一种泡沫混凝土制备和裂纹改善毕业论文
2020-07-07 21:56:16
摘 要
泡沫混凝土作为一种新型轻质材料,因其良好的力学性能以及使用功能,在大体积回填工程、保温隔热工程及轻质制品制造等方面都得到了广泛的应用。然而,随着泡沫混凝土应用的进一步推广,其易开裂的缺陷也渐渐显露出来,并严重影响其生产与使用。本实验从配方方面着手,意在研究外加剂掺量的改变对泡沫混凝土试样抗裂性能的影响。
本实验中采用了化学发泡的方法,以铝粉作为发泡剂制备泡沫混凝土试样,首先确定一个适当的水灰比,接着通过单因素实验,观察各种外加剂对泡沫混凝土试样的影响,测试其力学性能确定泡沫混凝土的各组分最佳掺入量:水灰比为0.56;发泡剂铝粉掺量2.0%;NaOH助剂掺量1.4%;稳泡剂掺量0.6%;减水剂掺量0.2%;聚丙烯纤维掺量0.6%;早强剂掺量1.0%。该配方下试样的稳态导热系数为0.123W/(m•K),瞬态导热系数为0.1211W/(m•K),3d抗压强度可以达到0.90MPa,28d抗压强度能够达到1.80MPa,吸水率38%。
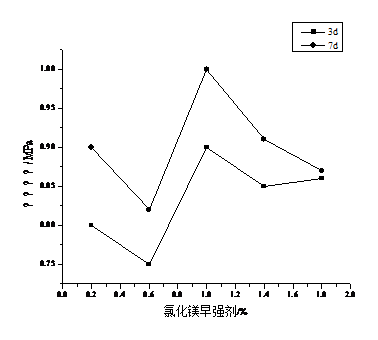
根据实验总结,对裂纹进行等级划分,并通过实验研究外加剂对泡沫混凝土的抗裂性能的影响,最终达到改善泡沫混凝土开裂问题的目的。实验发现:聚羧酸减水剂对开裂初始时间影响不大,适量的减水剂通过提高泡沫混凝土基体的流变性和收缩能力降低泡沫混凝土开裂风险,试样的裂纹宽度明显降低,在提高泡沫混凝土力学性能的同时,也提高了抗裂性能;早强剂MgCl2能够很好地提高泡沫混凝土抗裂能力,不仅推迟初始开裂时间,同时裂纹宽度也有着明显降低趋势。这是因为早强剂在体系中通过水化反应,提高泡沫混凝土的致密性,提高了内部水分扩散能力,导致试样硬化后失水率降低,当掺量超过0.4%时,开裂初始时间和裂纹宽度都保持一个相对稳定的范围内;聚丙烯纤维能够减少泡沫混凝土内部细小微裂纹,纤维会在裂纹之间起到桥接作用,阻止裂纹发展。
关键词:泡沫混凝土 开裂 性能
ABSTRACT
As a new type of lightweight material, foam concrete has been widely used in large volume backfill engineering, thermal insulation engineering and lightweight product manufacturing because of its excellent mechanical properties and use functions.However, with the further promotion of the application of foam concrete, its easy cracking defects are gradually exposed, and seriously affect its production and use.This experiment started from the formulation aspect, intending to study the effect of changes in admixture dosage on the crack resistance of foam concrete specimens.
In this experiment, a method of chemical foaming was used. Aluminum foam was used as a blowing agent to prepare foamed concrete samples. First, an appropriate water-cement ratio was determined. Then through single-factor experiments, the amount of admixtures such as aluminum powder blowing agent, NaOH additive, foam stabilizer, and polycarboxylic acid water reducer was changed. The influence of various factors on the foam concrete samples was observed and the mechanical properties of the samples were determined. The optimum blending amount of each component of foam concrete: water-cement ratio 0.56; foaming agent aluminum powder 2.0%; NaOH additive 1.4%; foam stabilizer 0.6%; %; polypropylene fiber content 0.6%; early strength agent content 1.0%. The steady-state thermal conductivity of the sample is 0.123W/(m•K), the transient thermal conductivity is 0.1211W/(m•K), the 3d compressive strength can reach 0.90MPa, and the 28d compressive strength can reach 1.80. MPa, water absorption 38%.
According to the experiment summary, the classification of cracks was made, and the effect of admixtures on the anti-cracking performance of foam concrete was experimentally studied, and finally the purpose of improving the cracking problem of foamed concrete was achieved. The experimental results show that the polycarboxylate water reducing agent has little effect on the initial cracking time. The proper amount of water reducing agent reduces the cracking risk of the foam concrete by increasing the rheology and shrinking ability of the foam concrete matrix. The crack width of the sample is obviously reduced, and the foam is increased. At the same time, the mechanical properties of concrete also improve the crack resistance; early strength agent MgCl2 can well improve the crack resistance of foam concrete, not only delaying the initial cracking time, but also has a significant decrease in crack width. This is because the early strength agent passes through the hydration reaction in the system to improve the compactness of the foamed concrete and improve the internal moisture diffusion capacity, resulting in a decrease in the water loss rate after hardening of the sample. When the amount exceeds 0.4%, the initial cracking time is The crack width is kept within a relatively stable range; polypropylene fibers can reduce the fine microcracks inside the foamed concrete, and the fibers will act as bridging between the cracks, preventing crack growth.
Key Words: Foamed concrete; Crack; performance
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题背景 1
1.2 泡沫混凝土的特性 2
1.2.1 轻质和保温隔热 2
1.2.2 隔音耐火 3
1.2.3 低弹抗震 3
1.2.4 其他性能 3
1.3 国内外研究现状 3
1.4 裂纹分析方法 6
1.5 本课题研究意义 6
第二章 实验原料与仪器 8
2.1 实验原料 8
2.1.1 水泥 8
2.1.2 铝粉发泡剂 8
2.1.3聚羧酸减水剂 8
2.1.4 聚丙烯纤维 8
2.1.5 矿渣粉 9
2.1.6 其他原料 9
2.2 实验仪器 9
第三章 实验流程和方法 10
3.1 泡沫混凝土试样的制备 10
3.2 泡沫混凝土力学性能测试方法 11
3.3.1 干密度测试方法 11
3.3.2 抗压强度测试方法 11
3.3 各组分掺量确定 12
3.3.1 水灰比 12
3.3.2 发泡剂铝粉 13
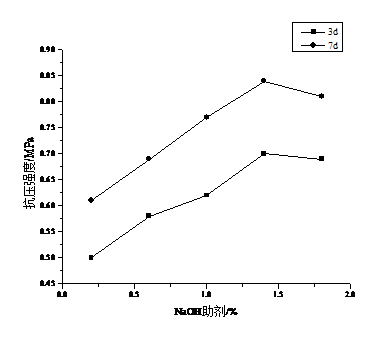
3.3.3 助剂NaOH 14
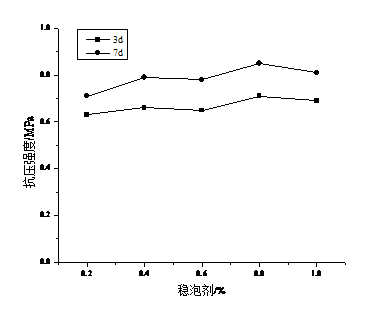
3.3.4 稳泡剂 15
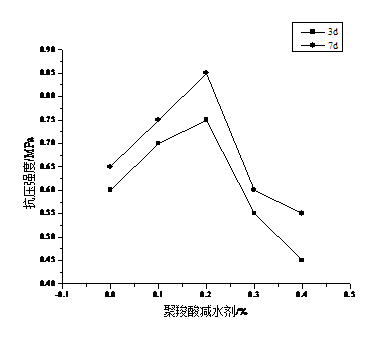
3.3.5 聚羧酸减水剂 16
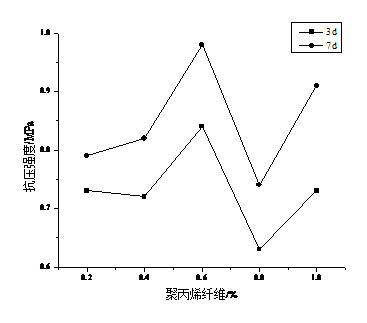
3.3.6 聚丙烯纤维 17
3.3.7 早强剂 18
3.3.8 矿渣粉 19
3.4 泡沫混凝土的其他性能 20
3.4.1 吸水率测试 20
3.4.2 导热系数测定 21
3.5 本章小结 22
第四章 泡沫混凝土抗裂性能的提高和改善 23
4.1 泡沫混凝土裂纹评定标准和实验方法 23
4.1.1 裂纹评定标准 23
4.1.2 实验方法 24
4.2 泡沫混凝土的抗裂性能 25
4.2.1 减水剂对泡沫混凝土抗裂性能的影响 25
4.2.2 早强剂对泡沫混凝土抗裂性能的影响 26
4.2.3 纤维对泡沫混凝土抗裂性能的影响 27
4.2.4 养护对泡沫混凝土抗裂性能的影响 28
4.3 本章小结 29
第五章 结论与展望 30
5.1 结论 30
5.2 展望 30
参考文献 32
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题背景
在建筑工程的施工过程中,混凝土的应用对于整个建筑工程的科学性建设有着至关重要的作用[1]。在我国现有的400多亿平方米的建筑面积中,每年用于新建建筑近20亿平方米,其中高能耗建筑会多达95%[2]。资源的不停的挖掘和利用最终用促使能源短期,造成严重的危机现象,使可持续发展的进程缓慢。我国于2010年以前采用的新型墙体材料仅占发达国家的18%,且粘土砖占了我国墙体材料的80%左右,但粘土砖生产耗能高、施工劳动强度大、毁田多、抗震性能差、质量难以控制[3]。所以,降低资源消耗与发展低碳工业就成为了建设建筑工程中一个关键的调整方向。泡沫混凝土轻质环保,因此它作为一种新型的建筑材料,越来越被大家所重视。泡沫混凝土除了上述特性,还有隔热,耐火的功能,并且隔音效果也很好,尤其是在减震能够体现它优越质的特性。平常使用时,还可以够把工业生产过程产生的废渣利用起来,推动了中国建筑行业提出的建设节能工程的实行。所以由此看来,在将来的建筑项目选材、施工中,泡沫材质的混凝土还将继续展现它的优势特点并且使用范围还会被无限拓宽。
同时在保温材料方面,在我国,我们经常采用的具有保温性能的建筑材料大部分是泡沫有机材质,主要有聚苯乙烯,挤塑聚苯乙烯和聚氨酯。尽管这些材质容易加工,在致密程度与保温效果方面都表现较为突出,不过也有着自身的不足,比如未能考虑到它的安全性,性能也不够稳定,材质的熔点低,其中最突出的缺点就是普遍存在比较严重的防火安全隐患,因为这种有机材质在燃烧的过程中会产生很高的热量,释放出许多烟尘,会对人体造成危害,并且火势会迅速扩散,不易控制,结果会导致人员不易被解救,发生伤亡的事故。我国中央电视台大楼曾经发生的火灾事件就是因为当时建筑材料使用了不易阻燃的有机保温材料,此外还有上海“11·15”静安区特大火灾、南京中环大楼火灾、济南奥体中心大火等都造成了严重的后果,公安消防部门也加大了对新建项目的审察检验力度。而在无机保温材料岩棉、矿渣棉虽然保温效果良好,但其生产过程对人体有害,不符合绿色建筑的要求。泡沫混凝土这种新型建材与上述材料相比,其轻质、保温、耐火、环保节能等特点显得尤为突出,因此也备受关注。
相关图片展示:


您可能感兴趣的文章
- 蒸养纤维掺杂高铁低钙水泥混凝土的抗海水冲磨性能研究文献综述
- TIPA对水泥-锂渣体系力学性能和水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- TEA对锂渣-水泥复合粘结剂流变性能及水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- 硫酸铝无碱液体促进剂的效果研究烷醇胺对硅酸盐水泥水化过程的影响外文翻译资料
- 新型C-A-S-H/PCE纳米复合材料:设计表征和对水泥水化的影响外文翻译资料
- 工业中碳捕获技术以及以水泥回转窑作为核心的吸附再生器外文翻译资料
- Ca/Al层状双氢氧化物的制备及其结构对水泥早期强度的影响外文翻译资料
- 蒸汽养护后混凝土养护方法对混凝土机械强度和透气性的影响外文翻译资料
- 含白云石或石灰石的偏高岭土水泥在相组成与抗压强度的异同外文翻译资料
- 与硅质铁尾矿结合的混凝土的耐久性外文翻译资料




