壳聚糖对污泥颗粒化过程中出水水质的影响毕业论文
2020-02-19 15:21:39
摘 要
好氧颗粒污泥(Aerobic Granular Sludge,AGS)是由微生物本身凝结而成的微粒状的活性污泥。它具有沉降性能好、脱氮除磷效果好等优点,但好氧颗粒污泥技术存在着一些局限性:颗粒化过程时间较长、系统运行的稳定性较差等。有研究表明,向活性污泥中添加壳聚糖可以加快厌氧颗粒污泥的形成速率,然而其对好氧颗粒污泥的影响还不清楚,此外,壳聚糖的加入是否会对反应器出水水质产生影响,是不是会影响SBR反应器运行的稳定性,目前尚不清楚,这些需要我们进一步地探索。
本文在两个SBR反应器中接种取自武汉某污水处理厂的好氧池污泥,设置对照组(RA)和添加壳聚糖的实验组(RB),分别培养好氧颗粒污泥,通过测定反应器运行期间进出水水质的变化特征,探讨壳聚糖的投加对好氧污泥颗粒化过程中出水水质的影响进而得出其对SBR运行稳定性影响。通过连续测定SBR反应器60天的进出水水质情况,做出各污染物去除率及进出水浓度曲线。得出如下结论:
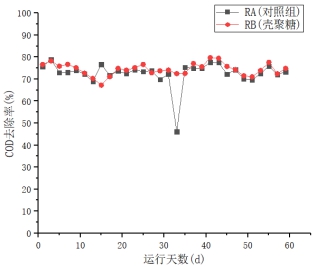
(1)在污泥颗粒化过程当中,RA(对照)、RB(添加壳聚糖)的COD的去除率整体在70%以上。COD的去除率RB略高于RA,壳聚糖对颗粒污泥的COD的去除有一定的促进作用。
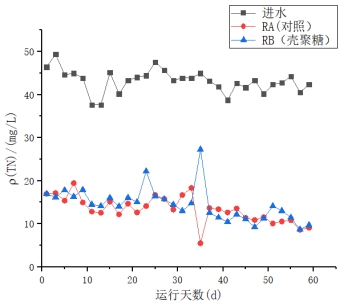
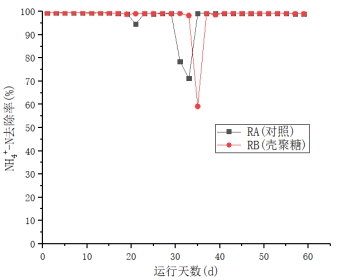
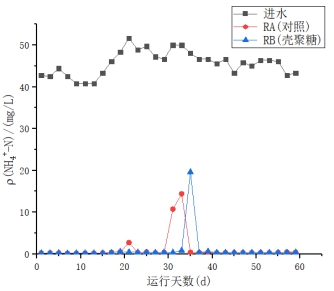
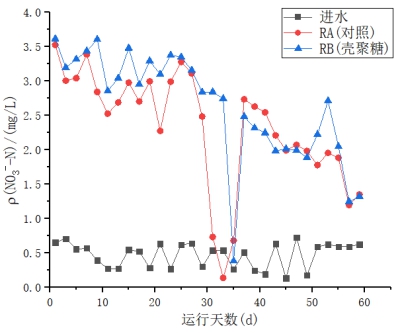
(2)在污泥颗粒化进程当中,随着反应时间的增加,出水中的NO3-浓度呈下降趋势。该SBR系统有非常良好且稳定的氨氮去除效果,RA(对照)、RB(添加壳聚糖)中氨氮去除率均保持在99%以上,出水氨氮达到一级A标准,壳聚糖对此SBR系统的氨氮的去除无明显影响。在反应后期(运行50天后),RA、RB的总氮去除率到达80%以上。且未添加壳聚糖的反应器TN的平均去除率略高于添加壳聚糖的反应器,这表明添加壳聚糖可能会对SBR反应器TN的去除有一定的抑制作用。
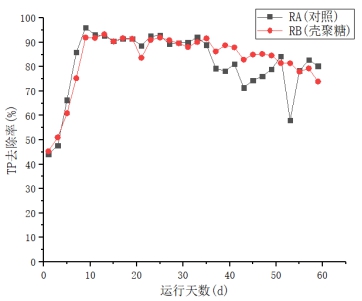
(3)在反应的第18-50天,RA(对照)、RB(添加壳聚糖)均对PO43-有较好的去除效果,去除率在97%左右。此SBR系统在反应后期(50天后)对于PO43-的去除稳定性不高。RA、RB的TP平均去除率在81%左右,去除率均随着时间的变化在较大幅度波动,该SBR系统去除TP的稳定性不高。由于实验组的TP、PO43-的平均去除率高于对照组,可知壳聚糖对颗粒污泥去除TP、PO43-有一定的促进作用。
综上所述,壳聚糖对该SBR反应器运行稳定性无明显影响,对于氨氮、TP、PO43-、COD的去除,壳聚糖有一定的促进作用,但添加壳聚糖可能会对SBR反应器TN的去除有一定的抑制作用。
关键词:SBR反应器;好氧颗粒污泥;壳聚糖;出水水质
Abstract
Aerobic Granular Sludge (AGS) is an activated sludge in the form of particles formed by the coagulation of microorganisms themselves. but the aerobic granular sludge technology has some limitations: the granulation process takes a long time, and the stability of the system operation is poor. Studies have shown that the addition of chitosan to activated sludge can accelerate the formation of anaerobic granular sludge, but its effect on aerobic granular sludge is still unclear. In addition, whether the addition of chitosan to the effluent quality of the reactor It is unclear whether the impact will affect the stability of the SBR reactor operation, which requires further exploration.
In this paper, aerobic sludge from a sewage treatment plant in Wuhan was inoculated in two SBR reactors, and a control group (RA) and an experimental group (RB) with chitosan were added to culture aerobic granular sludge. The variation characteristics of the water quality of the inlet and outlet water during the operation of the reactor were measured, and the influence of the addition of chitosan on the effluent quality during the granulation of aerobic sludge was investigated to determine its effect on the stability of SBR operation. By continuously measuring the water quality of the inflow and outflow of the SBR system for 60 days, the pollutant removal rate and the inflow and outflow concentration curve were made. The following conclusions are drawn:
(1) In the process of sludge granulation, the removal rate of COD of RA (without chitosan) and RB (added chitosan) is over 70%. The removal rate of COD is slightly higher than that of RA, and chitosan has only a small promotion effect on the removal of COD from granular sludge.
(2) In the process of sludge granulation, the concentration of NO3- in the effluent decreased with the increase of reaction time. The SBR system has a very good and stable ammonia nitrogen removal effect. The ammonia nitrogen removal rate of RA (without chitosan) and RB (added chitosan) is maintained above 99%, and the effluent ammonia nitrogen reaches the first-class A standard. Sugar has no significant effect on the removal of ammonia nitrogen from this SBR system. At the end of the reaction (after 50 days of operation), the total nitrogen removal rate of RA and RB reached 80% or more. The average removal rate of the reactor TN without chitosan added was slightly higher than that of the chitosan-added reactor, which indicates that the addition of chitosan may have a certain inhibitory effect on the removal of TN from the SBR reactor.
(3) On the 18th to 50th day of the reaction, RA (without chitosan) and RB (added chitosan) all have good removal effect on PO43-, and the removal rate is about 97%. This SBR system did not have high removal stability for PO43- at the end of the reaction (after 50 days). The average removal rate of TP of RA (without chitosan) and RB (added chitosan) was about 81%, and the removal rate fluctuated greatly with time. The stability of TP removal in this SBR system is not high. . Since the average removal rate of TP and PO43- in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group, it was found that chitosan could promote the removal of TP and PO43- from granular sludge.
In summary, chitosan has no significant effect on the stability of the SBR reactor. For the removal of ammonia nitrogen, TP, PO43-, COD, chitosan has a certain promoting effect, but the addition of chitosan may be SBR. The removal of the reactor TN has a certain inhibitory effect.
Keywords: SBR reactor; aerobic granular sludge; chitosan; effluent quality
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1好氧颗粒污泥的研究进展 1
1.1.1 好氧颗粒污泥简介 1
1.1.2 好氧颗粒污泥在去除污染物方面的作用 1
1.1.3 好氧颗粒污泥国内外研究进展 2
1.1.4 好氧颗粒污泥技术的局限性 4
1.2 壳聚糖对于污泥颗粒化过程的影响 4
1.2.1 壳聚糖简介 4
1.2.2 壳聚糖在污泥颗粒化过程研究进展 4
1.3 研究的目的、意义及内容 6
1.3.1 研究的目的及意义 6
1.3.2 研究的内容 7
第2章 材料与方法 8
2.1 污泥来源 8
2.2 实验用水 8
2.3 实验装置 9
2.3.1 SBR装置 9
2.3.2 SBR生物脱氮除磷工艺 9
2.4 实验方法 10
2.5 出水水质测定 11
2.5.1 实验试剂 11
2.5.2 水质测定方法 12
2.5.3 实验仪器设备 13
第3章 结果与讨论 14
3.1 壳聚糖对污泥颗粒化过程中出水水质的影响 14
3.1.1 污泥颗粒化过程中去除COD的效果 14
3.1.2 污泥颗粒化过程中脱氮效果 15
3.1.3 污泥颗粒化过程中除磷的效果 17
3.2 小结 19
第4章 结论与展望 21
参考文献 22
致 谢 25
第1章 绪论
污水生物处理可分为生物膜法和活性污泥法两大类,活性污泥法常见的工艺有序批式活性污泥法(SBR)等。SBR是通过周期性调控反应器好氧、缺氧、厌氧状态,来实现较为良好的污水脱氮除磷效果。
好氧颗粒污泥(Aerobic Granular Sludge,AGS)是由微生物自身聚集而成的微粒状的活性污泥。与传统的污水生物处理方法相比,它具有沉降性能好、不易发生污泥膨胀、脱氮除磷效果好等优点,因此这项技术具有非常良好的应用前景。
目前为止,已经有学者利用SBR反应器培养出好氧颗粒污泥,但对于污泥颗粒化过程中出水水质的研究还很有限,且对于颗粒化过程中反应器系统稳定性研究少之又少,需要我们进一步地探索。
1.1好氧颗粒污泥的研究进展
1.1.1 好氧颗粒污泥简介
Mishillla[1]在1991年首次利用好氧上流式污泥床反应器(AUSB)培育出AGS。自此,海内外学者开启了对于AGS的研究。AGS在外观上一般是白色或淡黄色的球形微粒,粒径在0.3-6mm之间[2]。将AGS与普通的活性污泥做比较,其有着不易发生污泥膨胀,抗冲击能力强,可承受高有机载荷等的特点[3],与厌氧颗粒污泥相比,其具有沉降性能好,结构致密,污泥膨胀少,适用范围广的特点[4]。近年来,对于AGS的大量国内外研究成果表明:AGS可以用于处理多种类型的工业废水[4-6]。
1.1.2 好氧颗粒污泥在去除污染物方面的作用
1.1.2.1 好氧颗粒污泥的脱氮作用
好氧颗粒污泥具有一定的厚度,由于其规则、紧密的结构,使得溶解氧浓度从颗粒外部至内部分布不均匀,因此,从外至内分别是好氧区域,缺氧区域和厌氧区域[4]。需氧或厌氧时,有机物在氨化微生物的作用下可转化为氨氮;在好氧情况下,亚硝化菌和硝化菌可将氨氮转化为亚硝酸根(NO2-)和硝酸根(NO3-); 在缺氧区内,反硝化细菌可将NO2-与NO3-还原为N2[5]。
由于AGS的独特构造和氧浓度扩散梯度的存在,为参与脱氮过程的多聚磷酸盐细菌,硝化菌和反硝化聚磷菌(DPB)等菌提供了良好的共生环境,且AGS的结构紧密,可以减弱污染物对微生物的影响,加强对一些敏感菌(如硝化细菌)的庇护[6],因此在颗粒污泥中富含大量的 DPB和硝化细菌这使得AGS的脱氮能力强。
1.1.2.2 好氧颗粒污泥的除磷作用
AGS的外部位于好氧区域。可以过量吸收磷,而其内部为厌氧区,因此,好氧颗粒污泥内的磷积累细菌可以利用外层吸收的磷,并释放出磷酸盐,在好氧颗粒污泥内部产生了磷沉淀[4],将AGS技术与传统的生物除磷技术做比较可以发现,AGS具有更高的磷的去除效率。
生物除磷(BPR)即是利用了聚磷微生物(PAOs)具有厌氧磷释放和需氧(或缺氧)过量磷吸收的特征[8],在一个厌氧-好氧或厌氧-缺氧交替的环境下,聚磷菌发挥作用,最终使得好氧或缺氧段混合溶液中磷的浓度大大降低,最后利用排出大量的富含磷的污泥来达成从污水中除磷的目的[7]。
1.1.2.3 好氧颗粒污泥去除COD作用
化学需氧量COD(Chemical Oxygen Demand)常被用作表示污水中有机物含量多少的指标。在AGS的产生过程中,活性污泥中的异养微生物需要从外部基质中吸收养分来维持其代谢。在外源基质充足时,部分基质被异养微生物用于自身的代谢与生长,而剩余的营养物质被摄取并储存于好氧颗粒污泥中[9]。因而,好氧颗粒污泥在实际生活中可用以去除污水中的还原性物质,进而可以有效地降低污水中的COD。当外源基质不足时,好氧颗粒污泥还可以利用自身储存的物质来维持其代谢的需求[10]。
1.1.3 好氧颗粒污泥国内外研究进展
1997 年,E.Morgenroth[11]等在SBR中,通过采取较短的沉降、出水时间来筛选出沉降性能好的污泥,反应40天后,在SBR中成功培养出了颗粒污泥。从那时起,国内外许多学者开始使用SBR反应器开展对AGS的研究[12]。
影响好氧颗粒污泥去除氮,磷等污染物的因素包括: 温度、底物中各物质的比例、溶解氧饱和度、接种污泥类型等。在这方面,海内外学者做了如下探索。
通过改变反应器中基质中每种物质的比例,可以加速好氧污泥的造粒过程,并且可以改善颗粒污泥除去污染物的效果。张晓健等探讨了处于不同的SBR系统操作条件对AGS的造粒过程和除磷效果的影响。 最终的结果表明,对生物除磷效果和好氧污泥颗粒化最有利的条件为反应温度恒温22℃,COD/TN=24.66,COD/TP=58.25[13]。而有学者以SBR为反应器,采用改变底物中的P/COD比的方式,来探讨AGS在不同P/COD比时的除磷效果,结果发现在实验过程中,从废水中去除的磷以微生物中的多磷酸盐(poly-P)的形式积累,增加底物的P/COD比例可以刺激好氧颗粒的P积累能力[7]。
有研究表明溶解氧饱和度会对SBR反应器的脱氮效率产生影响,若不控制溶解氧的饱和度,COD、磷的去除率均能达到95%以上,但总氮的去除率仅为34%。因此,为了提高氮的去除效果,在反应的前35天内将溶解氧饱和度控制在40%,总氮和磷的去除率可达97%以上[4]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: