膜冷凝过程研究毕业论文
2020-07-02 22:53:25
摘 要
在工业生产过程中,水资源需求量大且会排放出大量烟气。如果能对废气中的水能加以回收利用,就可以减少工业生产所需的水量,就能在一定程度上解决水资源短缺的问题。因此,能够清洁高效回收工业废气中的水的膜冷凝技术成为本课题的研究重点。
本课题研究了不同膜材料在膜冷凝过程中的性能。首先对PVDF膜进行Hyflon AD40H,40L,60三种改性,然后对四种膜材料的孔径、孔隙率、力学性能、电镜、接触角、水力击穿压等进行表征并将其用于膜冷凝实验过程中,对冷凝水进行回收并计算出回收率。最后比较四种膜在膜冷凝实验中回收水的性能的差异,并结合膜的表征数据分析将膜冷凝用于工业生产中的可行性,并且经过对比选出较为适合在工业生产中使用的膜材料。
关键词:烟气 微孔疏水膜 Hyflon AD改性 膜冷凝器 回收水
Study on different membrane materials in the membrane condensation process
Abstract
In the industrial production process, the demand for water resources is large and large amounts of smoke are emitted. If the water energy in the waste gas can be recycled, the amount of water needed for industrial production can be reduced, and the problem of water shortage can be solved to some extent. Therefore,the membrane condensation technology that can clean and efficiently recover the water in the industrial waste gas has become the research focus of this topic.
The performance of different membrane materials in the process of membrane condensation was studied. First, the PVDF membrane was modified by Hyflon AD40H, 40L, 60. Then the pore size distribution, porosity, tensile strength, electron microscope, contact angle and hydraulic breakdown pressure of the four membrane materials were characterized and used in the process of membrane condensation, and the condensate was recovered and the recovery rate was calculated. Finally, the difference of the performance of the four kinds of membrane in the film condensation experiment was compared, and the feasibility of applying the membrane in the industrial production was analyzed with the characterization data of the membrane, and then membrane materials which are suitable for industrial production are selected after comparison.
Key Words:Flue gas;Microporous hydrophobic membrane;Hyflon AD modified;
Membrane condenser;Water recovery
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2目前几种传统收集水技术 1
1.3 膜冷凝在废气处理中的意义及研究现状 2
1.3.1膜冷凝在废气处理中的意义 2
1.3.2膜冷凝的研究现状 2
1.4膜冷凝器的操作原理 4
1.5膜材料的选择 5
1.6对膜材料进行疏水改性的方法 6
1.7课题研究目的与内容 6
1.7.1研究目的 6
1.7.2研究内容 7
第二章 实验内容 8
2.1 实验药品和仪器 8
2.1.1 实验药品 8
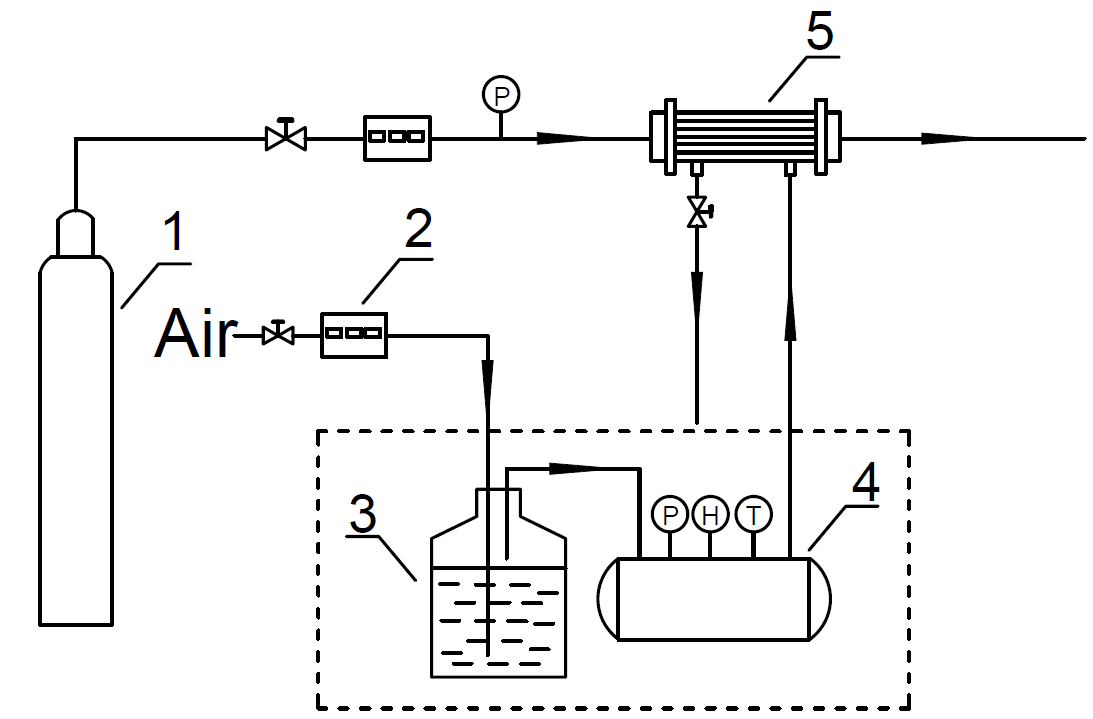
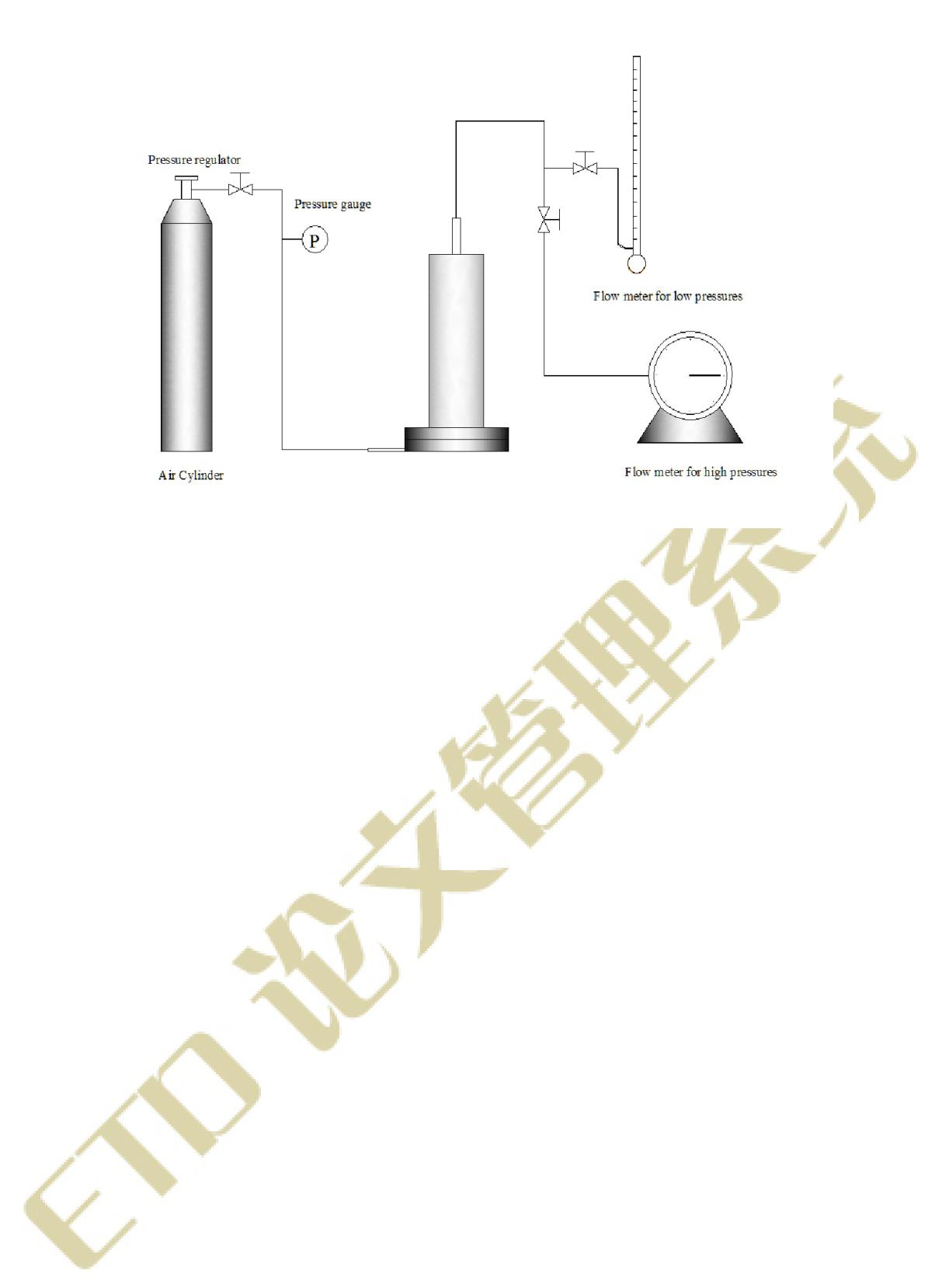
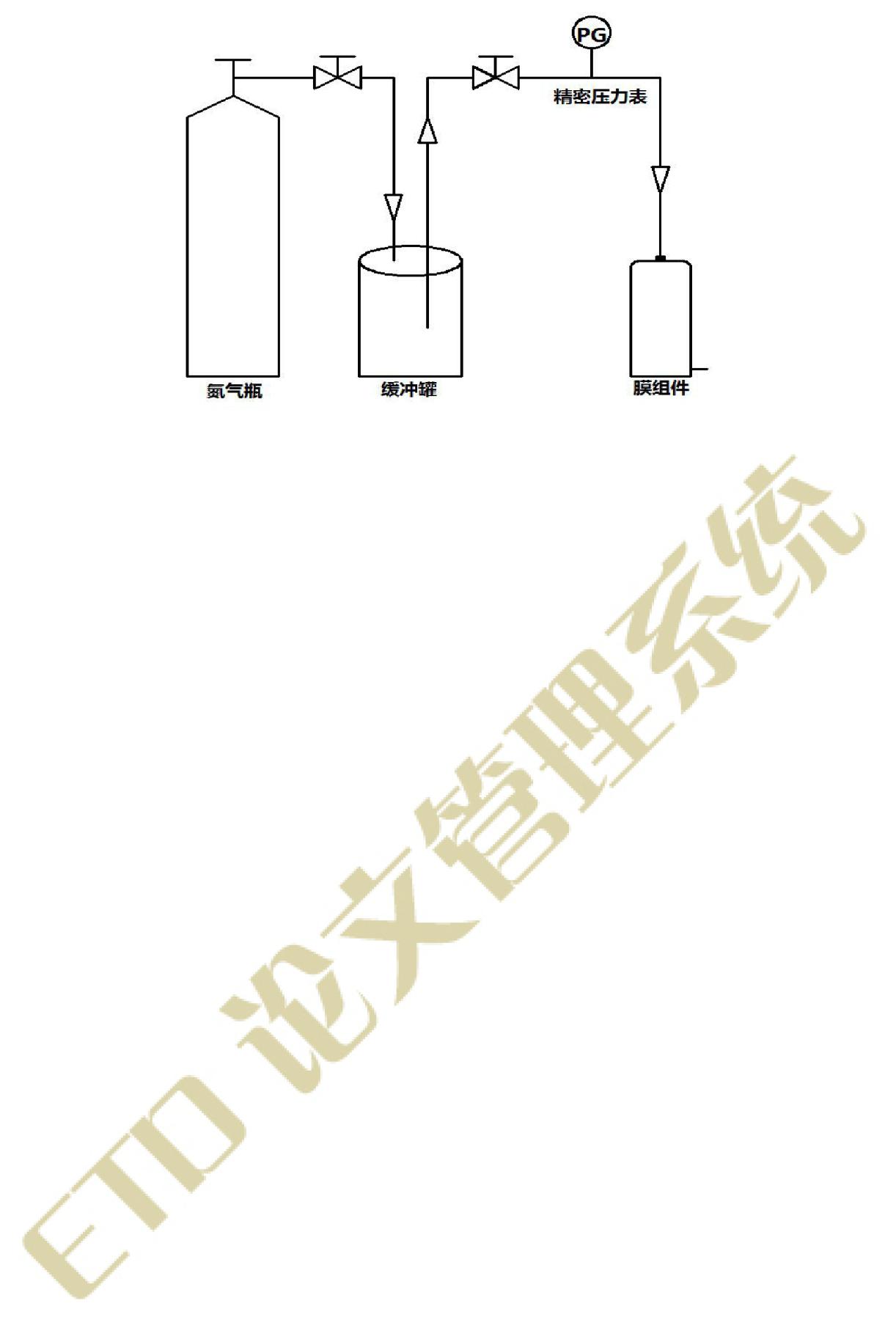
2.2膜材料对膜冷凝过程的影响 9
2.2.1实验流程 9
2.2.2 分析及表征方法 10
第三章 实验结果与讨论 13
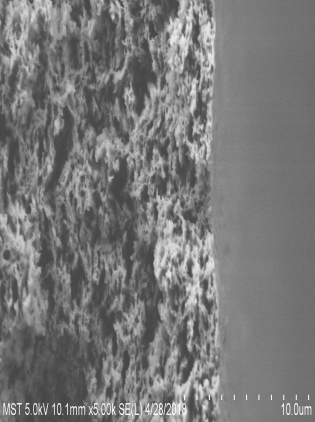
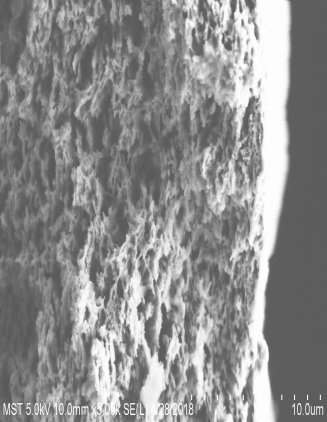
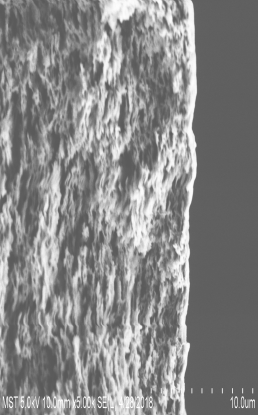
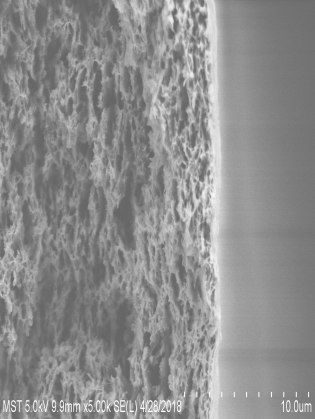
3.1膜的电镜图 13
3.2膜的力学性能的测定 13
3.3膜的孔径的测定 14
3.4膜的孔隙率的测定 14
3.5膜的疏水性能表征的检测 15
3.6膜冷凝实验 16
第四章 结论与展望 18
4.1结论 18
4.2展望 18
参考文献 19
致谢 22
第一章 文献综述
1.1 引言
近年来,水资源的短缺已经成为世界各国需要面临的问题。根据专家估计,2025年世界上将会有25亿人面临缺水的问题,大约有三分之二的人会生活在缺水的地区。因此,当前迫在眉睫的事是要解决水资源短缺的问题。
由于水的需求不断增长,饮用水的供应渐渐成为一个环境问题。其中,工业用水占全球用水的22%左右[1]。在工业中,发电厂的水资源消耗的是最大的,其用于冷却、加热设备以及清洗。它被用来消耗、再利用、加工、转化和排出,所以发电厂的烟囱或冷却塔排出的蒸发水量十分庞大。能源需求和消费量每年都在增长,迫使发电厂产生更多的电能和热能,导致大量水蒸气和大量污染气体排放,造成了很大的空气污染和水资源浪费。废气流中含有的水分离和回收一方面受到限制,另一方面可以被视为新的水资源。如果工业可以通过收集蒸发的水来补充自己的水循环,并因此使其在进水上的要求最小化,那么更多的水也可以用于其他地方[2]。因此,能够高效回收工业废气中的水的膜冷凝技术成为本课题的研究重点。
1.2目前几种传统收集水技术
目前,通过气体收集蒸发的水的主要传统技术有:冷凝冷却[3,4],液体和固体吸附[5]以及低温分离[6]。
液体吸收法的不足是对环境危害较大,需要投入的资金较多。冷凝法回收水分的确定是得到的水的纯度较低,这导致了其后处理工艺花费大并且要求高;低温分离则因为花费大导致其工艺并不经济实用。另外,回收烟气中的水,传统工艺还存在所需要的设备成本高,设备占地面积大的问题。
相关图片展示: