熔盐法制备氮掺杂碳与MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体及其超级电容器性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 16:57:18
摘 要
全球人口增长,化石能源的逐渐枯竭及其带来的环境问题正严重威胁着人类的生存和发展。大力发展绿色可再生能源已成为世界各国的共识。由于绿色能源的自身特点,必须加大对储能器件与体系的研发。
与二次电池(Battery)相比,超级电容器(Supercapacitors)因其更大的功率密度、更佳的循环稳定性和工作温度适应性等诸多优势获得了较为广泛的应用。一方面,目前商业化程度最高的碳材料虽然具有高导电性、高化学稳定性等优点,但能量密度相对较小。因此,对碳材料进行微观形貌或结构的优化成为当下提高电容器能量密度的研发方向之一,而其中对碳材料进行异质原子(如N原子)掺杂是一种较为常见的改性途径。氮掺杂碳基极片在基本保留常规碳材料的良好导电性和大比表面积之外,还可以在表面发生法拉第赝电容反应,有利于电容器发挥出更佳的电化学性能。另一方面,过渡金属氧化物(如氧化锰,MnxOy)作为一种常见的赝电容材料,结构中存在着大量氧化位点,其理论比电容一般远高于双电层电容,且储量丰富、价格低廉、环保无毒,应用前景广阔。
本文以此为出发点,考虑通过熔盐法制备一种氮掺杂碳的MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体复合电极。通过双电层电容(N掺杂碳)与赝电容(MnxOy)的协同效应,以获得一种既具有双电层电容高导电率、高循环稳定性又具有赝电容高比电容优点的复合电极材料,集两者之所长,以期满足高性能超级电容器的要求,具体开展工作如下:
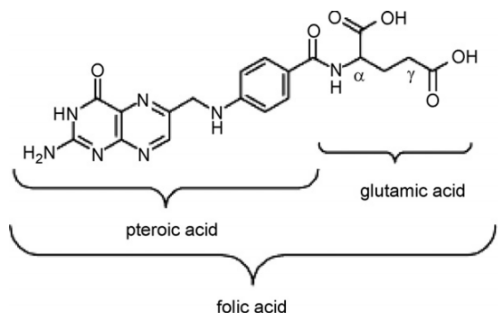
采用叶酸(C19H19N7O6)为碳源,四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O)为锰源,将两者在60℃、中性条件下(pH=7.0)通过简单的水相共混反应一步合成前驱体材料。以氯化钠(NaCl)作为熔盐模板,经高能球磨和高温(800℃,Ar气氛)煅烧退火处理后,完成杂化体的制备。通过对电极表面的形貌观察和物相分析,证实了所制备的多孔复合电极为一种氮掺杂碳的MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体。同时复合电极还表现出较大的比表面积(437.0 m2/g)。本文还分别制备和讨论了不同比例的叶酸、氯化锰摩尔量对所制备复合电极的形貌及电化学性能的影响。
复合电极的电化学性能通过组装三电极体系进行了评价。以1 A/g的电流密度对摩尔比1:2(叶酸:氯化锰)的电极进行充放电,首周循环比容量达到了239.76 F/g,库伦效率97.8%,且倍率性能良好,在10 A/g的电流密度下比容量衰减至149.53 F/g。材料还表现出较好的循环稳定性(1000圈循环容量衰减至55.46%),该氮掺杂碳与MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体制备简单,性能优良,将较好地提升传统碳基超级电容器的各项电化学性能。
关键词:超级电容器;氮掺杂碳材料;MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体;熔盐法
Abstract
Global population growth and the environmental problems caused by the gradual depletion of fossil energy are seriously threatening the survival and development of human beings. Vigorously developing green energy has become the consensus all around the world. Due to the characteristics of green energy, it is essential to increase the research and development of energy storage devices and systems.
Compared with traditional battery energy storage devices, supercapacitors have been widely used due to their advantages such as greater power density, better cycle stability and operating temperature adaptability. On the one hand, the most commercialized carbon materials have the advantages of high electrical conductivity and high chemical stability, but the energy density is relatively small. Therefore, the optimization of the microstructure or structure of carbon materials has become one of the research and development directions for improving the energy density of capacitors. Among them, the heterogeneous atom (such as N atom) doping carbon materials is a common modification method. Nitrogen-doped carbon-based electrode can combine the Faraday pseudocapacitance reaction on the surface with the good conductivity of conventional carbon material, which is make for the capacitor to exert better electrochemical performance. On the other hand, transition metal oxides (such as manganese oxide, MnxOy) as a common tantalum capacitor material, there are a large number of oxidation sites in the structure, the theoretical specific capacitance is generally much higher than the electric double layer capacitance, and the reserves are abundant. The price is low, environmental protection and non-toxic, and the application prospect is broad.
Taking this as a starting point, a MnxOy nanoparticle hybrid composite electrode with nitrogen-doped carbon was prepared by molten salt method. Through the synergistic effect of electric double layer capacitor (N-doped carbon) and tantalum capacitor (MnxOy), a composite electrode having the advantages of high electrical conductivity, high cycle stability and high capacitance of tantalum capacitor is obtained. Materials, set the strengths of both, in order to meet the requirements of high-performance supercapacitors, the specific work is as follows:
Using folic acid (C19H19N7O6) as the carbon source and manganese chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O) as the manganese source, the precursors were synthesized by a simple aqueous phase blending reaction at 60℃ under neutral conditions (pH=7.0). Body material. The preparation of the hybrid was completed after sodium chloride (NaCl) was used as a molten salt template and calcined and annealed by high-energy ball milling and high temperature (800 ℃ , Ar atmosphere). The morphology and phase analysis of the electrode surface confirmed that the prepared porous composite electrode was a nitrogen-doped carbon MnxOy nanoparticle hybrid. At the same time, this electrode also showed a huge specific surface area (437.0 m2/g). The effects of different ratios of folic acid and manganese chloride on the morphology and electrochemical properties of the prepared composite electrode were also prepared and discussed.
The electrochemical performance of this electrode was estimated by a three-electrode system. The electrode with a molar ratio of 1:2 (folic acid: manganese chloride) was charged and discharged at a current density of 1 A/g. The specific capacity of the cycle reached 239.76 F/g in the first week, the coulombic efficiency was 97.8%, and the rate performance was good. The specific capacity of this electrode at 10 A/g is attenuated to 149.53 F/g. The material also exhibits good cycle stability (1000 cycles capacity decay to 55.46%). The nitrogen-doped carbon and MnxOy nanoparticle hybrids are simple to prepare and have excellent performance, which will better enhance the traditional carbon-based supercapacitor. Various electrochemical properties.
Key words: Supercapacitor; Nitrogen doped carbon material; MnxOy nanoparticle hybrid; Molten salt method
目录
摘要 I
Abstract III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
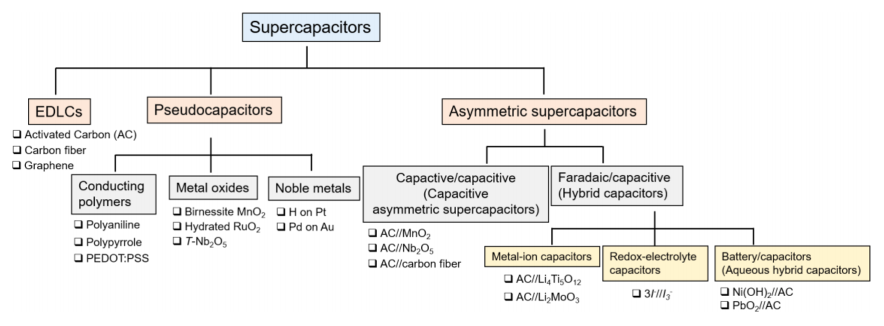
1.2 超级电容器简介 2
1.2.1超级电容器概述 2
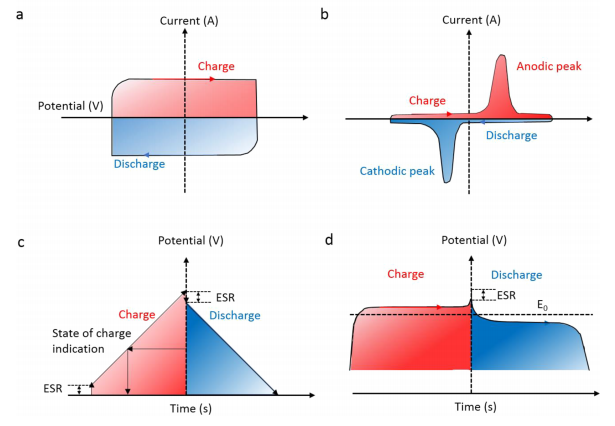
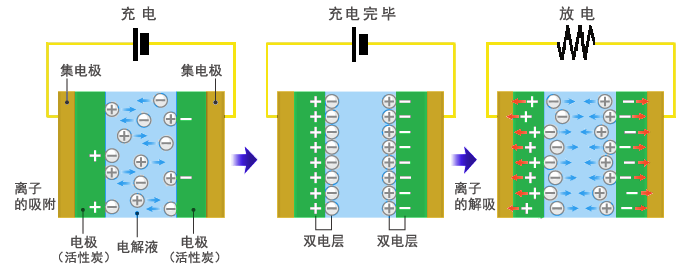
1.2.2 双电层电容器 4
1.2.3 法拉第赝电容器 5
1.2.4 碳电极材料 5
1.2.5 过渡金属(MnxOy)电极材料 6
1.3 超级电容器的电化学参数 7
1.3.1 比电容 7
1.3.2 电压窗口 7
1.3.3 内阻 7
1.3.4 能量密度 7
1.3.5 功率密度 8
1.3.6 循环稳定性 8
1.4 熔盐法概述 8
1.5 本论文的研究目的和主要内容 8
1.5.1 研究目的 9
1.5.2 研究内容 9
第二章 氮掺杂碳和MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体电极材料的制备与超级电容器性能研究 10
2.1引言 10
2.2实验试剂 10
2.3实验仪器 11
2.4氮掺杂碳与MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体前驱物的制备 12
2.5氮掺杂碳和MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体电极材料的表征 13
2.5.1表面微观形貌SEM分析 错误!未定义书签。
2.5.2 衍射谱XRD分析 14
2.5.3 X射线能谱分析 15
2.5.4 气体吸附分析 17
2.5.5 同步热重分析 18
2.6氮掺杂碳和MnxOy纳米粒子杂化体电极材料的电化学表征 19
2.6.1循环伏安测试(CV) 19
2.6.2恒流充放电测试(GCD) 20
2.6.3循环稳定性测试 22
2.6.4交流阻抗谱测试(EIS) 22
2.7 本章小结 23
第三章 结论与展望 24
3.1 结论 24
3.2 展望 24
参考文献 26
致谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
随着现代移动电子设备、新能源汽车等设备对供电需求的不断增加,研发出更高效率的储能系统已成为助力现代化建设的重中之重。其中,超级电容器(Supercapacitors)又称为电化学电容器,如图1-1的比功率-比能量图(Ragone)所示,超级电容器的性能介于物理电容器与二次电池之间,兼有物理电容的大功率密度和二次电池的高能量密度,填补了静电电容器与二次电池之间的空白[1]。超级电容器还具备极佳的循环稳定性和较广的适用工作温度窗口等显著优点,在可再生能源发电并网、信息通讯、新能源汽车、航空航天等领域都取得了较为广泛的应用。
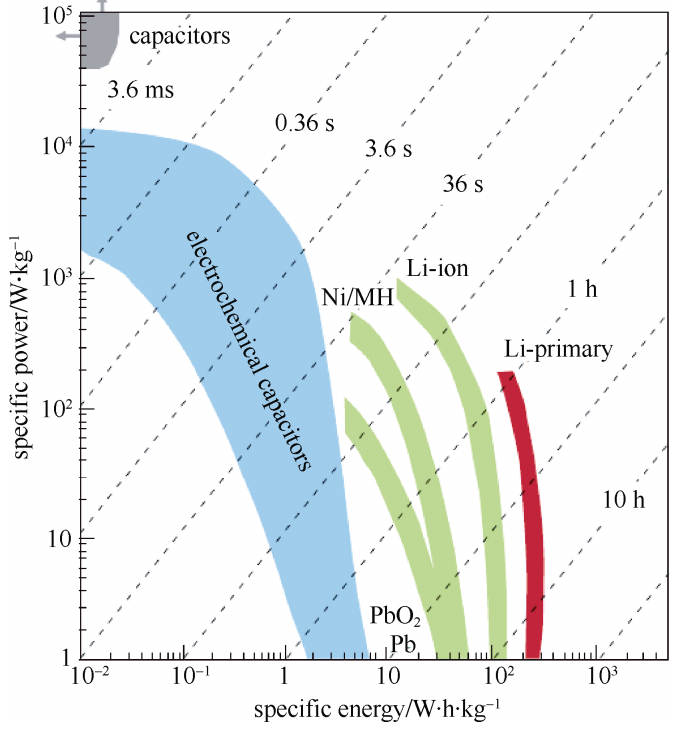
图1-1 不同储能器件的能量密度-功率密度对比图
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 激光作用下ZrNiSn合金热电材料组成、结构和性能的演化规律开题报告
- 原位生长于碳纤维表面的钒氧化物柔性电极制备开题报告
- 锂硫电池用TixOy-S/HGs复合材料的制备与性能开题报告
- MnO2纳米片修饰ZnO纳米棒阵列的气敏性能研究开题报告
- 基于三维碳基孔结构和电解质协同优化的微型超级电容器文献综述
- 基于C-MEMS工艺的微型混合锂离子电容器构筑及性能开题报告
- 多孔碳负载钼基纳米材料作为高性能析氢电催化剂文献综述
- Cu掺杂ZnxCd1-xS纳米晶的制备与性能研究开题报告
- 用于光伏的III-V族半导体低成本生长外文翻译资料
- 太阳能电池中的GaSb / InGaAs 量子点阱混合结构有源区外文翻译资料




