正交法优化设计表面分子印迹材料的制备工艺及其分离行为研究毕业论文
2020-07-07 22:10:08
摘 要
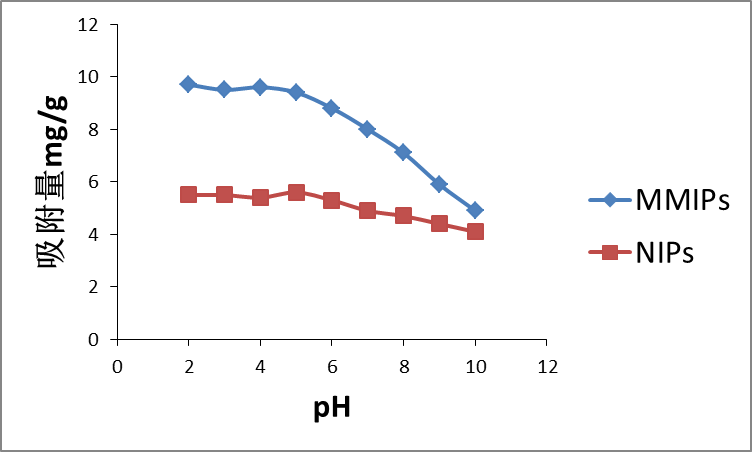
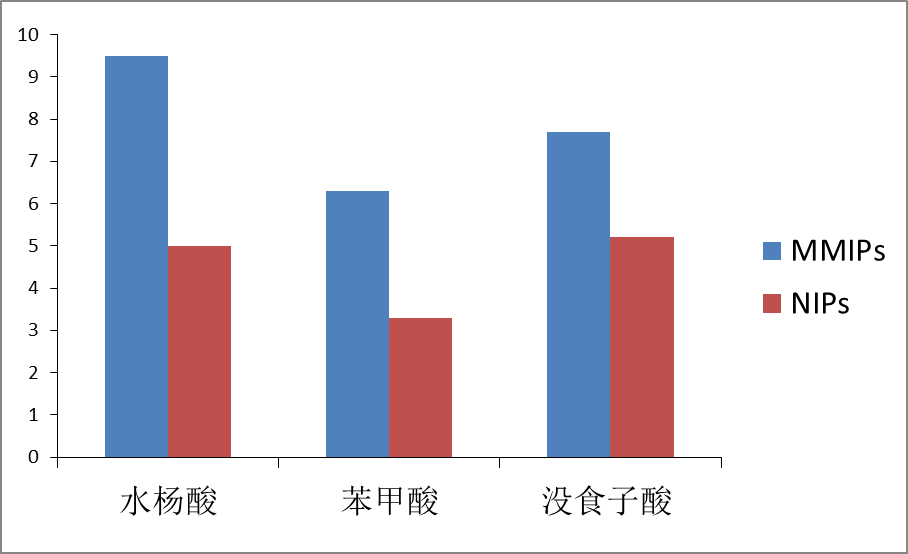
本文简介了水杨酸及其处理现状,并综合概述了分子印迹(Molecularly Imprinting,MIP)的基础内容。以凹凸棒土为表面载体,水杨酸为模板分子,多巴胺为功能单体制备了表面分子印迹聚合物(MMIPs),并对其相关的吸附性能进行了探究。采用正交试验法确定了最优的制备条件:取0.0475g多巴胺,水杨酸与多巴胺的摩尔比为1:2,凹凸棒土1.5g,反应时间12h。吸附实验数据表明:MMIPs对水杨酸有更高的吸附性能,其最大吸附量比NIPs高出70%左右;准二级动力学模型和Langmuir等温吸附模型更适用于MMIPs的吸附行为,且吸附过程是自发放热的; MMIPs的吸附量受pH的影响较大而NIPs则不明显,在酸性条件下MMIPs的吸附效果最好,当pHgt;6后吸附量随pH的增大迅速下降;此外,MMIPs对水杨酸及其结构类似物表现出了一定程度的吸附选择性,但选择性不明显。
关键词:分子印迹,水杨酸,多巴胺,凹凸棒土
Optimization of preparation process of surface molecularly imprinted polymers by orthogonal test and Study of the
adsorption behavior
abstract
In this paper, the salicylic acid and its treatment status are briefly introduced,and summarized The principle, components, preparation and application of molecular imprinting. On this basis, the novel surface molecularly imprinted polymers were prepared by using attapulgite as the surface carrier, salicylic acid as template molecule and dopamine as function,and their related adsorption properties were explored. The optimum preparation conditions were determined by orthogonal test:0.0475g dopamine, salicylic acid:dopamine(molar ratio)= 1:2, 1.5g attapulgite, reaction time=12h. According to the Adsorption experimental data: MMIPs has higher adsorption capacity for salicylic acid, and its maximum adsorption capacity is about 70% higher than that of NIPs; The adsorption behavior of MMIPs conforms to the quasi-second order kinetic model and the Langmuir isothermal adsorption model, and its adsorption process belongs to spontaneous process and exothermic process; Moreover, The adsorption capacity of MMIPs and salicylic acid was influenced by pH obviously while NIPs was not affected by pH, The adsorption of MMIPs is the best under acidic conditions, When pHgt;6 the adsorption capacity decreases rapidly with the increase of pH; Besides, MMIPs showed a certain degree of selectivity to salicylic acid and its structural analogues, however, the selectivity was not obvious.
Key words: Molecular imprinting, salicylic acid, dopamine, Attapulgite
目录
摘要 I
abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 水杨酸的简介及其处理现状 1
1.1.1水杨酸的简介 1
1.1.2水杨酸废水处理现状 1
1.2 分子印迹技术 2
1.2.1分子印迹技术的介绍 2
1.2.2分子印迹聚合物(MIPs)的制备要素 2
1.2.3分子印迹技术的应用 5
1.3 凹凸棒土的特性及在分子印迹中的应用 6
1.4 正交实验法 6
1.5 本课题的研究内容 7
1.5.1实验的研究意义 7
1.5.2实验内容 7
第二章 实验部分 8
2.1 试剂与仪器 8
2.2 分析方法及标准曲线绘制 8
2.2.1水杨酸标准曲线 9
2.2.2苯甲酸标准曲线 9
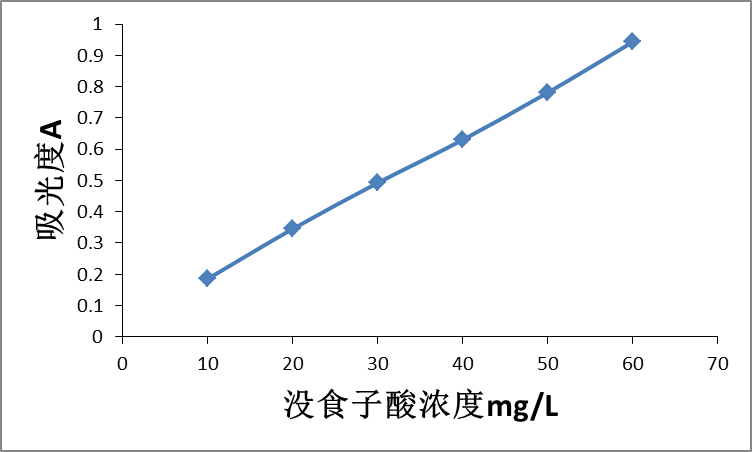
2.2.3没食子酸的标准曲线 10
2.3 表面印迹聚合物(MMIPs)的制备 11
2.4 正交实验设计 11
2.5 吸附实验 12
2.5.1吸附动力学实验 12
2.5.2吸附热力学实验 12
2.5.3溶液pH对吸附效果的影响 13
2.5.4选择性吸附实验 13
第三章 实验结果与讨论 14
3.1 正交实验 14
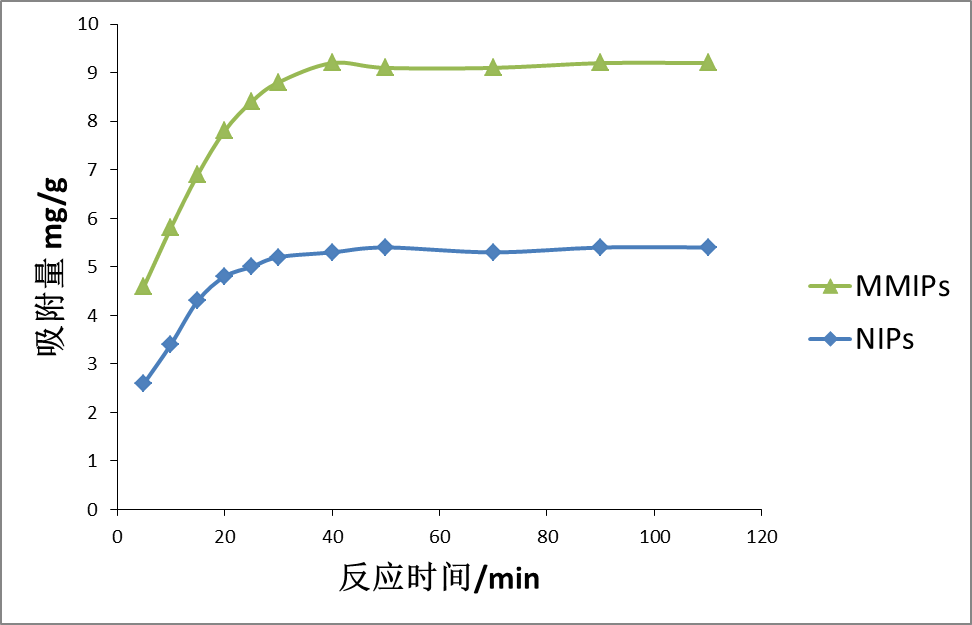
3.2 吸附动力学 15
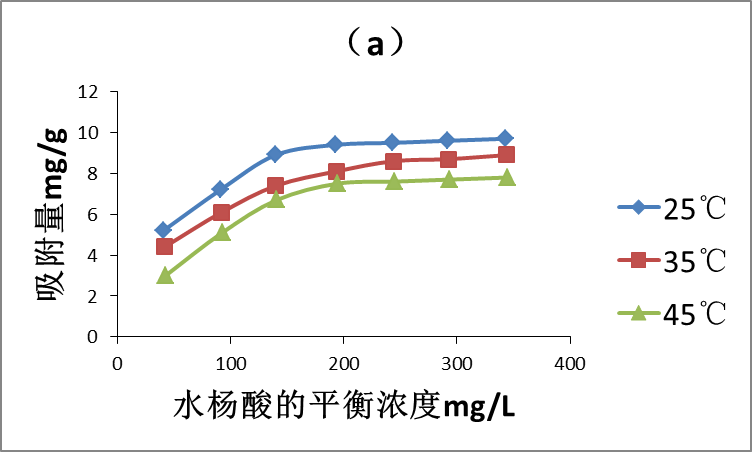
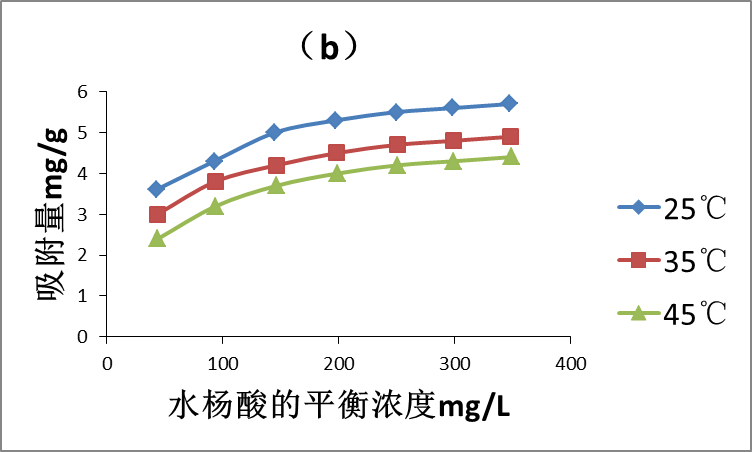
3.3 吸附等温线 16
3.4 吸附热力学 18
3.5 pH的影响 19
3.6 吸附选择性 20
第四章 结论与展望 20
4.1 结论 20
4.2 展望 21
参考文献 23
致谢 25
绪论
水杨酸的简介及其处理现状
1.1.1水杨酸的介绍
水杨酸(salicylic acid)是一种有机酸,学名为邻羟基苯甲酸,易溶于脂类物质而难溶于水,广泛的存在于高等植物体内。水杨酸是很多有机物合成中非常重要的中间体,广泛应用于医药、食品、农药、化妆品、防腐剂等生产生活领域。因同时具有羟基和羧酸两种官能团, 所以水杨酸同时具备酚和羧酸的性质,其最早用于合成阿司匹林,之后也作为主要原料用于合成冬青油、止痛灵、食品防腐剂以及水胺硫磷、甲基异硫磷等杀虫剂[1]。除了水杨酸外,水杨酸类物质还包括了水杨酰胺、乙酞水杨酸和水杨酸甲酯等,而其分子结构类似物为苯甲酸、原儿茶酸和没食子酸。
在我国现阶段的工业生产过程中,每生产1 t 水杨酸就会产生15 t 有毒有机化工废水,这类废水往往含酚量和含盐量较高,酸性偏强以及难以生物降解[2]。从相关的研究中可知,对于生物机体而言,水杨酸会对组织中的蛋白质造成一定程度的腐蚀,且目前化工生产中产生的水杨酸废水量大,过量水杨酸的排放会造成水体和大气的严重污染,进而危害生物体和自然环境的健康发展。因此,对水杨酸废水的高效处理技术具有重要的研究意义。
1.1.2水杨酸废水的传统处理方法及不足
水杨酸废水属于强酸性有毒有机工业废水,其高盐、含酚且难生物降解。目前,水杨酸废水的传统处理法虽然有一定的处理效果,但都存在一些不足之处,越来越难以满足目前的生产要求。
相关图片展示: