光伏器件保护玻璃的亲水与抗污性能研究毕业论文
2020-02-13 18:03:23
摘 要
能源是人类社会发展中不可或缺的物质基础,人类也从未停止过对能源的探索。近年来,新能源技术已逐渐成为全球各大发达国家与部分发展中国家科技的研究的重点。太阳能作为新型无污染的清洁能源,是新能源探索路上的重要课题。在过去几十年里,硅太阳能电池在生产成本降低和生产效率提升方面都取得了巨大的进步,光伏发电也已逐步融入主流能源结构。光伏器件的关键技术是光伏电池技术,而因光伏器件必须安装在户外太阳辐照时间长的地方,保护玻璃的清洗便成为了需要解决的问题。同时,安装在户外的玻璃器件也容易引起眩光危害。本文通过溶胶-凝胶法,制备了用于光伏器件保护玻璃的具有光致亲水性能的薄膜,使其具有更强的抗污能力。同时,本文还利用了化学蒙砂的原理,对玻璃基片进行了处理,提高了玻璃的雾度,使其具备了防眩性能,同时仍保有了较高的透射率。
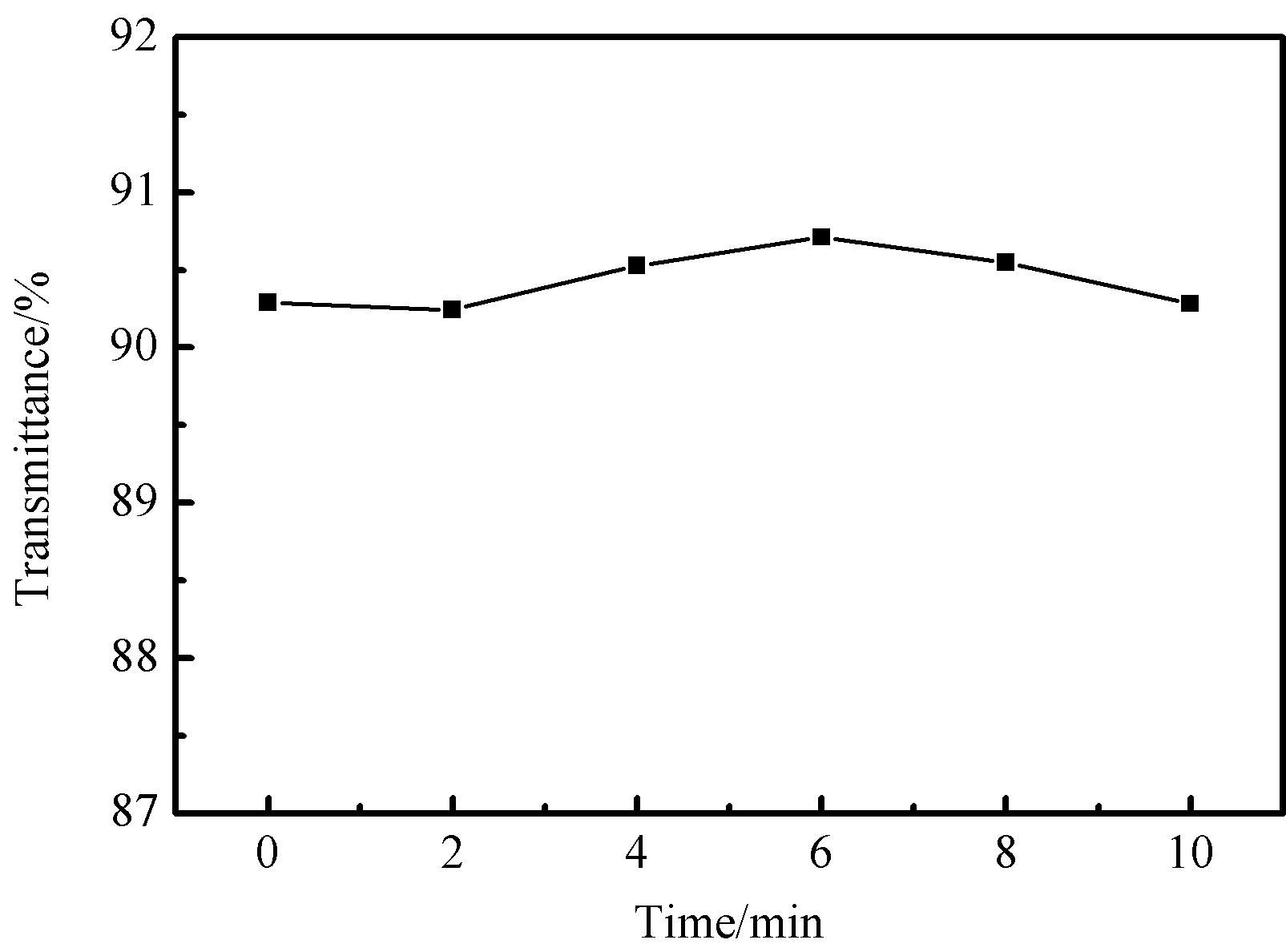
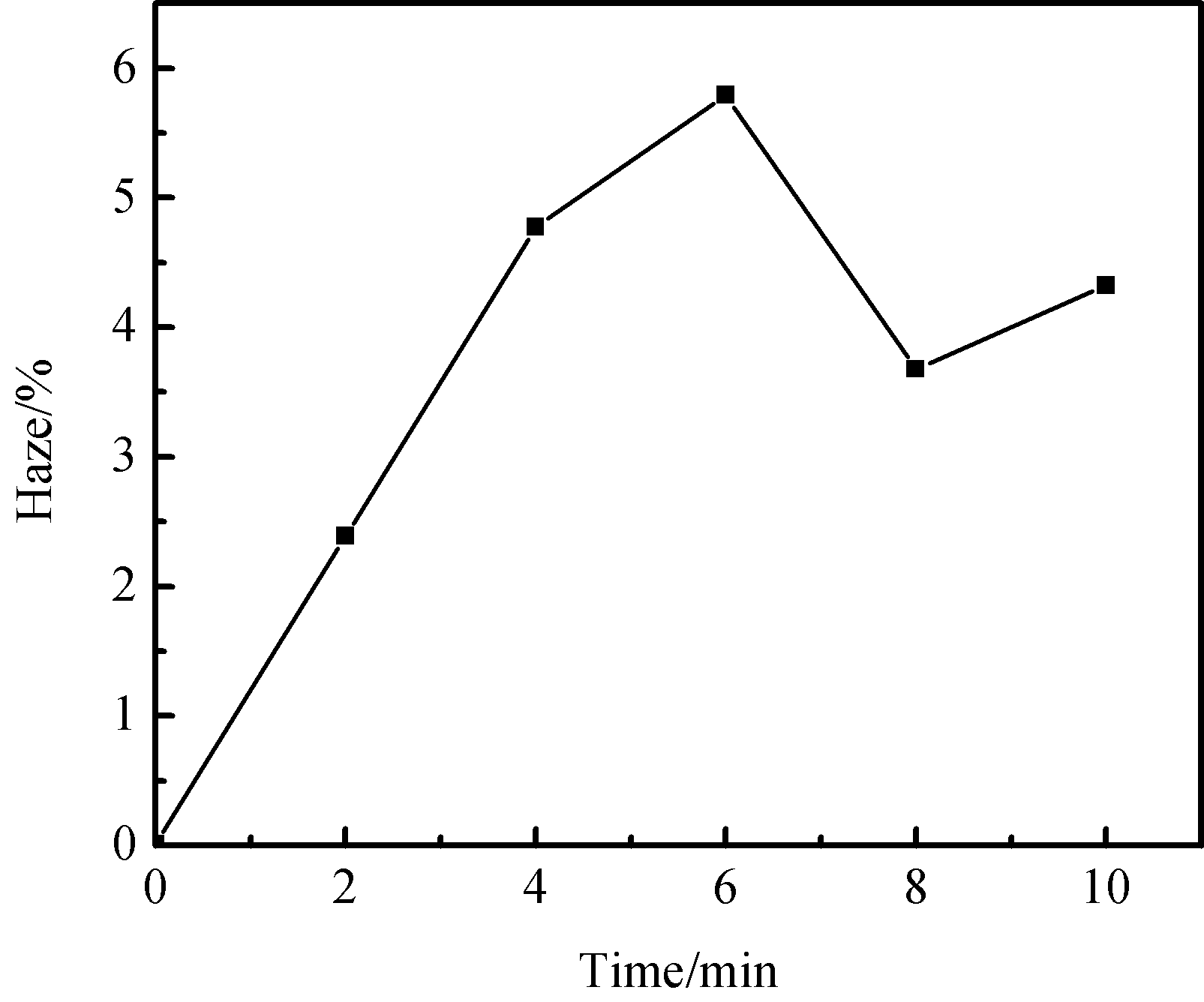
本文利用了化学蒙砂法的原理对玻璃基片进行了处理,选择使用NH4F、CaF2、H2SO4反应提供HF,通过加入K2SO4引入与氟硅酸根离子溶度积更小的K ,最后加入了促进剂诱导玻璃基片产生所需要的形貌。实验探究了反应时间对玻璃的可见光波段平均的总光通量以及雾度的影响,对不同反应时间玻璃表面形貌与成分进行了分析,探究了蒙砂液中K2SO4含量对玻璃的可见光平均总光通量以及雾度的影响。最后得出在本研究的反应条件下的最佳反应条件为蒙砂处理时间6min,蒙砂液中K2SO4wt%= 3wt%,此时玻璃基片的雾度最高,为5.79%,可见光波段的平均总光通量为90.71%,相较于玻璃原片提高约0.42%
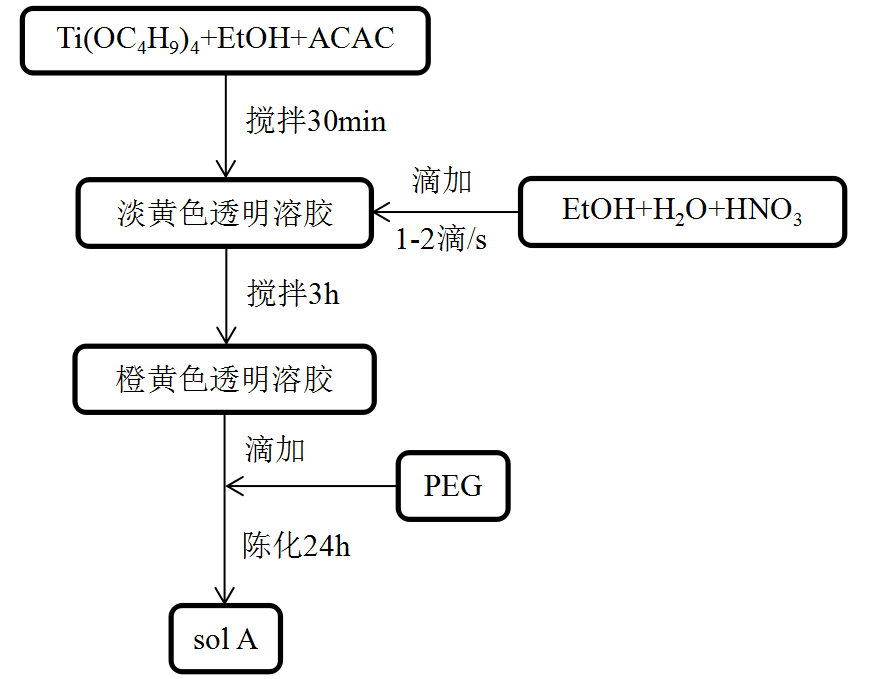
本文选择溶胶凝胶法配制TiO2溶胶,在配制过程中,我们选择以钛酸正四丁酯为前驱体,乙酰丙酮和硝酸为负催化剂,在乙醇溶剂中进行钛酸正四丁酯与水的反应,并通过在钛酸正四丁酯的醇溶液中加入模板剂聚乙二醇(PEG)来减小TiO2晶粒大小并诱导其成孔。实验设置中,我们改变TiO2溶胶中PEG的加入量以及最终溶胶中SiO2溶胶与TiO2溶胶的Si、Ti物质的量之比,探究了PEG加入量和SiO2溶胶加入量对薄膜的可见光波段平均透射率以及光致亲水性能的影响。当SiO2at%为20%时,在光照120min后的水接触角最小。当PEGwt%=2wt%,SiO2at%=20at%时,薄膜光致亲水性能最佳,光照120min后水接触角为5.4°。
最后,本文以实验中最佳的溶胶-凝胶制备方法,在防眩效果最好的玻璃表面进行镀膜,发现防眩效果依然存在,光致亲水性能较好,光照120min后水接触角为6.2°。
关键词:光伏玻璃;溶胶-凝胶法;光致亲水;化学蒙砂法;防眩玻璃
Abstract
Energy is an indispensable material basis for the development of human society. Humans have never stopped searching for energy. In recent years, new energy technology has gradually become the focus of the research for science and technology in developed countries and some developing countries. As an environmentally friendly clean energy, solar energy is an important subject on the road of new energy exploration. In the past few decades, great progress in reducing production costs and improving production efficiency has been made in silicon solar cells, and photovoltaic power generation has been gradually integrated into the mainstream energy structure. The key technology of photovoltaic devices is photovoltaic cell technology. However, the cleaning of protective glass has also become a problem to be solved because photovoltaic devices must be installed in outdoor places with long solar irradiation time. At the same time, the glass devices installed in the outdoor are easy to cause glare hazard. The photohydrophilic thin films for protecting glass of photovoltaic devices have been prepared by sol-gel method in this paper. With these thin films, the protecting glass can be equipped with stronger anti-fouling ability. Meanwhile, the method of chemical frosting is also used to treat the glass substrate, which improves the haze of the glass, and makes it possess anti-dazzle property, while still maintaining high transmittance.
In this paper, the principle of chemical frosting method was utilized to treat glass substrates. NH4F, CaF2 and H2SO4 were used to generate HF. By adding K2SO4, K was introduced which has smaller solubility product with fluosilicate ion. Finally, an accelerant was added to induce the desired morphology of glass substrates. The experiment has explored the influence of reaction time on the average total transmittance and haze in the visible band of the glass, and has analyzed the surface morphology and composition of the glass with different reaction time. And then the influence of K2SO4 content in the frothing solution on the average total transmittance and haze of the glass have been explored. Finally, it is concluded that the best reaction condition under the conditions of this study is the frothing treatment time for 6min, and K2SO4wt%= 3wt% in the frothing solution. At this time, the haze of glass substrate is the highest (5.79%), and the average total transmittance in the visible band is 90.71%, which is about 0.42% higher than that of blank glass substrate.
In this paper, TiO2 thin films was prepared by sol gel method. In the process of preparation, we choose tetrabutyl titanate as precursor, acetyl acetone and nitric acid as catalyst. The reaction of tetrabutyl titanate and water took place in ethanol solvent. And by adding PEG to the tetrabutyl titanate alcohol solution to reduce TiO2 grain size and induce its hole. In the experimental setting, we changed the amount of PEG added into TiO2 sol and the ratio of SiO2 sol in the final sol, and explored the influence of the amount of PEG added and the amount of SiO2 sol added on the average transmittance of visible band and photohydrophilic of the film. While SiO2at% is 20%, the water contact Angle is the minimum after 120min of illumination. When PEGwt%=2wt% and SiO2at%=20at%, the photohydrophilic properties of thin films were the best, and the water contact Angle was 5.4° after 120min of irradiation.
Finally, in this paper, the best sol-gel preparation method in the experiment was applied to coating the glass surface with the best anti-glare effect. It was found that the anti-glare effect still existed, and the photohydrophilic was good with the water contact Angle 6.2° after 120min of illumination.
Key Words:Photovoltaic glass; Sol-gel; pohtohydrophilic; Chemical frosting; Anti-glare glass
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2玻璃表面的亲水与抗污改性 2
1.2.1固体表面的亲水性能 2
1.2.2TiO2薄膜的光致亲水性能 3
1.2.3玻璃表面镀膜对玻璃透射率的影响 4
1.2.4玻璃亲水薄膜的制备方法 5
1.3玻璃防眩改性 7
1.3.1眩光 7
1.3.2防眩玻璃及雾度 7
1.3.3化学蒙砂法制备防眩玻璃的原理 7
1.4表面粗糙度对玻璃亲水性的影响 8
1.5本研究的意义与内容 8
第2章 实验设计与性能表征 10
2.1实验试剂与仪器 10
2.2实验仪器 10
2.3防眩玻璃基片的制备 11
2.4防眩玻璃的表面结构与性能的表征 12
2.4.1紫外-可见分光光度计(UV) 12
2.4.2电子探针(EPMA) 12
2.4.3X射线衍射(XRD) 12
2.5亲水抗污薄膜的制备 13
2.5.1TiO2溶胶的配制 13
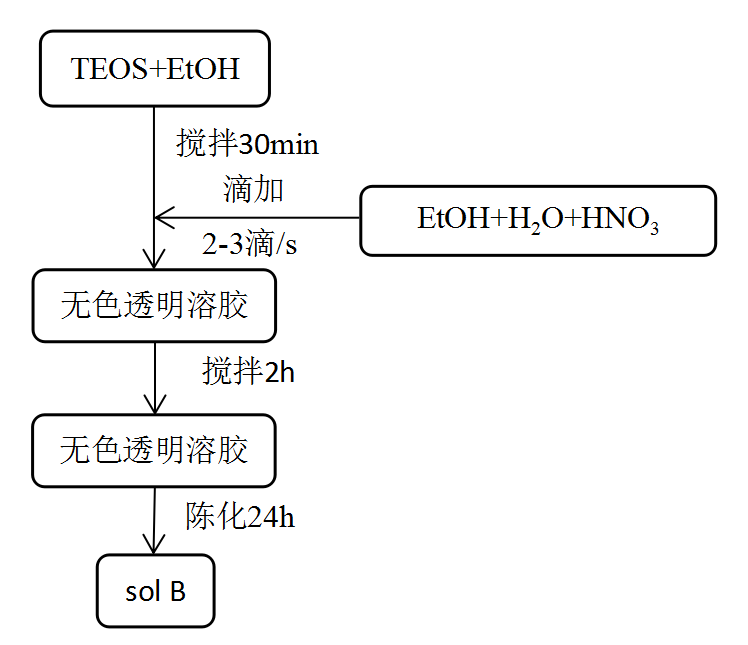
2.5.2 TiO2/SiO2溶胶的配制 14
2.5.3提拉法镀膜以及热处理 14
2.6亲水薄膜的组成结构与性能的表征 15
2.6.1紫外-可见光透射率分析 15
2.6.2光致亲水性能 15
2.6.3防雾性能 15
2.7在玻璃基片蒙砂面上镀膜 15
第3章 化学蒙砂法处理玻璃基片的结果与分析 16
3.1蒙砂时间对玻璃基片的影响 16
3.1.1可见光透射率与雾度 16
3.1.2表面形貌与微区分析 19
3.1.3X射线衍射 20
3.2蒙砂液中K2SO4含量对玻璃基片的影响 20
3.2.1可见光透射率与雾度 20
3.3本章小结 22
第4章 溶胶凝胶制备亲水抗污薄膜的结论与分析 24
4.1PEG加入量对亲水抗污薄膜的影响 24
4.1.1可见光透射率 24
4.1.2表面亲水性 25
4.2SiO2溶胶的加入量对自清洁薄膜的影响 26
4.2.1可见光透射率 26
4.2.2表面亲水性 27
4.3本章小结 29
第5章 在蒙砂玻璃基片上镀亲水薄膜 30
5.1可见光透射率与雾度 30
5.2表面亲水性 30
5.3本章小结 31
第6章 结论与展望 32
6.1 结论 32
6.2展望 32
参考文献 34
致 谢 37
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
能源是人类社会发展过程中不可或缺的物质基础,而由于能源匮乏,我们不断寻找着如太阳能、风能、生物质能等的新型能源以替代化石能源。同时,我国已进入能源革命的战略机遇期,能源规划与发展是我国“第十三个五年计划”期间的重点[1]。太阳能作为一种可再生的清洁能源,广泛推广使用更是可以缓解由于过量化石燃料燃烧,而导致的全球变暖问题。太阳能,即是太阳光辐射的能量。太阳能的利用形式主要分为三种:太阳能光热转化、光化学转化与光电(光伏)转化。过去几十年,硅太阳能电池在生产成本降低和生产效率提升方面都取得了巨大的进步,光伏发电也已逐步融入主流能源结构。在全球部分地区,太阳能并网发电的成本已可以和化石燃料燃烧发电相竞争[2]。目前光伏组件技术中,最关键的技术是硅太阳能电池技术,其次为保护光伏电池的光伏玻璃技术。而目前,硅太阳能电池技术发展已日趋成熟,光伏玻璃技术仍具有较大的发展空间。研究表明,就目前研究进展而论,每当光伏组件效率提高1%,则其发电成本将相当于下降7%[3]。这是一个相当可观的数据,也是光伏组件走向市场化生产时,生产者们越来越关注光伏器件保护玻璃的重要原因。
太阳能电池板通过吸收太阳光中的能量,使其中半导体材料的价带电子跨越禁带进入导带,同时在价带产生空穴的方式,形成载流子电子-空穴,再利用材料的p-n结结构产生电流。所以,对于光伏玻璃,其最重要的功能之一就是使尽可能多的太阳光能够被太阳能电池板利用。空气环境中存在灰尘和油污染物,很容易在玻璃上覆盖,遮挡阳光,影响阳光辐照穿透光伏器件的保护玻璃,减少发电量。因为当入射光照射到保护玻璃表面的灰尘及其他污物时,部分能量会被污物吸收,还有一部分能量会被散射向四周,而被散射的能量中最终只有一部分能再次照射到保护玻璃上,如图1-1所示。
图1-1 光伏器件表面被灰尘覆盖时太阳光照射示意图
M.C.Alonson等人做了灰尘对光伏电池板发电影响的实验,理论计算得出,当电池板被灰尘遮盖50%时,电池板发电效率将损失19%;当电池板全部被灰尘遮盖时,功率损失率将达到79%。张利等人在50W多晶硅光伏电池表面做的灰尘实验则表明,当电池板被遮盖一半以上时,电池的开路电压与短路电流都将降低至洁净表面的3%,输出功率更仅为洁净表面的0.1%[4]。而定期人工清洗维护在人员调度成本以及清洗设备与耗材方面都存在较大消耗,甚至在自然环境恶劣的地区,人工清洗还存在安全隐患。因此,做好光伏器件保护玻璃表面的改性,使其具备一定抗污性能,对于安装在室外,利用太阳光进行发电的光伏器件来说是有意义且有必要的。图1-2为清洁前后光伏器件表面对比实物图,左为清洗前,右为清洗后,可以看出清洗前光伏器件表面被遮盖现象非常严重,阻挡了大量本会照射到电池板上的太阳辐射。

以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 激光作用下ZrNiSn合金热电材料组成、结构和性能的演化规律开题报告
- 原位生长于碳纤维表面的钒氧化物柔性电极制备开题报告
- 锂硫电池用TixOy-S/HGs复合材料的制备与性能开题报告
- MnO2纳米片修饰ZnO纳米棒阵列的气敏性能研究开题报告
- 基于三维碳基孔结构和电解质协同优化的微型超级电容器文献综述
- 基于C-MEMS工艺的微型混合锂离子电容器构筑及性能开题报告
- 多孔碳负载钼基纳米材料作为高性能析氢电催化剂文献综述
- Cu掺杂ZnxCd1-xS纳米晶的制备与性能研究开题报告
- 用于光伏的III-V族半导体低成本生长外文翻译资料
- 太阳能电池中的GaSb / InGaAs 量子点阱混合结构有源区外文翻译资料




