纤维素水凝胶的制备及在锌离子电池中的应用研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 17:42:03
摘 要
当代科技急速发展,同时人类对能源的需求也急剧增加,但化石燃料已经无法维持人类对能源的需求,且化石燃料的燃烧会带来大量污染,人们必须寻找更加清洁高效的能源。
目前主要研究的方向是可再生能源,如太阳能,风能,潮汐能等等,但这些能源缺点也很明显,受到天气,时间的影响巨大,所以我们需要寻找储能装置来将此类能源储存起来,供需要的时候使用。现在市场上售卖最多的就是锂离子电池,但人们越来越关注锂资源有限、成本过高和安全性不佳等问题。寻找成本低,可靠性高的电池成了关键问题,在这种情况下,可以二次充电的水系锌离子电池出现在研究人员手中,实现了科研人员对环保且安全的电池的需求。
锌离子电池自发明以来,以其成本低、资源充足、制备方便等独特的特点而受到人们的广泛关注。特别是许多研究人员已经将经典的碱性锌锰电池转移到高度可逆的体系中,但锌电池很难做成二次电池,因为锌电池反复充放电极易影响电池寿命和稳定性。
因此人们开始寻找一种固体电解质来使用在锌离子电池中,水凝胶作为一种含可调水量的亲水聚合物网络,在电化学存储领域引起了广泛的关注。这可以归因于水凝胶中截留的水可以溶解和传导离子,为设计储能装置的独特聚电解质提供了巨大的机会。
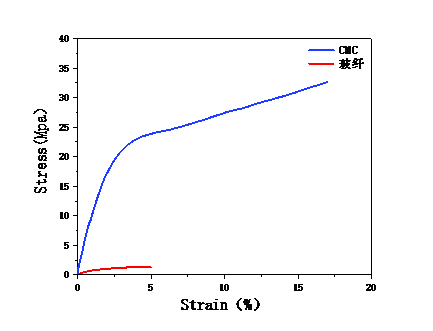
本文使用羧甲基纤维素制得的凝胶聚合物,只需要简单的浇铸就可以制得凝胶膜,对膜进行表面形貌的观测和吸液率等的计算,以及电导率的测试,证实该膜具有良好的电化学性能,而拉伸强度测试则证明该膜具有优良的机械性能,可以有效防止锌离子电池充放电过程中产生的枝晶破坏膜结构造成短路。
关键词:锌离子电池 羧甲基纤维素 凝胶电解质
Abstract
Contemporary science and technology are developing quickly, and the human demand for energy are increasing rapidly, but fossil fuels have been unable to provide human demand for energy, and the combustion of fossil fuels will bring a lot of pollution, people must find cleaner and more efficient energy.
At present, the main research direction is renewable energy, such as solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy and so on, but these energy shortcomings are also obvious, which are greatly affected by weather and time. It is important for us to find energy storage devices to store these kind of energy for use when needed. At present, the most popular is lithium-ion batteries, which have the advantages of high energy density, high output voltage, low self-discharge, long cycle life and environment friendliness. Although the current high energy density lithium-ion batteries have occupied the commercial rechargeable battery market, more and more attention has been paid to the problems of limited lithium resources, high cost and unsafe, and the regulation of organic electrolytes. The degree of modelling limits their further development. It is a key issue to find low cost and high reliability batteries. Rechargeable zinc-water ion batteries not only pave the way for environmentally friendly and safe energy storage, but also reduce the manufacturing cost of next generation batteries.
Since its invention, zinc ion batteries have attracted wide attention because of their unique characteristics such as low cost, sufficient resources and convenient preparation. Particularly, many researchers have transferred the classical alkaline zinc-manganese batteries to highly reversible systems. However, zinc batteries are difficult to make secondary batteries because repeated charging and discharging of zinc batteries can easily affect the life and stability of batteries .
Therefore, people began to search for a solid electrolyte to be used in zinc ion batteries. Hydrogel, as a hydrophilic polymer network with adjustable water content, has attracted wide attention in the field of electrochemical storage [7-12]. This can be attributed to the fact that the water intercepted in the hydrogel can dissolve and transmit ions, which provides a great opportunity for designing unique polyelectrolytes for energy storage devices.
In this paper, the gel polymer made by carboxymethyl cellulose can be prepared by simply casting. The gel film can be obtained. The surface morphology of the film and the calculation of the liquid absorption rate and conductivity test show that the film has good electrochemical performance. The tensile strength test shows that the film has excellent mechanical properties and can effectively prevent zinc ion battery from charging.
Keywords: zinc ion battery carboxymethyl cellulose gel electrolyte
目录
摘要 3
Abstract 4
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 锌离子电池简介 1
1.2.1 锌离子电池发展概况 1
1.2.2 锌离子电池工作原理 3
1.2.3 锌离子电池正极 3
1.2.4 锌离子电池负极 4
1.2.5锌离子电池电解质 4
1.3 凝胶电解质简介 4
1.3.1 凝胶电解质发展概况 4
1.3.2 纤维素水凝胶 5
1.3.3 凝胶电解质的制备方法 5
1.4 本文的研究目的和内容 6
1.4.1 研究目的 6
1.4.2 研究内容 6
第二章 实验材料与研究方法 7
2.1 实验试剂 7
2.2 实验仪器 8
2.3 材料物理性能表征 8
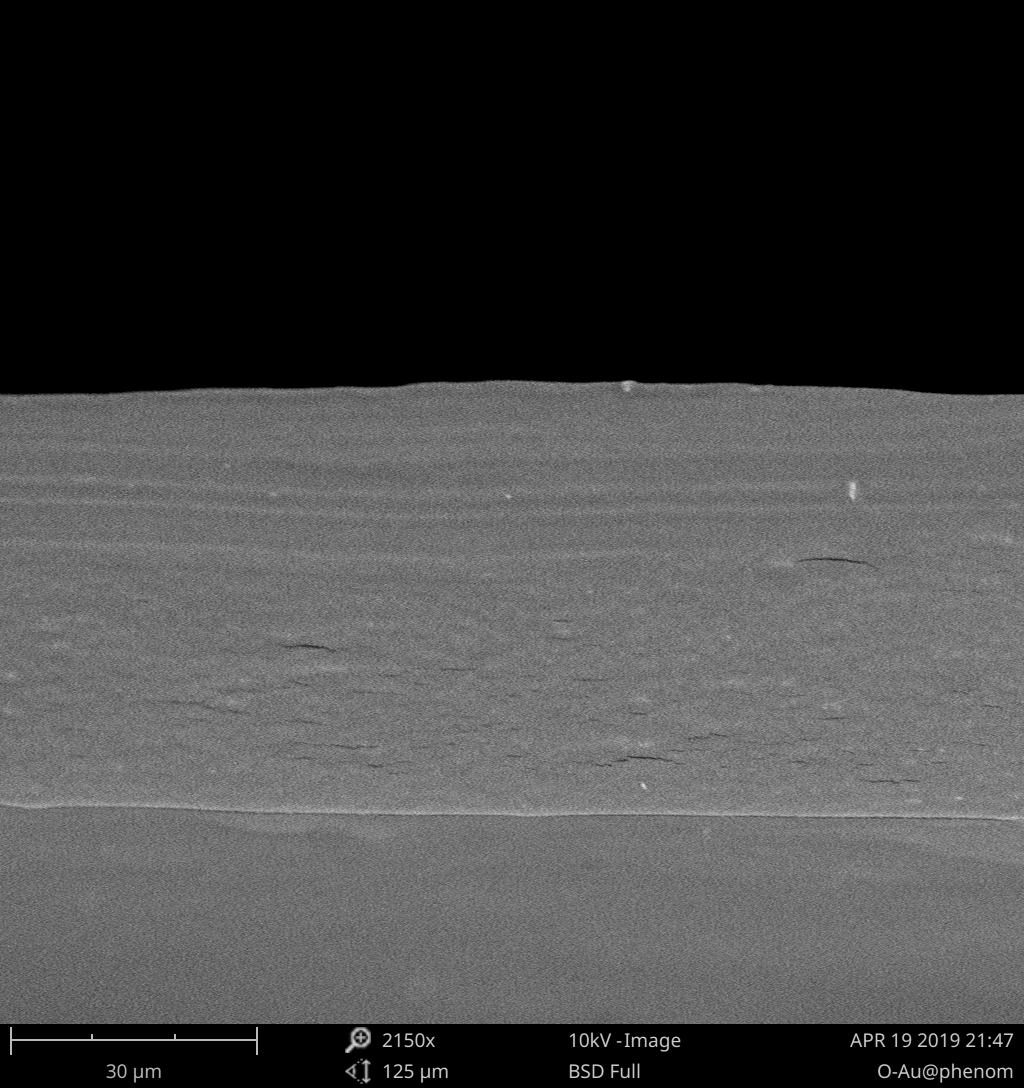
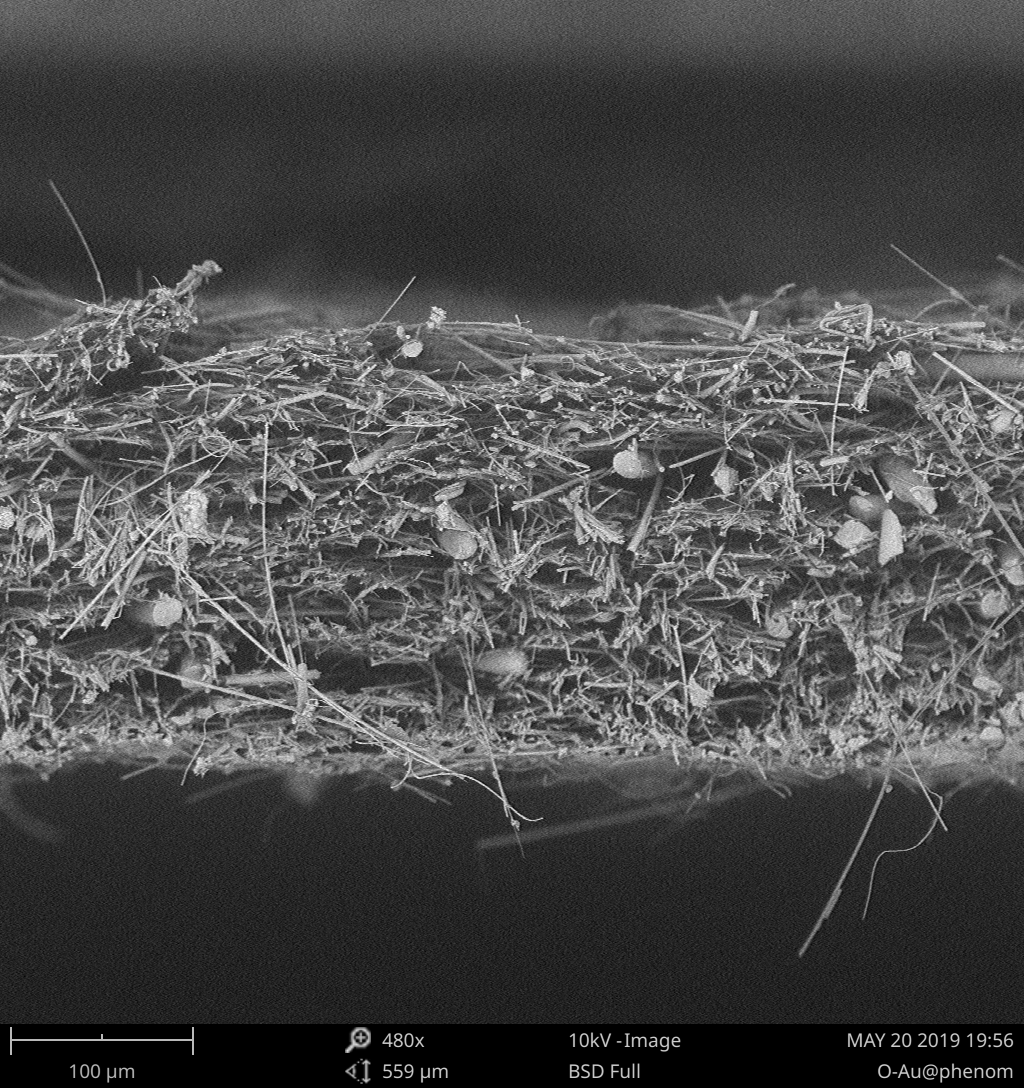
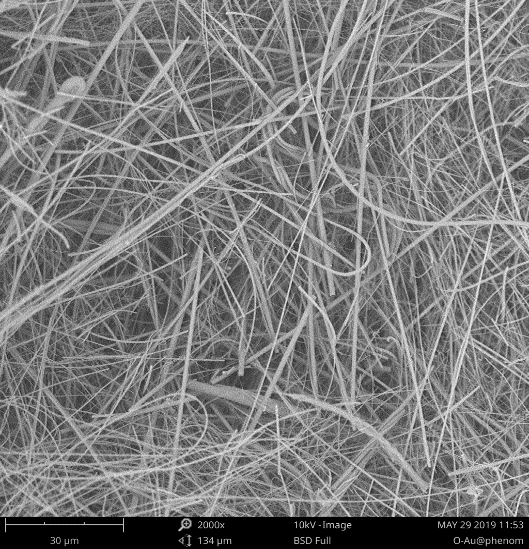
2.3.1 形貌表征 8
2.3.2 吸液率与孔隙率表征 9
2.3.3 力学性能表征 9
2.3.4 热稳定性表征 9
2.4 电化学性能测试 10
2.4.1 离子电导率测试 10
2.4.2 电化学窗口测试 10
2.4.3 锌离子迁移数测试 10
2.4.4 循环伏安测试 11
2.4.5 恒电流充放电测试 11
第三章 羧甲基纤维素水凝胶 12
3.1 羧甲基纤维素水凝胶的制备 12
3.2 物理性能 13
3.2.3力学性能 14
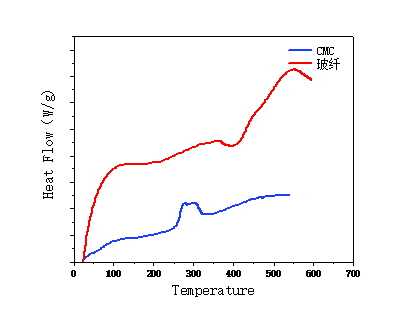
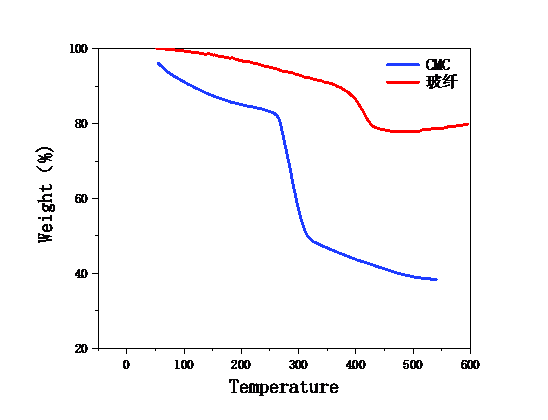
3.2.4 热稳定性 15
3.3 电化学性能 15
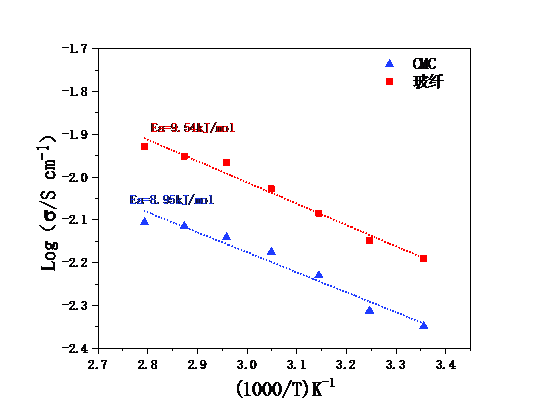
3.3.1 离子电导率 15
3.3.2 电化学窗口 17
3.3.3 锌离子迁移数测试 17
3.3.4 循环伏安曲线 18
3.3.5 恒电流充放电曲线 19
3.4 抑制锌沉积的能力 21
第四章 结论与展望 22
4.1 结论 22
4.2 展望 22
参考文献 23
致谢 26
绪论
引言
如今的人类对能源的需求量迅速增加,可是主要的化石能源本身却在不断减少,人们的目光开始投向了天空和海洋。风能和潮汐能作为较易获得的可再生能源得到了人类的青睐,但此类能源需要大容量的储能设备来进行存储以便后期使用,因此储能设备的发展需求也得到了各国的重视。目前主要的商用储能设备为锂离子电池,但是锂资源有限,锂离子电池成本过高且安全性较低等问题大大阻碍了锂离子电池的发展。而人类社会有大量日常使用的或可穿戴设备使用的是锂离子电池,所以现在急需发展一种成本更低,安全性更高的电池,而锌离子电池正好满足了这一要求。
可充电水系锌离子电池采用的水系电解液,相比较与锂离子电池的有机电解液具有无毒无害,安全性高,成本低等优点,且水系电解液的离子电导率比有机系电解液高两个数量级,所以水系电池的功率密度更高[1],且能降低制作成本。除此之外,锌离子电池还可以制成超薄的可弯曲电池,为可穿戴电子设备的发展做好了铺垫。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:



您可能感兴趣的文章
- 激光作用下ZrNiSn合金热电材料组成、结构和性能的演化规律开题报告
- 原位生长于碳纤维表面的钒氧化物柔性电极制备开题报告
- 锂硫电池用TixOy-S/HGs复合材料的制备与性能开题报告
- MnO2纳米片修饰ZnO纳米棒阵列的气敏性能研究开题报告
- 基于三维碳基孔结构和电解质协同优化的微型超级电容器文献综述
- 基于C-MEMS工艺的微型混合锂离子电容器构筑及性能开题报告
- 多孔碳负载钼基纳米材料作为高性能析氢电催化剂文献综述
- Cu掺杂ZnxCd1-xS纳米晶的制备与性能研究开题报告
- 用于光伏的III-V族半导体低成本生长外文翻译资料
- 太阳能电池中的GaSb / InGaAs 量子点阱混合结构有源区外文翻译资料




