基于铁电薄膜的负微分电容行为研究毕业论文
2020-07-11 18:09:04
摘 要
我们知道薄膜的生长与温度这一条件的关系密切,温度的高低,影响着薄膜生长的择优取向与结晶程度,所以本文中在实验中着重分析了温度这一因素在氧化铪薄膜的制备过程中究竟有哪些影响。另外,除了温度这一宏观调控之外,我们还从微观的角度出发,在薄膜材料中掺杂少数的铝元素,探究其对薄膜材料的负电容效应的的影响。
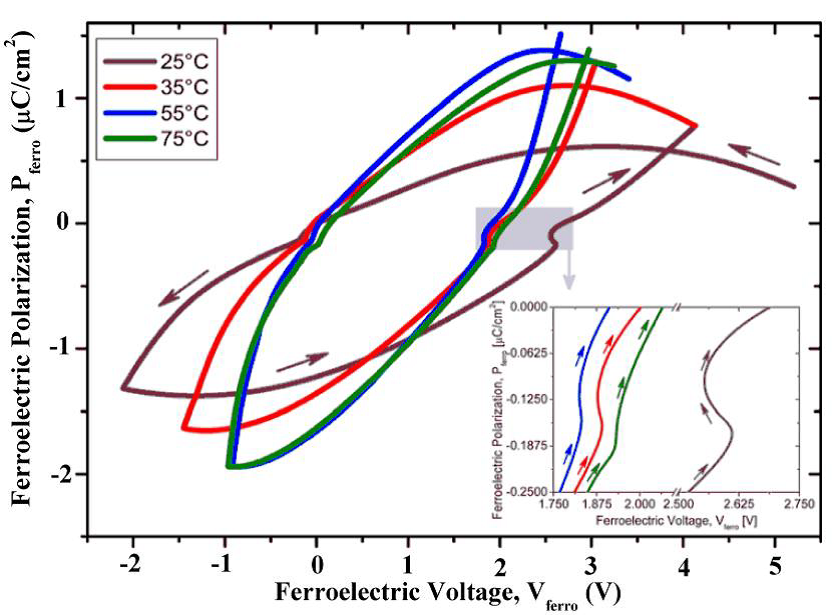
由于铁电薄膜材料的负电容效应受到温度直接影响,所以我们对于一定厚度的铁电薄膜的集体管,选取多个温度进行调控,直至选出一个最佳的。最终我们发现,一旦温度达到最佳后,负电容效应处于最明显的状态,而当温度继续变化时,负电容效应便会开始减弱直至消失。可见,这一发现,对不同温度下的铁电场效应晶体管的设计提供了重要的理论基础。
关键词:铁电体;铁电薄膜;二氧化铪;负电容效应;高K材料
Abstract
We know that the growth of the thin film is closely related to the temperature, and the temperature level affects the preferred orientation and crystallinity of the thin film growth. Therefore, in this paper, the temperature was analyzed during the preparation of the yttrium oxide thin film. What are the effects? In addition, in addition to the macroscopic control of temperature, we also proceed from the microscopic point of view, doping a small amount of aluminum in the thin film material, and exploring its influence on the negative capacitance effect of the thin film material.
Since the negative capacitance effect of the ferroelectric thin film material is directly affected by temperature, we select a plurality of temperatures for the collective tube of a certain thickness of the ferroelectric thin film until an optimal one is selected. Finally, we found that once the temperature is optimal, the negative capacitance effect is in the most obvious state, and when the temperature continues to change, the negative capacitance effect starts to weaken until it disappears. It can be seen that this discovery provides an important theoretical basis for the design of ferroelectric field effect transistors at different temperatures.
Keywords: ferroelectrics; ferroelectric thin films; hafnium dioxide; negative capacitance effect; high-K materials
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1铁电体 1
1.1.1铁电体及其分类 1
1.1.2 铁电体的特征 2
1.1.3铁电体的研究历史及其现状 4
1.2 铁电薄膜材料 5
1.2.1铁电薄膜材料及其制备 5
1.2.2铁电薄膜材料的应用 6
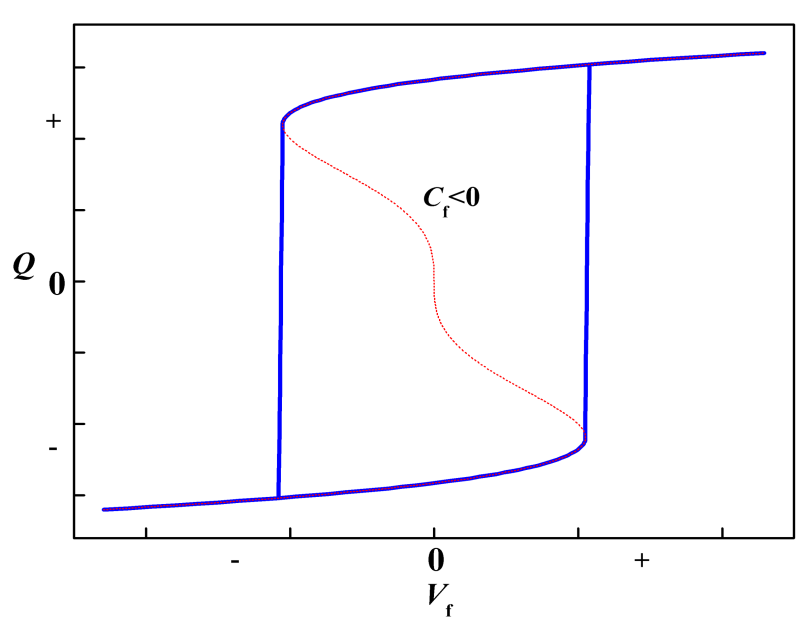
1.3铁电薄膜的负电容效应及其研究现状 6
1.4本篇论文涉及的主要内容及研究意义 8
1.4.1主要内容 8
1.4.2 重要意义 9
第2章 实验 10
2.1制备薄膜样品 10
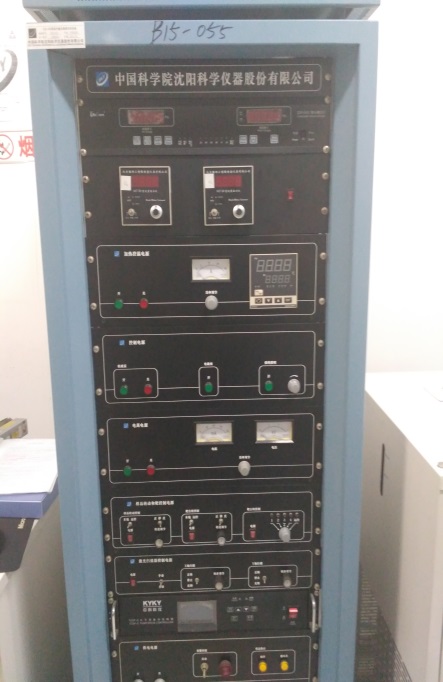
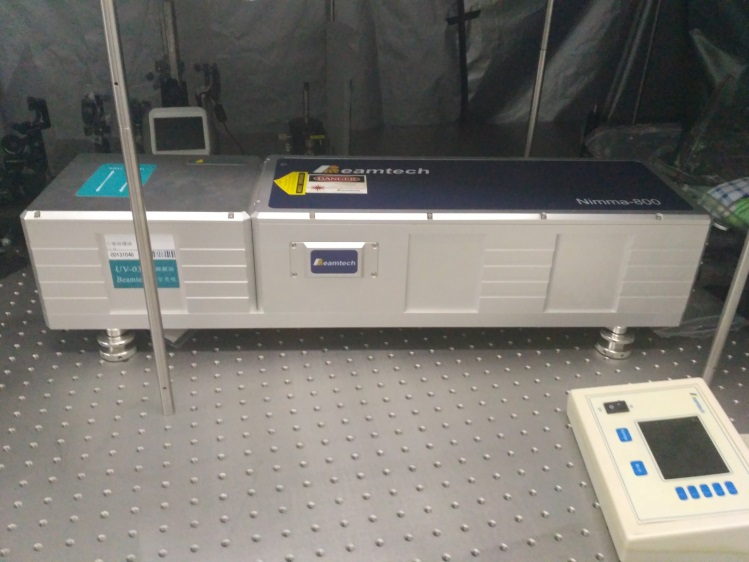
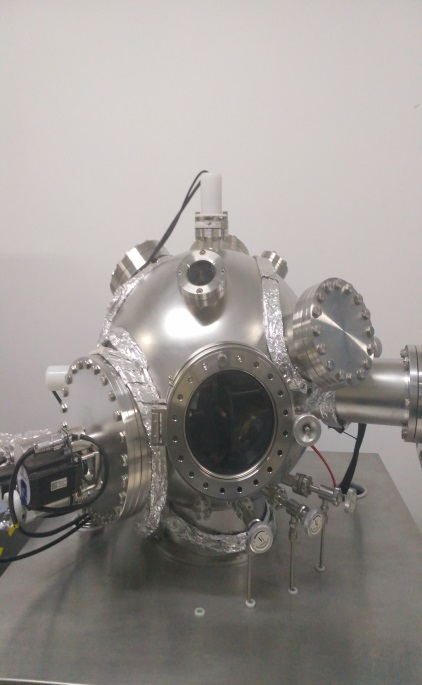
2.1.1 PLD-450型脉冲激光溅射沉积系统(型号:PLD45BA02) 10
2.1.2 靶材 11
2.1.3 基片 12
2.1.4 实验步骤 12
2.2 XRD测试表征 14
2.2.1 XRD衍射仪 14
2.2.2 X射线 15
2.2.3 实验步骤 16
2.3 真空蒸镀法蒸镀电极 17
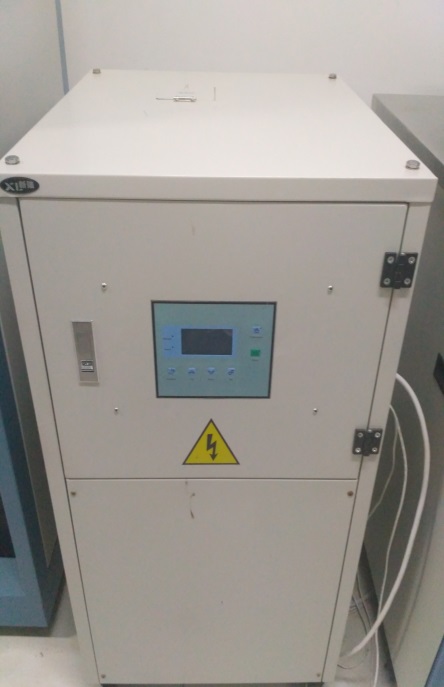
2.3.1 DMDE-450光学多层镀膜机 17
2.3.2 蒸镀法 18
2.3.3 实验步骤 18
2.4 C-V测试 20
第3章 氧化铪薄膜的XRD分析 21
3.1 引言 21
3.2 温度对氧化铪薄膜的制备的影响 22
3.2.1 硅基片上的氧化铪薄膜 22
3.2.2 二氧化硅上面的二氧化铪薄膜 23
3.2.3 结论总结 27
3.3 不同掺杂比下的氧化铪薄膜 27
第4章 氧化铪薄膜的C-V曲线 29
第5章 总结amp;展望 31
5.1 总结 31
5.2展望 31
参考文献 32
致谢 34
第1章 绪论
1.1铁电体
1.1.1铁电体及其分类
,是能够自发极化的介电晶体,而在32个晶体学点群中,有可能具有自发极化的,有可能存在铁电体的,只存在于1()、2()、m()、mm2()、3()、3m()、4()、4mm()、6()、6mm()的晶体中。因为只有这10个具有特殊极性方向。如下图1.1所示,不同电介质材料在32个晶体学点群中以及与铁电体的。
图 1.1
目前一般认为,有关铁电体的研究与探索开始于1920年,是由法国学者Valasek第一次在罗息盐中发现其具有铁电电滞回线,从而引出了“铁电性”这一概念,从而具有这种铁电性的晶体则被称为铁电体。紧随其后,人们开始逐渐发现更多的“铁电体”材料,如钛酸钡陶瓷、酸二氢钾晶体等。随着后来人们发现越来越多的“铁电体”,开始对其进行分类。一般铁电体被分为五大种,分别是含氧、含氟、含氢键、含其他离子的、还有就是铁电液晶等聚合物。其中,又根据晶体结构的空间排列方式不同将含氧八面体的铁电体分成:①钨青铜型铁电体,其通式为,例如等;②铌酸锂型铁电体,其中典型的有、、等;③铋层状钙钛矿结构铁电体,其中有及其掺杂系列等;④钙钛矿型铁电体,这一类型的所占数量最多,而其通式为,例如。
1.1.2 铁电体的特征
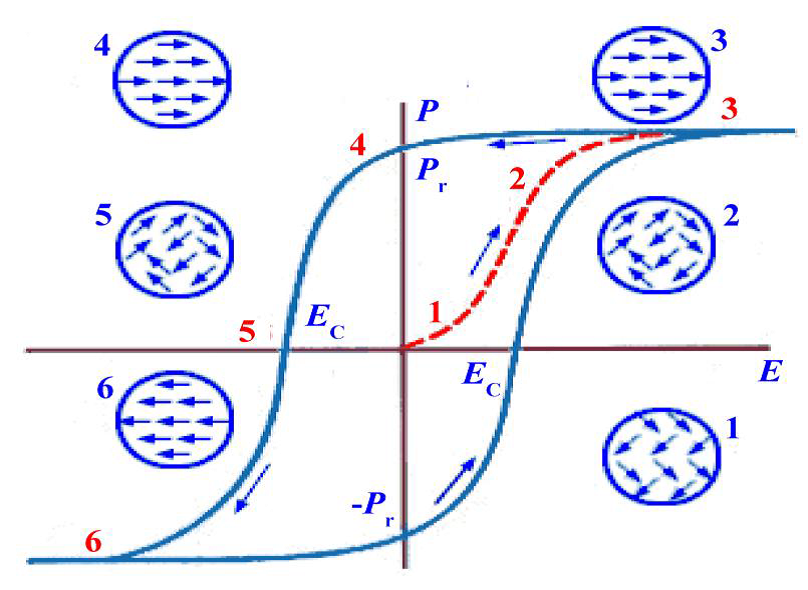
图 1.2
相关图片展示: