MgO膨胀剂的水化与膨胀应力毕业论文
2020-07-07 21:58:03
摘 要
水泥混凝土材料在使用的过程中会受到一些因素的破坏,例如硫酸盐侵蚀,冻融破坏,收缩开裂等因素,这会对水泥的力学性能和耐久性产生严重的影响,这其中,收缩开裂是最常见的一种形式。而收缩应力会对水泥混凝土材料造成很大的破坏。所以为了补偿混凝土使用过程中会形成的收缩开裂,我们需要在混凝土中加入膨胀剂,膨胀剂在水化过程中产生了膨胀应力,而混凝土材料在使用过程中会产生收缩应力,而膨胀应力能去补偿产生的收缩应力,以达到减小开裂的效果。本文便是对MgO膨胀剂(MEA)的一些研究和探讨。目前MEA已经应用于许多大型工程中,由于其对水泥混凝土的收缩补偿是有效且长期稳定的,受到一致好评。水化程度,自由膨胀量,微观形貌,压实体的孔结构分析等方面是本文对氧化镁膨胀剂的研究重点,一般自由膨胀量被用作评判其性能的指标。但在实际使用过程中,由于混凝土受到的约束条件相对复杂,所以并不能单一的用自由膨胀量去评判MEA在实际混凝土使用过程中的膨胀性能。由于MEA的膨胀在混凝土内部产生了膨胀应力,所以我们将膨胀应力作为评判其膨胀性能的另一参数。
本文利用一套实验设备,测试了MEA在不同约束条件下产生的膨胀应力,同时研究了MEA吸水生成的氢氧化镁在吸水过程中产生的肿胀力,也对不同约束条件下MEA的水化程度和其水化生成的氢氧化镁的微观形貌进行了研究,主要得出的结论如下:
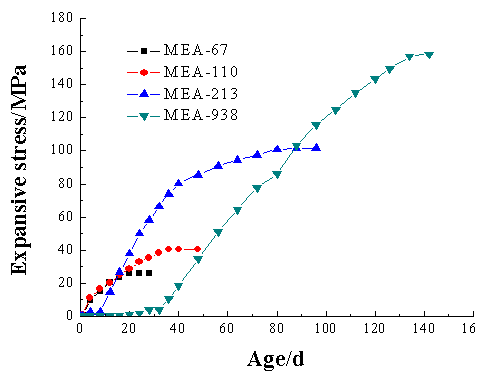
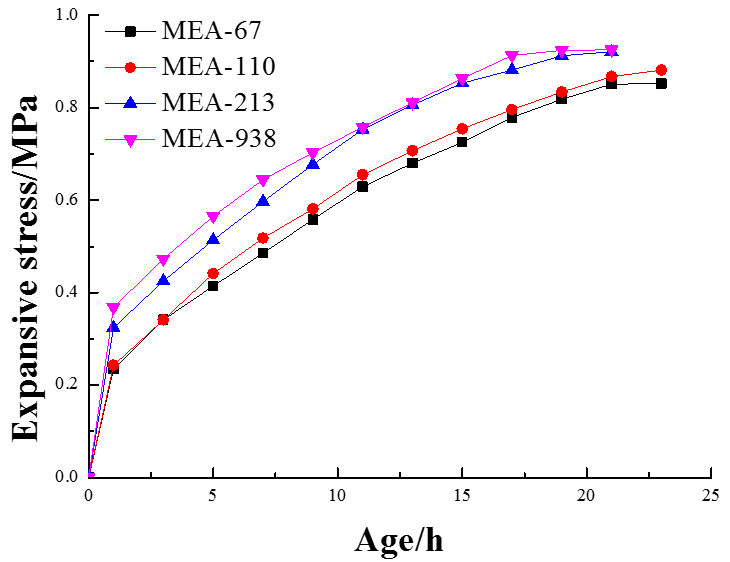
(1) 将压实体放在40℃水中进行处理,MEA-67、MEA-110,MEA-213和MEA-938会产生膨胀应力,其膨胀应力大小分别是25.7 MPa, 40.7 MPa, 101.6 MPa和150.6 MPa。由此可得出,当MEA压实体的活性较低时,往往能产生较大的膨胀应力。
(2)将 MEA的适量加入水泥中后,MEA会产生膨胀应力,从而去补偿水泥基材料的收缩应力,来达到减小收缩开裂的效果。
(3)水化环境和MEA活性会影响MEA的水化,高活性MEA水化生成晶粒尺寸小的Mg(OH)2。同时,碱溶液会影响Mg(OH)2的结晶习性,进而影响水化膨胀应力。
(4) MEA-67、MEA-110,MEA-213和MEA-938水化生成的Mg(OH)2压实体的膨胀应力约为2至3 MPa,由此可见相对于MEA水化产生的膨胀应力可忽略不计;表面积大的Mg(OH)2,其压实体具有较大的吸水肿胀应力。
(5) MEA-67、MEA-110,MEA-213和MEA-938压实体水化生成Mg(OH)2,将其进行干燥处理,然后再吸水,测其吸水肿胀应力均小于1 MPa,相对于MEA水化产出的膨胀应力可忽略不计,吸水肿胀应力对膨胀应力的贡献很小,推断主要是由结晶压力产生的。
ABSTRACT
In the process of use, the cement concrete material will be damaged by some factors, such as sulphate erosion, freeze-thaw damage, shrinkage cracking and other factors, which will have a serious impact on the mechanical properties and durability of cement, among which, shrinkage cracking is The most common form. Shrinkage stress can cause great damage to cement concrete materials. Therefore, in order to compensate for the shrinkage and cracking that will occur during the use of concrete, we need to add expansion agent to the concrete. The expansion agent will generate expansion stress during the hydration process, while the concrete material will produce contraction stress during use, and the expansion stress energy. To compensate for the contraction stress generated to achieve the effect of reducing cracking. This article is some research and discussion on MgO expansion agent (MEA). At present, MEA has been used in many large-scale projects. Because its compensation for cement concrete shrinkage is effective and long-term stable, it has been well received. The degree of hydration, the amount of free expansion, the micro-morphology, and the pore structure analysis of compacted bodies are the focus of this study on magnesium oxide expanders. Generally, the amount of free expansion is used as an index to judge its performance. However, in practical use, due to the relatively complex constraints imposed on the concrete, it is not possible to use a single amount of free expansion to judge the expansion performance of the MEA during use of the actual concrete. Since the expansion of the MEA creates an expansion stress inside the concrete, we use the expansion stress as another parameter to judge its expansion performance.
In this paper, a set of experimental equipment was used to test the expansion stress of MEA under different constraining conditions. Simultaneously, the swelling force of magnesium hydroxide generated by water absorption of MEA during water absorption was studied, and the degree of hydration of MEA under different constrained conditions was also studied. The microscopic morphology of the magnesium hydroxide produced by hydration has been studied. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) When the compacted body is treated in water at 40°C, the expansion stress is generated for MEA-67, MEA-110, MEA-213, and MEA-938. The magnitude of the expansion stress is 25.7 MPa, 40.7 MPa, 101.6 MPa, and 150.6, respectively. MPa. It can be concluded that when the MEA pressurization entity is less active, it can often produce greater expansion stress.
(2) After the appropriate amount of MEA is added to the cement, the MEA will have expansion stress, so as to compensate the contraction stress of the cement-based material, so as to reduce the shrinkage cracking effect.
(3) Hydration environment and MEA activity will affect the hydration of MEA, and high activity MEA hydration produces Mg(OH)2 with small grain size. At the same time, the alkali solution will affect the crystallization habit of Mg(OH)2, which will affect the hydration swelling stress.
(4) The expansion stress of Mg(OH)2 compacts produced by the hydration of MEA-67, MEA-110, MEA-213, and MEA-938 is about 2 to 3 MPa, which shows the expansion relative to the hydration of MEA. The stress is negligible; Mg(OH)2 with a large surface area has a large swelling stress in the compacted body.
(5) The hydration of MEA-67, MEA-110, MEA-213, and MEA-938 into a compacted body produces Mg(OH)2, which is dried, then reabsorbed, and the water swelling and swelling are all less than 1 MPa. The swelling stress produced by hydration of MEA is negligible, and the swelling stress of water absorption contributes little to the expansion stress, and it is inferred that it is mainly caused by the crystallization pressure.
目录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2水泥混凝土材料的收缩 1
1.3水泥混凝土材料收缩开裂的补偿措施 1
1.4 MEA的研究与应用 2
1.4.1膨胀剂的研究历史 2
1.4.2 MEA的膨胀机理 2
1.5 课题的内容与意义 3
研究内容: 4
第二章 原材料与实验方法 8
2.1 原材料 8
2.1.1菱镁矿 8
2.1.2 MEA 9
2.1.3 水泥 10
2.1.4氢氧化镁 10
2.2 试验方法 11
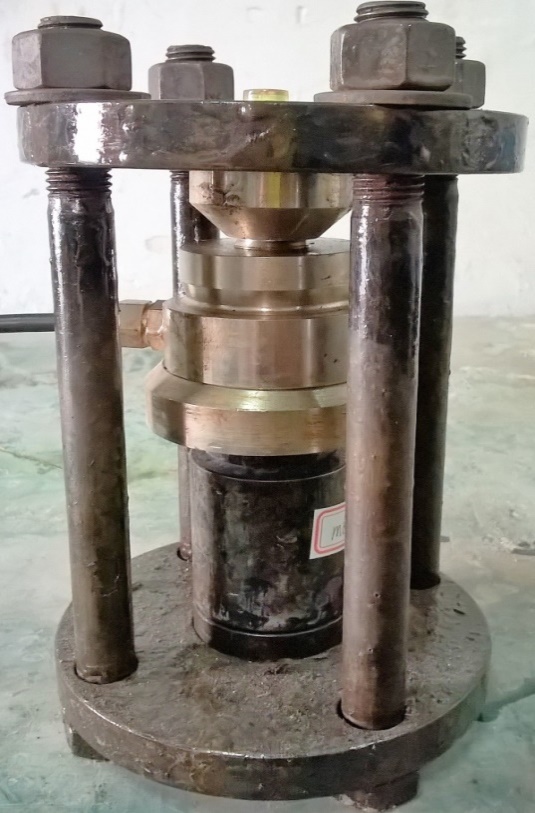
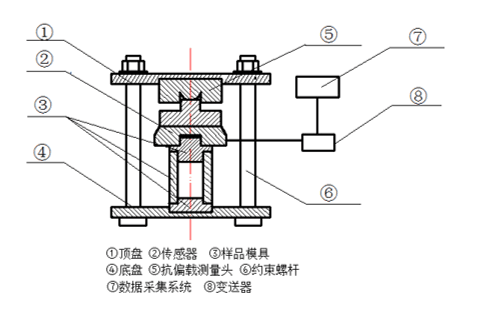
2.2.1膨胀应力测试装置 11
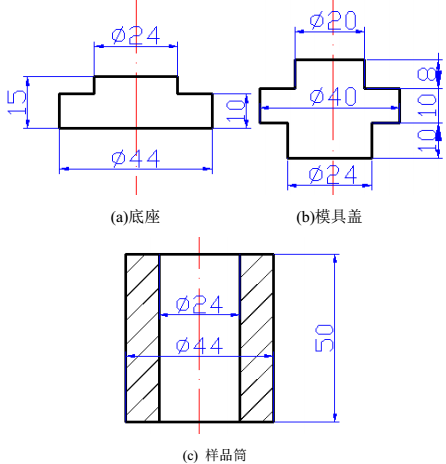
2.2.2 MEA压实体膨胀应力测试 13
2.2.3 氢氧化镁吸水肿胀应力测试 13
2.2.4 MEA压实体水化程度测试 13
2.2.5氢氧化镁的微观形貌 13
2.2.6 MEA压实体孔结构分析 14
2.2.7 MEA活性和掺量对水泥浆体膨胀量的影响 14
2.3 实验仪器 14
第三章 MEA压实体的膨胀应力 16
3.1 MEA压实体的膨胀应力 16
3.1.1活性指数对MEA压实体膨胀应力的影响 16
3.1.2养护溶液对MEA压实体膨胀应力的影响 17
3.2掺MEA水泥浆体的自由膨胀 18
3.3 Mg(OH)2压实体吸水肿胀应力的测试 20
3.4讨论 21
3.4.1 MEA压实体水中水化程度的测试 21
3.4.2 MEA压实体水中水化产物的SEM分析 22
3.4.3 MEA压实体碱溶液水化产物SEM分析 23
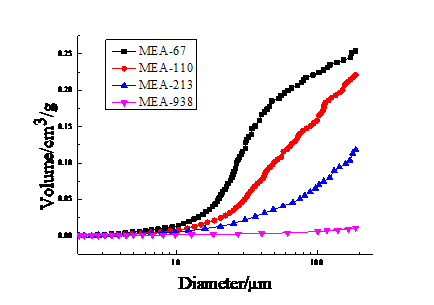
3.4.4 MEA压实体孔结构 24
第四章 结论与展望 25
4.1 结论 25
4.2 展望 26
参考文献 28
致 谢 31
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
水泥混凝土材料是我国乃至全世界使用最广泛的建筑材料,大量应用于房屋建造,桥梁,大坝等,和我们的生活息息相关,所以对混凝土材料的研究更是显得尤为重要。但即使研究多年,仍有许多问题困扰着我们,例如水泥的收缩开裂,极大的破坏了水泥混凝土材料的耐久性,同时也加速了一些其他形式的破坏。所以在水泥中加入膨胀剂是目前使用最广泛且有效的措施[1],而这其中氧化镁类膨胀剂便是使用最普遍的。而对于膨胀剂的膨胀机理目前仍存在许多争论,有固相体积增大理论,固相反应理论,吸水肿胀理论和晶体生长压理论[2]。对于这些理论,前人已经进行了大量的研究,但都未得到统一的结论。吸水肿胀理论[3]和晶体生长压理论[4]是被大家所普遍接受的。
1.2水泥混凝土材料的收缩
在混凝土的使用过程中,如果拉应力超过极限抗拉强度,则会引起开裂[5],且收缩变形时导致开裂的主要原因。
而最常见的收缩变形有塑性收缩,自收缩和干燥收缩。塑性收缩一般由材料表面的水分蒸发,或者模板材料,基地混凝土材料的吸水造成,因为这时有大量的水分流失,从而导致收缩变形;当材料在与外界没有水分交换的时候,水泥的水化会导致毛细孔中的水分迁移,从而产生毛细管力,来导致收缩变形,这种被称为自收缩,且自收缩也被称为自身体积变形[6];将材料放在不饱和的湿空气中养护时,材料内部的水分会因为压强差而转移至空气中,从而导致收缩变形,这种变形便被成为干燥收缩。
1.3水泥混凝土材料收缩开裂的补偿措施
在补偿水泥混凝土收缩开裂的方式中,利用膨胀剂是目前最为有效的措施,且得到了广泛利用,例如氧化镁膨胀剂,氧化钙膨胀剂和钙矾石类膨胀剂。氧化钙膨胀剂和MEA等是最常用的几种主要组分[7,8]。
相关图片展示:


您可能感兴趣的文章
- 蒸养纤维掺杂高铁低钙水泥混凝土的抗海水冲磨性能研究文献综述
- TIPA对水泥-锂渣体系力学性能和水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- TEA对锂渣-水泥复合粘结剂流变性能及水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- 硫酸铝无碱液体促进剂的效果研究烷醇胺对硅酸盐水泥水化过程的影响外文翻译资料
- 新型C-A-S-H/PCE纳米复合材料:设计表征和对水泥水化的影响外文翻译资料
- 工业中碳捕获技术以及以水泥回转窑作为核心的吸附再生器外文翻译资料
- Ca/Al层状双氢氧化物的制备及其结构对水泥早期强度的影响外文翻译资料
- 蒸汽养护后混凝土养护方法对混凝土机械强度和透气性的影响外文翻译资料
- 含白云石或石灰石的偏高岭土水泥在相组成与抗压强度的异同外文翻译资料
- 与硅质铁尾矿结合的混凝土的耐久性外文翻译资料




