基于深度学习的无线网络资源分配研究毕业论文
2020-04-12 16:18:45
摘 要
随着移动通信技术和智能终端技术的增强,移动多媒体业务和应用将有更加广阔的市场应用前景。新型移动多媒体业务不仅对数据传输速率有较高的要求,对于无线网络和移动终端的计算、存储能力也提出了新的要求。移动边缘缓存和计算技术通过在无线接入网侧部署小型数据中心或服务器,使无线接入网融合了缓存、计算和通信三大功能,由于其存储和计算能力相对有限,随着计算密集的移动多媒体应用规模的不断扩大,大量移动终端和应用将会对边缘结点有限的缓存、计算和通信资源产生激烈的竞争,其资源的有效性将会限制良好的用户体验。因此,为了解决上述问题,本文的具体研究内容如下:
本文立足存储、计算和通信融合的无线网络场景,面向动态自适应视频流媒体的传输,以缓存、计算和通信三大资源的协同利用为主题,结合深度学习相关算法,从计算虚拟网络运营商的综合收益角度建模,在信道状态、缓存容量和计算能力随时间变化的情况下,展开资源分配方面的研究并提出解决方案。该问题是典型的NP-hard问题,不存在多项式时间复杂度的算法可以求得其最优解,并且由于该问题涉及的自变量种类多,规模大,相互耦合,基于传统的方法难以得到该问题的解。因此,本文拟引入深度Q学习的求解思路,将运营商建模为一个Agent。拟将边缘节点、基站、用户以及传输链路等的状态,以及用户请求作为环境信息,将基站响应用户请求的方式作为动作,将运营商响应用户请求后获得的综合收益作为回报。Agent在与环境相互作用的过程中,通过采取动作,观察环境变化,获得反馈,从而不断改进它以后的行为,使长期积累的奖励最大化。随着迭代次数的不断增加,可以获得最优的策略。最后通过搭建仿真平台,验证了所提出的方案的有效性,具有良好的优化效果。
关键词:深度学习;资源分配;移动多媒体业务;移动边缘计算
Abstract
With the enhancement of mobile communication technologies and intelligent terminal technologies, mobile multimedia services and applications will have broader market application prospects. The new type of mobile multimedia services not only has high requirements for data transmission rate, but also puts forward new requirements for the calculation and storage capabilities of wireless networks and mobile terminals. Mobile edge caching and computing enables small-scale data centers or servers to be deployed on the radio access network side. This enables the wireless access network to integrate three functions: caching, computing, and communications. Because of its relatively limited storage and computing capabilities, it is computationally intensive. With the continuous expansion of the scale of mobile multimedia applications, a large number of mobile terminals and applications will have fierce competition for limited cache, computing and communication resources of edge nodes, and the effectiveness of their resources will limit the good user experience. Therefore, in order to solve the above problems, the specific research content of this paper is as follows:
This paper is based on the wireless network scenario of storage, computing, and communication convergence. It is oriented to the transmission of dynamic adaptive video streaming media. The theme of the three major resources of caching, computing, and communications is combined, and the deep learning related algorithms are combined to calculate virtual network operators. The comprehensive revenue perspective modeling, in the case of channel status, cache capacity, and computing power changes over time, expands resource allocation research and proposes solutions. This problem is a typical NP-hard problem. The algorithm with no polynomial time complexity can obtain the optimal solution. Because the problem involves many kinds of variables, large scale and mutual coupling, it is difficult to obtain the traditional method based on the traditional method. Solution to the problem. Therefore, this paper intends to introduce the solution of deep Q learning, and model the operator as an Agent. It is proposed that the status of edge nodes, base stations, users, and transmission links, and user requests be regarded as environmental information, and the manner in which the base station responds to user requests behaves as an action, and returns the comprehensive income obtained by the operator in response to the user request. Agent interacts with the environment by taking actions, observing changes in the environment, and gaining feedback, thereby continuously improving its subsequent behavior and maximizing long-term accumulation of rewards. As the number of iterations continues to increase, an optimal strategy can be obtained. Finally, the simulation platform is built to verify the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and has a good optimization effect.
Keywords: deep learning; resource allocation; wireless networks; mobile edge caching and computing
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究的背景、目的和意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 2
1.3 本文组织结构 4
第2章 相关原理和技术介绍 5
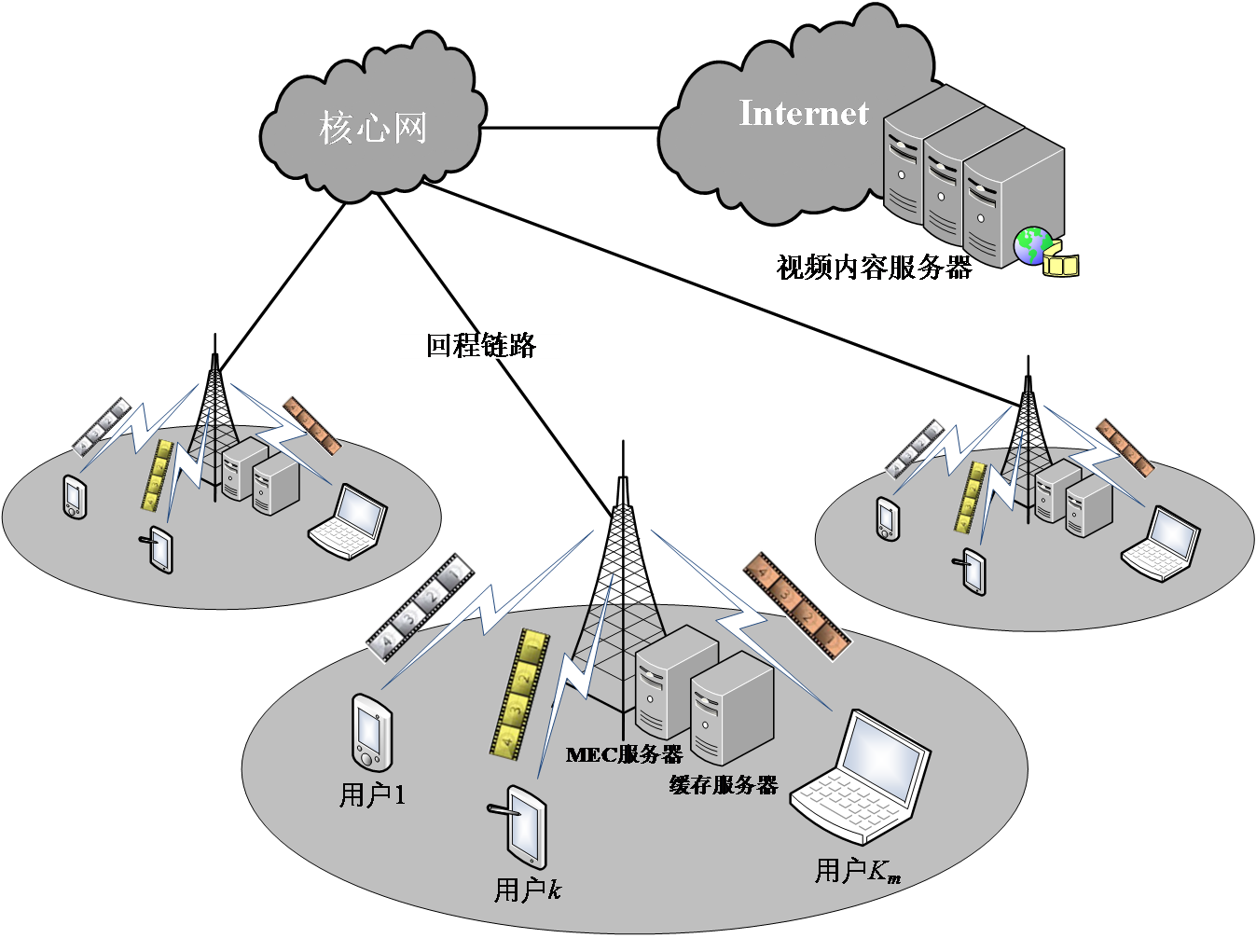
2.1 移动边缘计算和缓存 5
2.1.1 特点与关键技术 5
2.1.2 平台架构 7
2.1.3 应用场景 8
2.2 机器学习相关算法 10
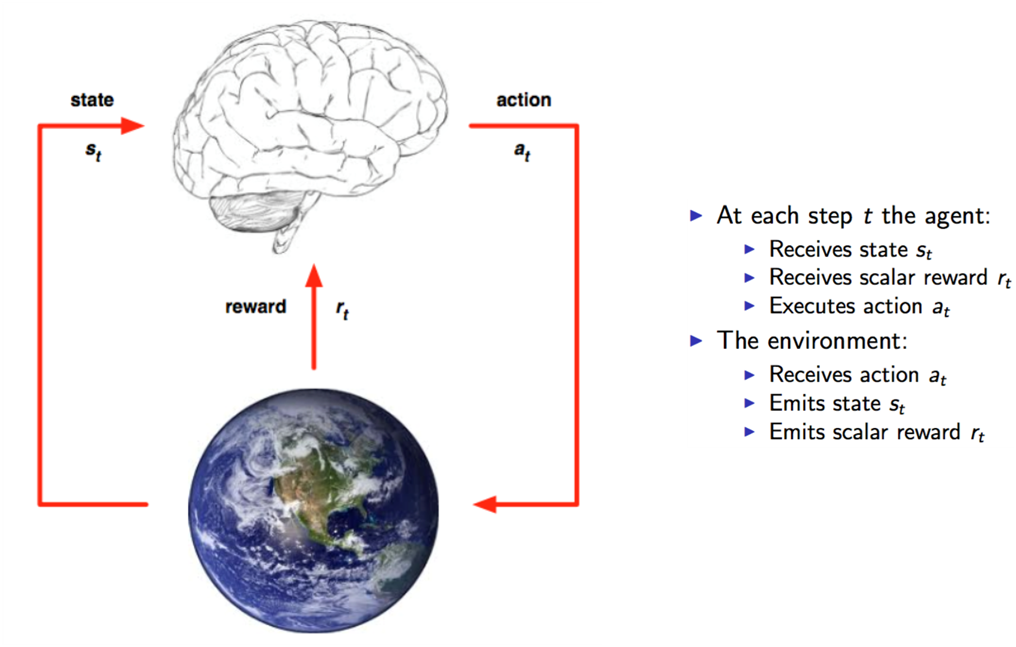
2.2.1 强化学习 11
2.2.2 Q学习 12
2.2.3 深度Q学习 13
2.3 本章小结 14
第3章 基于深度Q学习的资源分配方案设计与仿真 16
3.1 系统模型 16
3.2 问题建模 17
3.2.1 通信建模 17
3.2.2 计算建模 17
3.2.3 缓存建模 18
3.3 算法设计 19
3.3.1 状态空间 20
3.3.2 动作空间 20
3.3.3 回报函数 21
3.4 算法仿真 22
3.4.1 参数设置 22
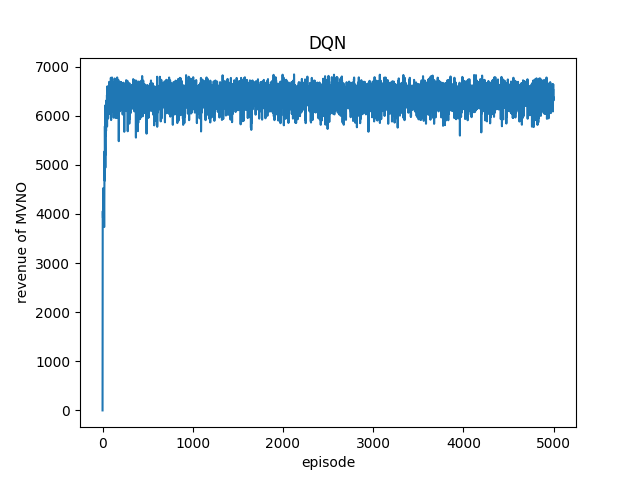
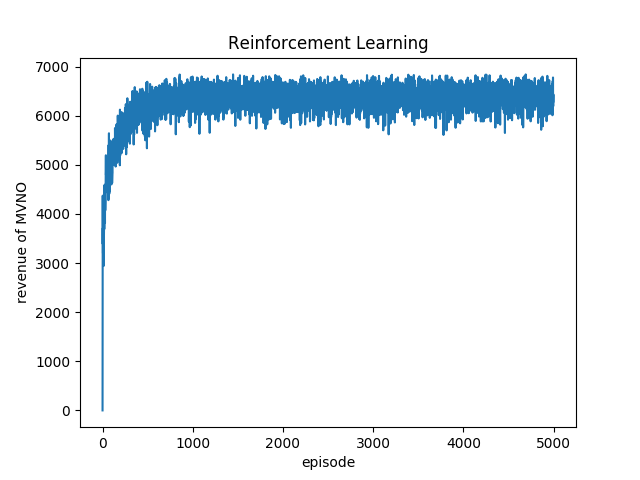
3.4.2 仿真结果分析 23
3.5 本章小结 24
第4章 总结和展望 25
4.1 本文总结 25
4.2 工作展望 25
致谢 27
参考文献 28
绪论
课题研究的背景、目的和意义
近年来,随着智能终端的普及和发展,以4K/8K超高清移动视频、流媒体、虚拟现实(Virtual Reality,VR)、增强现实(Augmented Reality,AR)等为代表的新型移动多媒体业务和应用不断涌现。例如,超高分辨率的屏幕越来越成为智能终端的标配,为新型移动多媒体业务的发展奠定了坚实的基础;在硬件设备方面,谷歌推出了眼镜、头盔等VR设备,三星宣布和Oculus合作推出虚拟现实头盔Gear VR;在软件平台方面,谷歌和苹果分别构建了AR应用程序软件平台ARcore和ARKit,将2D或3D元素添加到相机的实时场景中,使得这些元素看起来就存在于现实世界中。上述平台结合了设备运动追踪、相机场景捕捉、高级场景处理和便利显示,简化了AR体验的任务。可以预见,随着未来移动通信技术、智能终端技术的不断发展和进步,移动多媒体业务将有更加广阔的市场应用前景。
在移动多媒体业务高速发展的同时,对于数据传输速率提出了新的要求。由于用户群体在视频内容,显示设备和接入网络容量需求等方面的异质性日益增加,使得移动视频流式传输变得越发复杂。动态自适应流媒体(Dynamic adaptive streaming)技术,简单地说,就是将同一视频内容在不同的码率或者清晰度的条件下进行编码,得到不同清晰度的视频版本,当用户请求该视频内容时,服务器综合考虑该用户终端设备和网络条件等环境因素,向不同的用户传输合适码率或者清晰度的视频版本,可以提高用户整体满意程度[1],现已成为异构网络视频流传输的一种有效方法。此外,由于移动视频内容比其他内容类型具有更高的比特率,移动视频将产生大量的移动流量增长。根据行业内权威评估和预测[2],在2016年移动视频流量占所有类别移动总流量的60%,预计在2021年这一数字将会达到78%,从2016年到2021年的五年时间中,移动视频的数量将增加9倍。移动视频在2016年至2021年间的复合年增长率接近54%,高于整体平均移动流量复合年增长率的47%。据估计,在2021年每月产生的49艾字节的数据流量中,有38艾字节的数据属于视频。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
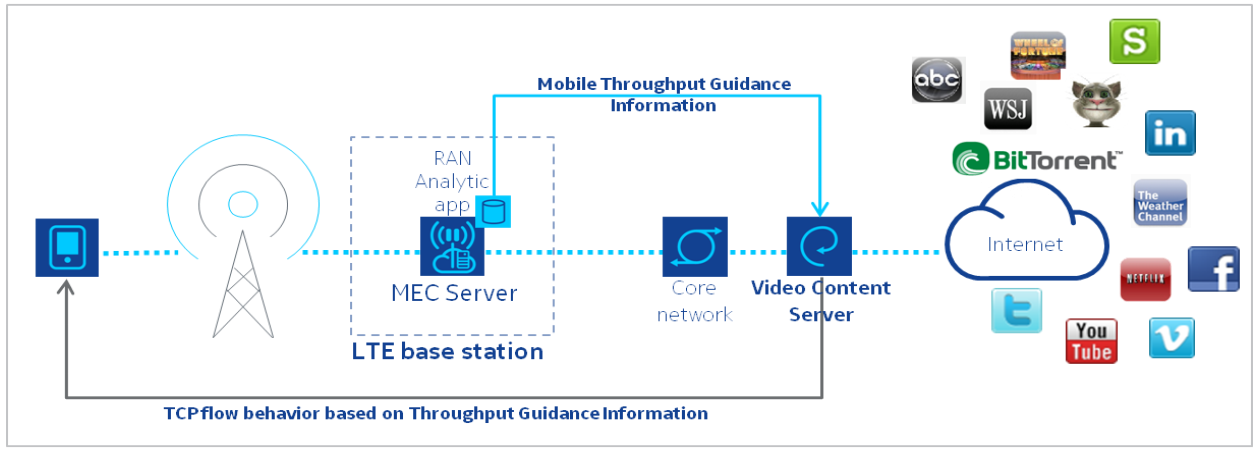
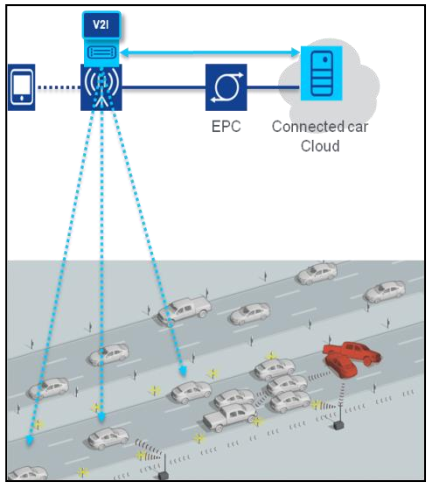
相关图片展示: