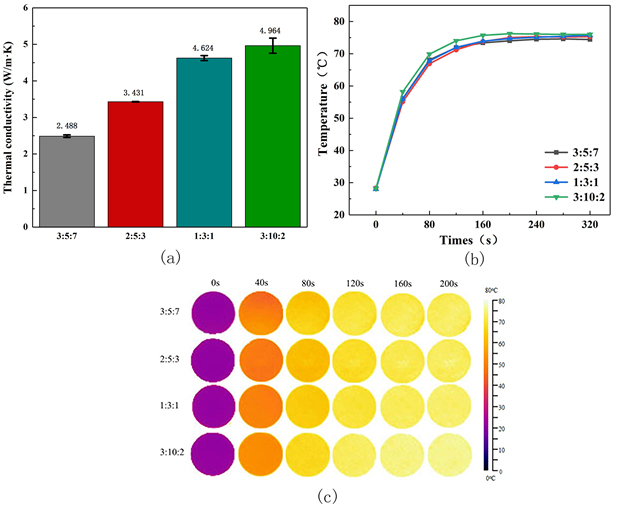
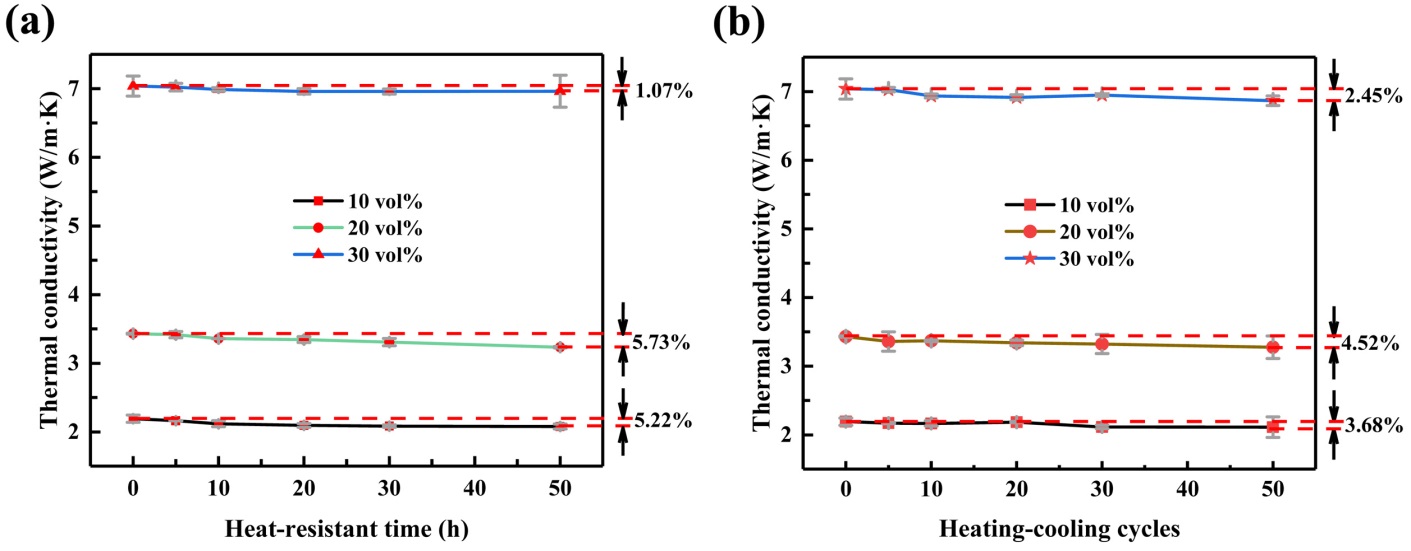
本课题采用高导热填料氮化硼、易成型加工的聚苯乙烯作为基体,添加了第三相无机填料(碳酸钙)作为填充粒子制备了三维导热网络的复合材料。进行了红外热成像、扫描电镜观察、X射线衍射分析、热冲击试验、热老化试验来表征复合材料的性能和结构,详细分析氮化硼以及碳酸钙含量对导热性能的影响。得到以下结论:(1)热压温度为170℃的样品,导热能力最好,配方为2:5:3的复合材料的导热率为3.432 W/(m·K)。(2)氮化硼可以改善聚苯乙烯的导热能力,在氮化硼含量为30vol%时,其导热率达到1.903W/(m·K)。(3)碳酸钙的加入可以使复合材料的导热能力有大幅度的提升,在氮化硼含量为30vol%、碳酸钙的含量为50vol%时复合材料导热率达到最高为7.04 W/(m·K)。(4)氮化硼/无机填料/聚苯乙烯三元复合材料的热稳定比较优异,在50次冷热冲击试验和50个小时热老化试验后热导率分别下降了0.1 W/(m·K)和0.15 W/(m·K)。
关键词: 导热高分子 聚苯乙烯 氮化硼 碳酸钙
Study on Preparation and Properties of Boron Nitride/ Calcium carbonate/polystyrene
Abstract
With the development of microelectronic integration technology and micro-encapsulation technology, electronic devices tend to be smaller, lighter, and higher-performance, and traditional thermal materials have been unable to meet people's needs. Polystyrene has the advantages of easy molding, low cost, insulation, etc. It is widely used in the light industry market, and is a suitable raw material for manufacturing optical chemical instrument parts and various instrument cases. If the polystyrene is modified, solution-melt blending of boron nitride and polystyrene results in a composite material having high thermal conductivity and high insulation while maintaining the original good processability. This will provide a viable solution for thermal materials in the field of microelectronics.
This topic intends to use high thermal conductivity filler boron nitride, easy to shape processing polystyrene plastic as the matrix. And in order to reduce the amount of the thermally conductive filler added and to form a three-dimensional heat conduction network of boron nitride in the matrix, a third phase inorganic filler (calcium carbonate) is added as the filler particles. We carried out infrared thermal imaging, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, thermal shock test, heat aging test to characterize the performance and structure of the composite, and detailed analysis of the influence of boron nitride and calcium carbonate content on thermal conductivity. The following conclusions were obtained:(1)The sample with a hot pressing temperature of 170℃ has the best thermal conductivity, and the thermal conductivity of the composite material with a formulation of 2:5:3 is 3.432 W/(m·K). (2) Boron nitride can improve the thermal conductivity of polystyrene. When the boron nitride content is 30vol%, the thermal conductivity reaches 1.903 W/(m·K). (3) The addition of calcium carbonate can greatly improve the thermal conductivity of the composite. When the boron nitride content is 30 vol% and the calcium carbonate content is 50 vol%, the thermal conductivity of the composite reaches a maximum of 7.04 W/(m· K). (4) Boron nitride/inorganic filler/polystyrene ternary composite material is excellent in thermal stability. The thermal conductivity decreases by 0.1 W/(m·K) after 50 thermal shock tests and 0.15 W/(m·K) after 50 hours heat aging test respectively.
Key Words: Thermal polymer Polystyrene Boron nitride Calcium carbonate
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
目录 IV
第一章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2导热机理 1
1.3提高复合材料导热率的方法 1
1.4导热填料简介 2
1.4.1金属导热填料 2
1.4.2无机非金属导热填料 2
1.5原料简介 3
1.6本研究目的和内容 3
第二章 实验部分 4
2.1实验原料及所用设备 4
2.2制备方法 5
2.2.1预压料的制备 5
2.2.2复合材料的制备 6
2.3测试与表征 7
2.3.1红外热成像测试 7
2.3.2扫描电镜测试 7
2.3.3 XRD分析 7
第三章 结果与讨论 8
3.1氮化硼/无机填料/聚苯乙烯三元复合材料的结构分析 8
3.1.1扫描电镜观察 8
3.1.2 XRD分析 9
3.2氮化硼/无机填料/聚苯乙烯三元复合材料的红外热成像图像 9
3.3复合材料的性能测试 14
3.3.1热稳定性测试 14
第四章 结论与展望 16
4.1结论 16
4.2展望 16
参考文献 17
致谢 19
第一章 绪论
1.1研究背景
随着微电子集成技术以及组装技术的迅猛发展,电子元器件和逻辑电路的体积不断减小,而工作频率却越来越高,产生的热量迅速积累,随着电子元器件工作环境温度的升高,其使用寿命将会下降,倘若热量不能及时消散,将严重影响电子元器件的在正常工作甚至会产生安全事故[1~3]。因此迫切的需求一种绝缘高导热的材料来解决微电子领域的散热问题。
传统的金属导热材料具有较高的导热率,但由于金属材料导电、电磁屏蔽、易腐蚀的性质限制了其在电子封装领域的运用[4]。而高分子材料高绝缘,力学强度优异、易成型及耐腐蚀等优点[5,6],倘若添加一种合适的填料,在保持高分子材料原本固有优势性能的同时改善其导热能力,便可有效的解决电子器件的封装问题。
1.2导热机理
不同性质的材料,其导热机理不同,常见的复合材料导热机理可以通过三种形式来实现:自由电子、晶格震动以及电磁辐射,其实质是固体内部的电子、声子以及光子的相互作用及碰撞[7]。我们都知道金属具有较好的导热性能,这是由于金属导热的载体是自由电子,电子质量轻,传热效率高,因此金属的导热率高[8]。对于非金属材料而言,由于没有自由电子的存在,再加上光子辐射导热的效果十分微弱,此时热量主要通过晶格的震动来进行传递但高分子材料结晶度低,晶格缺陷多,因此导热率很低[9]。而无机非金属材料当中晶体微粒长程有序,晶体结构完整,具有良好的导热性能,便可用来改善高分子材料的导热性能[7]。
1.3提高复合材料导热率的方法
导热率的高低是评判应用于微电子领域的复合材料的重要性质之一。提高材料的热导率能够有效延长电子元器件的使用寿命,并消除安全隐患。影响聚合物复合材料的导热率的因素有很多,而在其中起决定性作用的便是填料.填料的比例、填料的导热率、填料在复合材料当中的排列、取向等都对复合材料的导热率有着很大的影响[10]。
相关图片展示:

您可能感兴趣的文章
- 可聚合高分子模板增强制备高耐久超疏水涂层文献综述
- PVC/ABS合金的制备及性能研究开题报告
- 设计具有增强的赝电容及电催化性能的Co3O4/NiCo2O4双壳纳米笼结构外文翻译资料
- 光子上转换手性液晶:显著放大的上转换圆偏振发光外文翻译资料
- 氧空位型LiV3O8纳米片的快速稳定储锂性能研究外文翻译资料
- 应用于高性能钙钛矿太阳能电池的电子传输层的前体工程外文翻译资料
- 复合材料科学与技术 ——含碳纳米管的多孔导电弹性体复合材料悬浮在共连续聚合物的狭窄孔隙中的混合纳米复合材料外文翻译资料
- 一种用于先进锂硫电池源自聚罗丹宁纤维素的氮硫双掺杂碳外文翻译资料
- 短玻璃纤维增强聚丙烯控制界面和力学性能参数外文翻译资料
- 含Ca0的LaCO.0H纳米齿轮及其发光和脱NOx性能外文翻译资料




