Landsat8影像的土地覆被分类方法研究毕业论文
2020-07-15 21:10:27
摘 要
在研究区域土地利用情况时,土地覆被分类是重要参考依据。遥感技术为土地覆被分类研究提供便捷、全面、高效的监测,遥感影像为土地覆被分类提供可靠的数据支持。
本文以苏州市为研究区,以Landsat 5 TM影像为主要利用的遥感影像。Landsat 5是工作时间最长的卫星,是目前全球使用最广泛的遥感影像数据源。TM数据是一种光学遥感数据,含有七个波段。首先需要根据研究区的土地覆被特征来确定最佳的波段合成,并选择分类样本,使用不同的方法进行自动分类,分类后结合分类图的效果以及总体分类精度、Kappa指数,对上述分类方法进行比较。最后得出的研究结论如下
⑴ 最大似然分类法、支持向量机分类法、基于专家知识的决策树分类方法、人工神经网络分类法、面向对象的分类方法的总体分类精度为89.56%、89.63%、89.86%、89.76%、89.69%,Kappa指数分别为0.8603、0.8679、0.8809、0.8819、0.8602。从中可以看出,决策树分类方法精度相对最高。
⑵ 从生产者精度来看,同种土地覆被类型运用不同的分类方法产生的精度有所差异。首先,五种分类方法产生的水域分类结果的生产者精度都比较高,最高的是支持向量机方法,第二是决策树分类方法,而最大似然分类方法最低;接下来是林地的生产者精度相对来说略高,支持向量机分类方法最高,其次是决策树分类方法,最低的是最大似然分类方法;第三较高的覆被类型是城乡、工矿、居民用地,精度最高的是人工神经网络分类方法,支持向量机分类方法最低;生产者精度最低的土地覆被类型是未利用土地,分类精度最高的是支持向量机分类方法,为82.33%。
关键词:土地覆被分类;基于像元的分类方法;面向对象的分类方法
Study on land cover classification based on Landsat 5 TM images
—Take suzhou city as an example
Abstract
Land cover classification is an important basis for the study of land use in the region. Remote sensing image can provide real-time data support for land cover classification and realize convenient, comprehensive and efficient monitoring.
This paper takes suzhou city, jiangsu province as the research area and Landsat 5 TM image as the source of remote sensing image. Lansat 5 is the most widely used remote sensing image data source in the world and the longest working satellite. TM data belongs to optical remote sensing data, with seven bands. TM data belongs to optical remote sensing data, with seven bands. Based on geographical features in the study area to determine the best band synthesis, and select the classification samples, using the classification method based on pixels, maximum likelihood classification, support vector machine classification, decision tree classification method based on expert knowledge and artificial neural network classification and object-oriented classification method for automatic classification, classified according to the classification results after classification diagram and the overall accuracy and Kappa index, carries on the comparison to the above classification method. The main conclusions are as follows:
Maximum likelihood classification, support vector machine (SVM) classification, decision tree classification method based on expert knowledge and artificial neural network classification, object-oriented classification method of the overall classification accuracy of 89.56%, 89.63%, 89.86%, 89.76%, 89.86%, Kappa index were 0.8603, 0.8679, 0.8809, 0.8819, 0.8602. It indicates that the decision tree method has the highest precision and the maximum likelihood classification method has the lowest precision.
From the perspective of producer precision, the accuracy of each land cover type of the five classification methods is different. First of all, the five water area classification methods have high precision, the highest is the support vector machine method, the second is the decision tree classification method, and the maximum likelihood classification method is the lowest. Next, the producer precision of woodland is relatively high, and the support vector machine classification method is the highest, followed by the decision tree classification method, and the lowest is the maximum likelihood classification method. The third higher cover type is urban and rural, industrial and mining, residential land, the highest accuracy is artificial neural network classification method, the lowest support vector machine classification method; The land cover type with the lowest precision of the producer is unutilized land, and the one with the highest classification precision is the support vector machine classification method, which is 92.33%.
Key words: land cover classification; Image element based classification method; Object-oriented classification
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景、选题意义 1
1.1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.2 选题意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
1.2.1 国外研究现状 1
1.2.2 国内研究现状 2
1.3 研究目标、内容及方法 3
1.3.1 研究目标 3
1.3.2 研究内容 3
1.3.3 研究方法 4
1.4 技术路线 5
第二章 研究区概况与数据预处理 6
2.1 研究区概况 6
2.1.1 地理位置及地理范围 6
2.1.2 地形、地貌特征 6
2.1.3 气候、水文 6
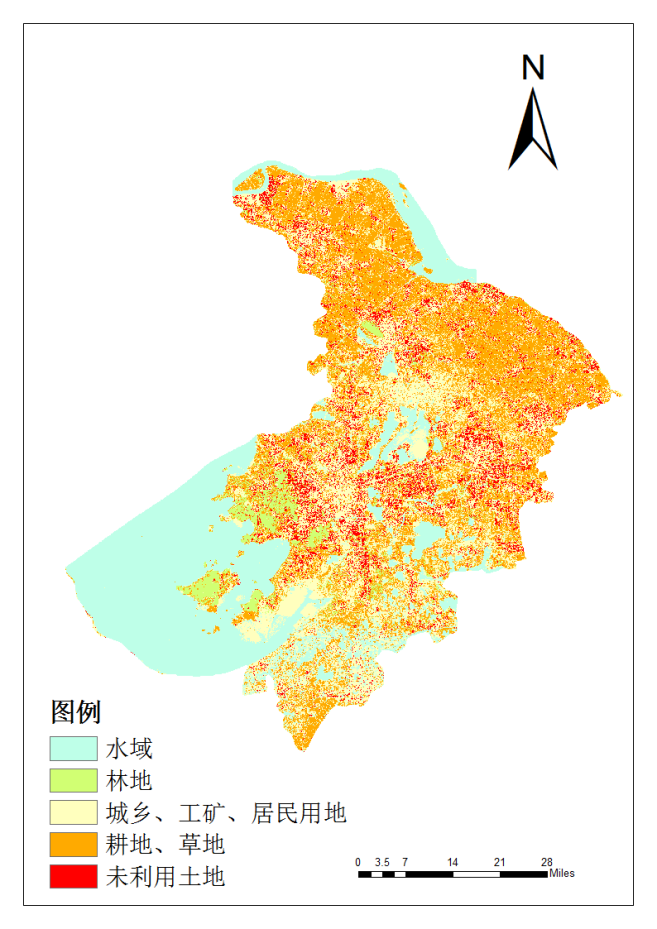
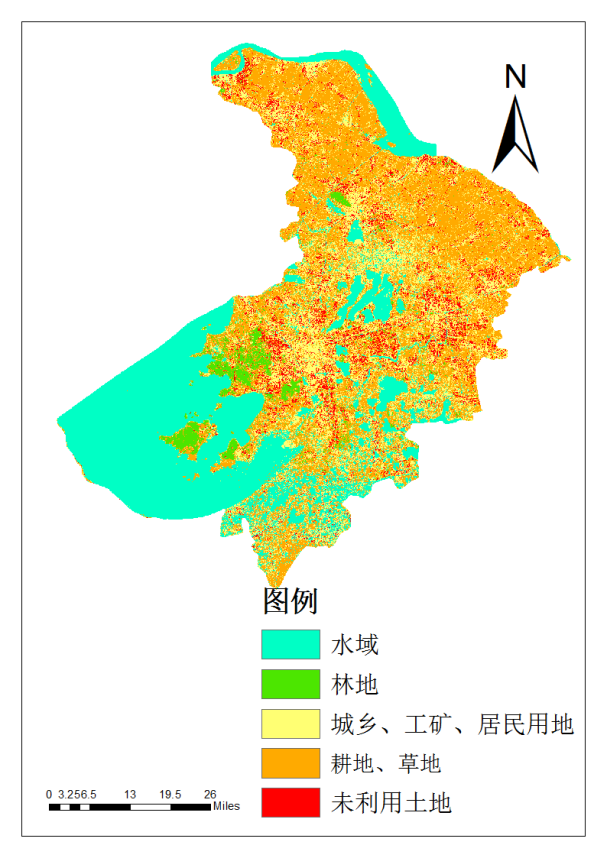
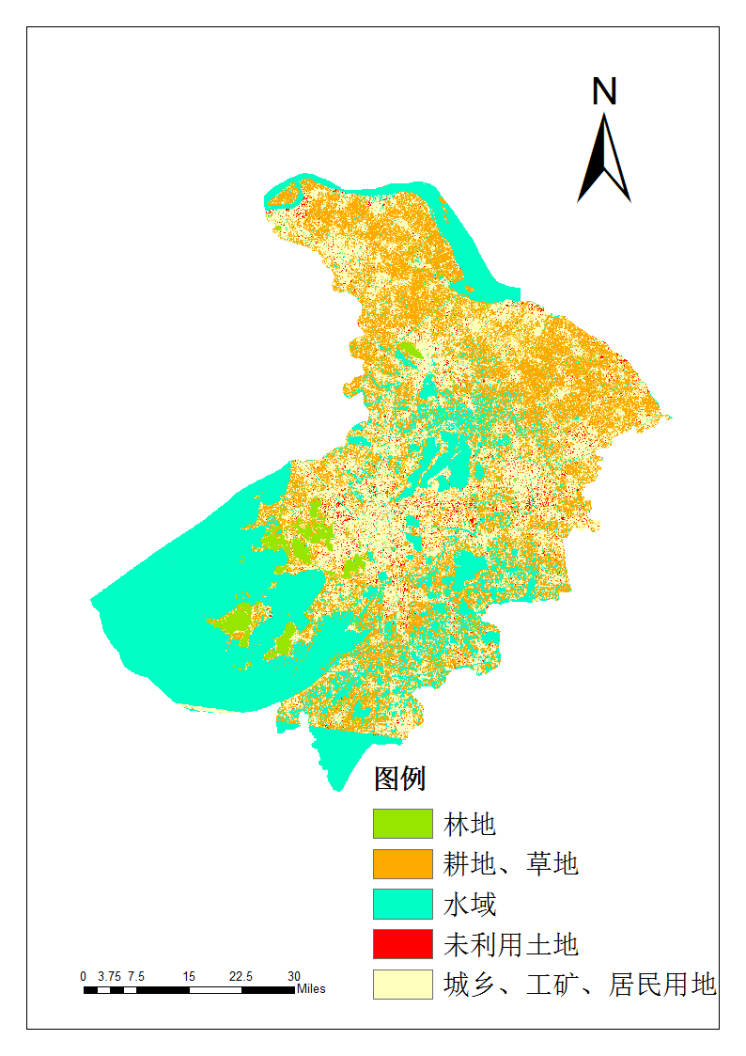
2.1.4 土地利用现状 6
2.2 数据来源及数据预处理 7
2.2.1 数据来源 7
2.2.2 数据预处理 7
第三章 遥感影像分类方法 8
3.1 遥感影像分类的概念及原理 8
3.1.1 非监督分类方法 8
3.1.2 监督分类方法 8
第四章 苏州市2010年土地覆被分类 11
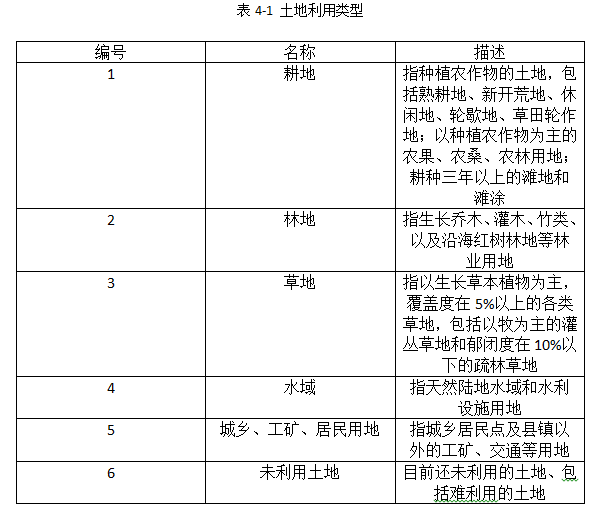
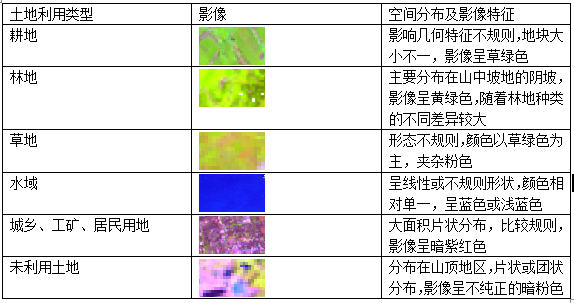
4.1 分类系统的确定 11
4.2 基于像元的苏州市土地覆被分类 11
4.2.1 最大似然分类方法 11
4.2.4 支持向量机分类方法 14
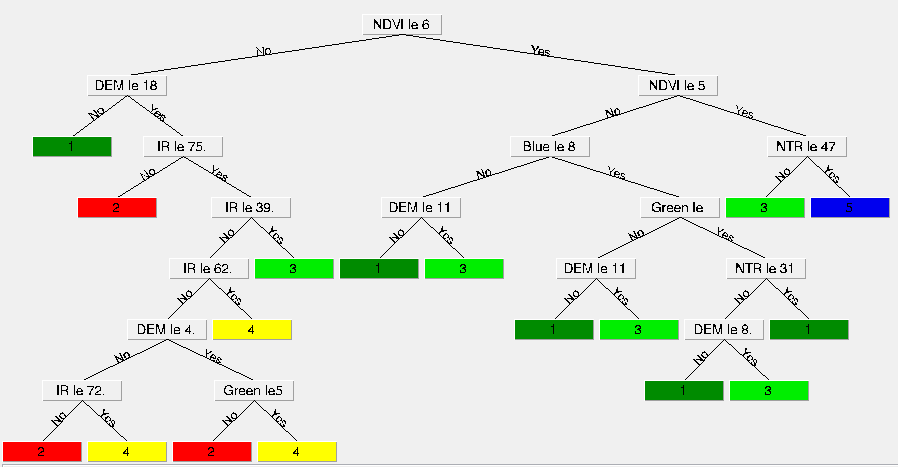
4.2.5 基于知识的决策树分类方法 15
4.2.6 人工神经网络分类方法 17
4.3 面向对象的土地覆被分类方法 19
4.3.1 影像分割 19
4.3.2 样本选择 21
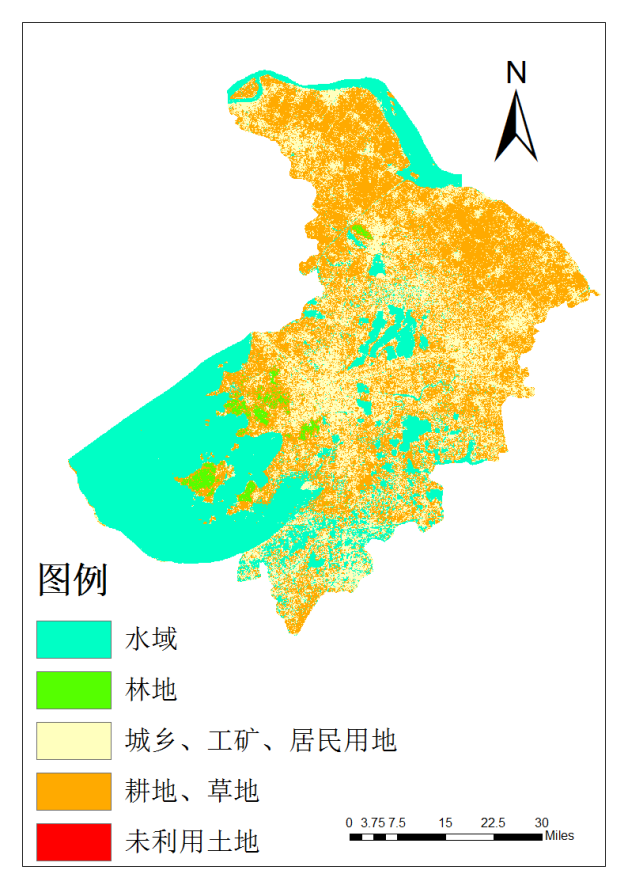
4.3.4 输出结果 22
4.4 精度评价 22
第五章 结论与讨论 25
5.1 结论 25
5.2 存在的问题与不足 25
参考文献 27
致谢 29
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景、选题意义
1.1.1 研究背景
结合摆万奇(中国科学院知识创新基地副研究员)等学者对土地覆被的定义,土地覆被可以被定义为覆盖地面的原生态的植被、土壤、湖泊等以及经过人工改造的建筑物。
研究土地覆被分类是生态系统、水资源和气候方面重要的信息来源。随着遥感技术和计算机技术取得巨大的进展,遥感技术已广泛运用于土地覆盖分类。遥感运用于土地覆被分类有着巨大的优势,遥感技术可以做到不直接接触观测对象而实现有效观测。其中,Landsat是中等空间分辨率的卫星,其影像数据应用广泛,可支持不同尺度的研究,目前已成为土地资源调查的主要遥感影像数据源之一。
1.1.2 选题意义
苏州市位于江苏省的南部,是长江三角洲城市群的一大重要城市,为长江经济带的发展起到了十分重要的作用。苏州全市地貌大部分是平原,只有在西部山区和太湖诸岛有丘陵的分布,山体最高在350米左右。论文对苏州地区进行土地覆被分类方法的探索,比较各种分类方法的优劣势,相信会对苏州今后的土地利用、动态监测管理有一定的帮助。
1.2 国内外研究现状
1.2.1 国外研究现状
近年来,遥感技术取得了突破性的发展,开始作为监测土地覆被变化的一种手段。遥感技术具有不直接接触地面物体的特点,能够做到远距离地对大范围区进行高效全面地的观测。但具有区域自然要素、社会环境的多样性与地物光谱特性的复杂性等局限性,地物状况很难直接、清晰地通过遥感手段反映出来[4]。
目视解译的分类技术是最早出现的土地覆被分类方法。它利用了目视判读人员的自身素养来提取空间信息,具有很高的灵活性,在对精度要求高的工作领域仍然被广泛应用[5]。但目视解译的工作量大,效率低且人力成本高,已不能满足人们对于土地覆被分类信息提取的需要。所以,随着计算技术的快速发展,人们对于遥感影像的分类研究重心已从目视解译转移到了计算机处理上[6]。在目前的遥感分类研究领域,用得最广泛的有最小距离法、平行六面体法、循环集群法等监督或非监督分类方法[7]。
相关图片展示: