聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜的制备与性能表征毕业论文
2020-07-02 22:58:16
摘 要
聚酰亚胺是一种性能优良的特种工程塑料,以其优异的热稳定性、耐高温性能性能,是隔热保温领域应用较为广泛的高分子材料。本文研究的聚酰亚胺多孔气凝胶膜结合了聚酰亚胺与气凝胶的特点,热稳定性良好,热传导率低,可长期在高温下使用,耐温范围比较广,是一种良好的隔热保温材料。但是目前关于气凝胶膜的制备不论是在工艺上或是成本上都存在待改进的地方。
本文旨在研究聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜的导热性能,主要工作是将实验工艺简单化,以期通过采用较为简便的工艺制备出综合性能较为优异的聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜。
本实验是通过简单的二步法合成前驱体聚酰胺酸,然后通过相转化法,热亚胺化制备聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜。本实验方法是在传统的聚酰亚胺气凝胶制备方法的基础上通过优化工艺条件,并根据结构与性能的关系,考察了膜结构对聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜性能的影响。其中,本实验选取了铸膜液浓度与膜厚度进行研究。并讨论了铸膜液浓度与膜厚度在相转化过程对膜的孔大小的影响,主要通过改变铸膜液浓度以及在涂膜过程中改变涂膜厚度进行实验,主要在红外、SEM、TAG、力学、导热性能五方面进行表征分析。结果发现,铸膜液浓度会影响相转化的过程中对溶剂/非溶剂间的的置换速率,随着浓度增加,形成的膜结构皮层及支承层致密度提高,从而影响孔的大小。另外,膜厚度会在膜形成的过程中对皮层与支承层的厚度有影响,随着膜的厚度增加,孔隙率减小,制备出的膜收缩率有所降低,膜的结构稳定性增强。本实验通过工艺条件优化对铸膜液浓度13%、14%、15%,膜厚度为150μm、300μm、450μm、600μm进行了考察。实验结果在浓度为15%,涂膜厚度为450μm的条件下制备出导热系数为0.032 W·m-1·K-1的气凝胶膜。
关键词:聚酰亚胺 气凝胶 多孔膜 相转化法 导热系数
ABSTRACT
Polyimide is a kind of special engineering plastic with excellent performance. With its excellent thermal stability and high temperature performance, polyimide is widely used in the field of thermal insulation. The polyimide porous aerogel membrane studied in this paper combines the characteristics of polyimide and aerogel, has good thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, can be used at high temperatures for a long time, and has a wide range of temperature resistance. Good thermal insulation material. However, at present, there are areas for improvement in the preparation of aerogel membranes either in terms of process or cost.
The purpose of this paper is to study the thermal conductivity of polyimide aerogel membranes. The main task is to simplify the experimental process in order to prepare a polyimide aerogel membrane with excellent overall performance through the use of a relatively simple process.
In this experiment, the precursor polyamic acid was synthesized by a simple two-step method, and then the polyimide aerogel film was prepared by phase inversion method and thermal imidization. The experimental method is based on the traditional polyimide aerogel preparation method ,with the method of the optimization of process conditions, and according to the relationship between the structure and performance, the influence of the membrane structure on the performance of polyimide aerogel membrane was investigated. Among them, this experiment selected casting solution concentration and film thickness for research. The effects of casting solution concentration and film thickness on the pore size of the membrane in the phase inversion process were discussed. The experiments were mainly carried out by changing the concentration of the casting solution and changing the film thickness during the coating process.The characterization analysis was performed in five aspects of Infrared, SEM, TAG, mechanics and thermal conductivity. As a result, it was found that the concentration of the casting solution will affect the replacement rate between the solvent and the non-solvent during the phase transformation. As the concentration increases, the density of the formed skin structure and support layer will increase, and the pore size will be affected. In addition, the thickness of the film has an effect on the thickness of the skin layer and the support layer during film formation. As the film thickness increases, the porosity decreases, the shrinkage of the prepared film decreases, and the structural stability of the film increases. In this experiment, the casting film concentrations of 13%, 14%, and 15% and the film thicknesses of 150μm, 300μm, 450μm, and 600μm were investigated by optimization of process conditions. The experimental results show that the aerogel film with the thermal conductivity of 0.032 W·m-1·K-1 was prepared under this conditions: 15% concentration and 450 μm thickness of the film.
KEYWORDS: Polyimide; Aerogel;Porous membrane;Phase transformation method; Thermal conductivity
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 聚酰亚胺 1
1.1.1 聚酰亚胺简介 1
1.1.2 聚酰亚胺性能 1
1.1.3 聚酰亚胺的合成途径 1
1.1.4 聚酰亚胺的应用 2
1.2 气凝胶 3
1.2.1 气凝胶简介 3
1.2.2 气凝胶的发展 3
1.3 聚酰亚胺气凝胶 4
1.4 相转化法制膜 7
1.5 本文研究的内容和意义 8
第二章 聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜的制备 9
2.1 实验仪器与药品 9
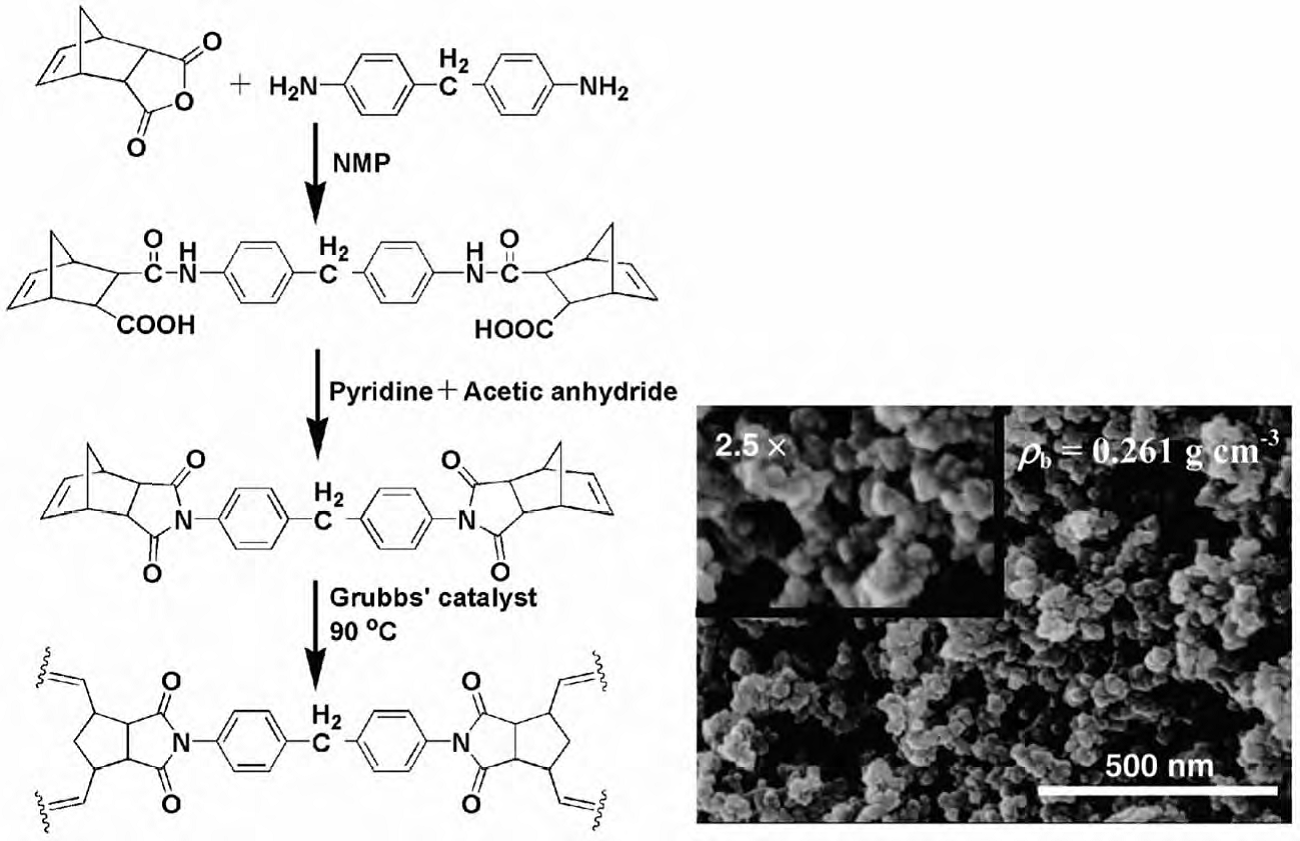
2.2聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜的制备 9
2.2.1 二步法制备聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜 10
2.2.2 工艺条件 10
2.3 表征手段 11
第三章 聚酰亚胺气凝胶膜性能表征结果与分析 13
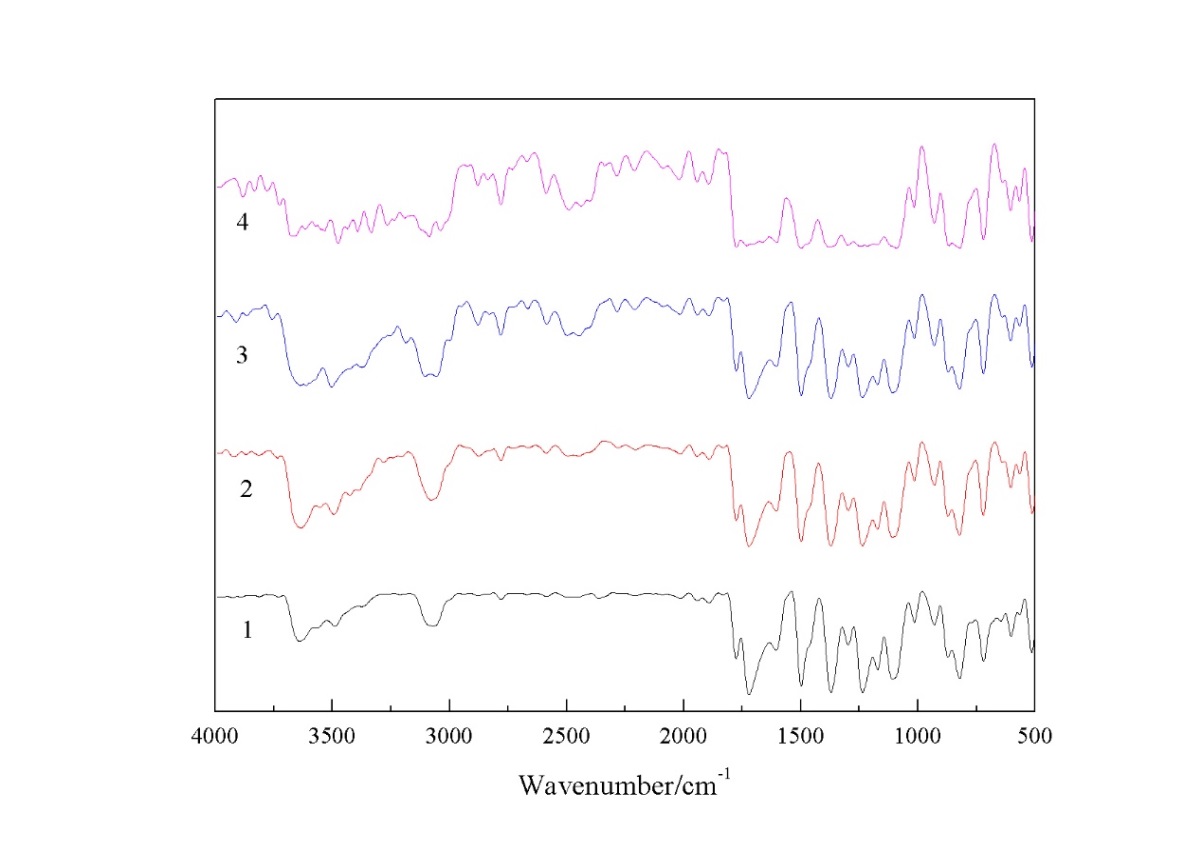
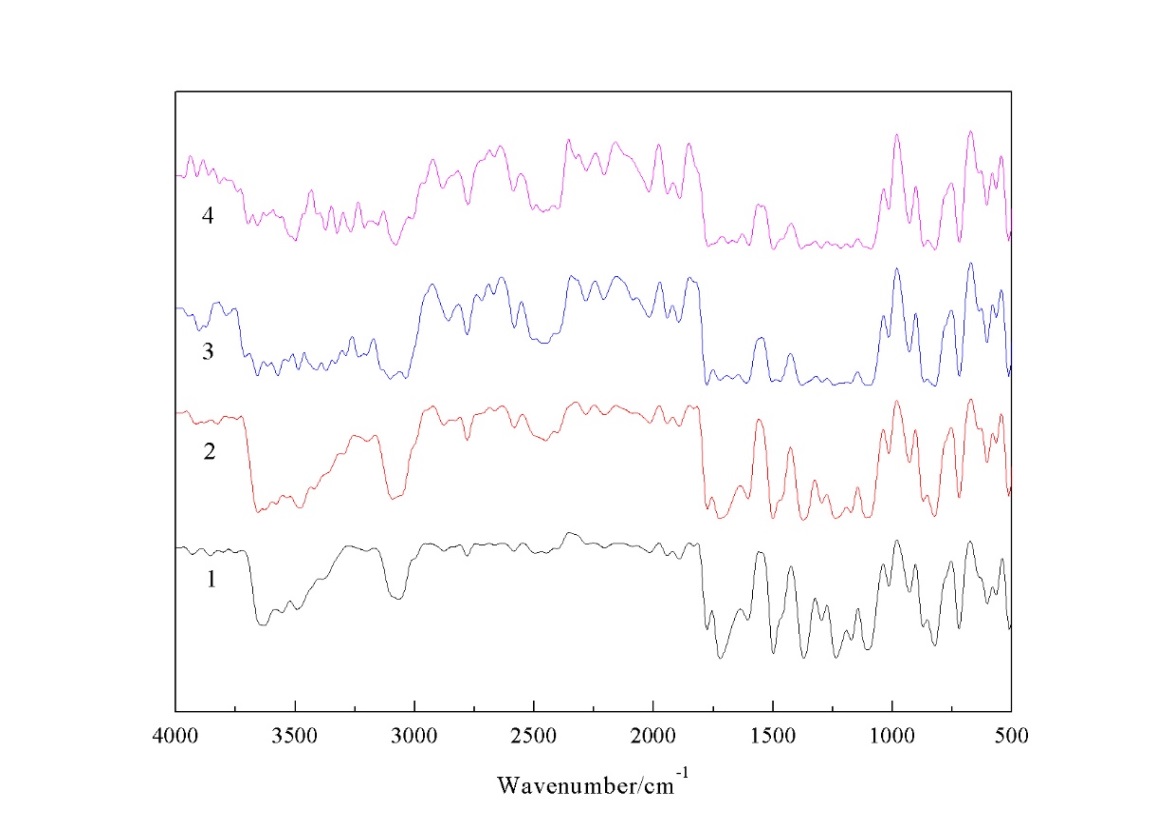
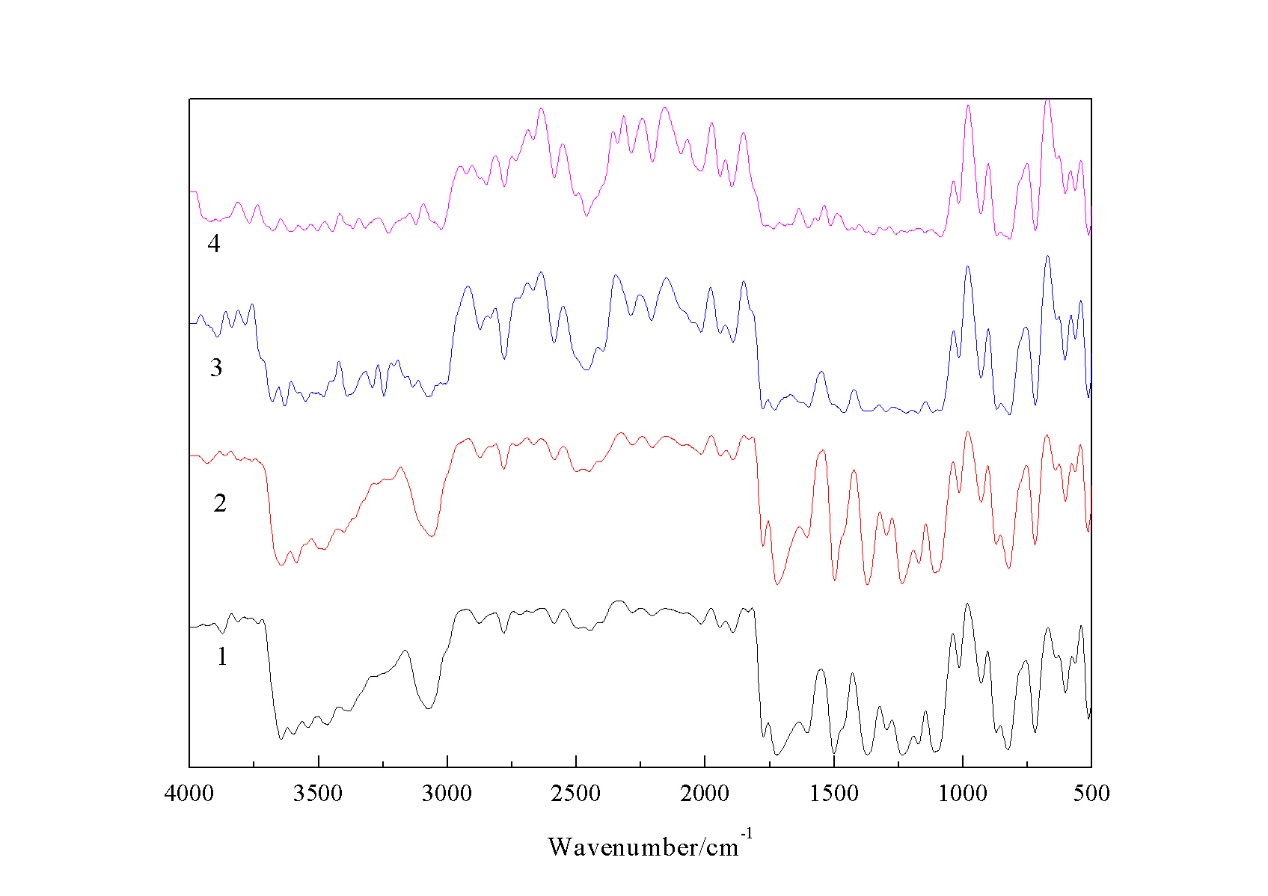
3.1 红外分析 13
3.2 热重分析表征 14
3.3 扫描电镜(SEM)表征 16
3.4 力学性能测试 17
3.5 热导率测试 18
第四章 结论 20
参考文献 21
致谢 23
第一章 文献综述
1.1 聚酰亚胺
1.1.1 聚酰亚胺简介
聚酰亚胺(Polyimide 简称PI)是一种分子链段上含有酰亚胺结构的功能性高分子聚合物,这种有机高分子材料综合性能极佳,尤其突出的是它可承受400℃的高温,不过不可长期暴露于此高温下,否则会缩短其使用寿命;它几乎不导电,可用来做电绝缘材料。聚酰亚胺这种特种工程材料,已在航空,航天,微电子,纳米,液晶,分离膜,激光等领域有广泛应用,因此,聚酰亚胺被列为“21世纪中最有希望的工程塑料之一”[2]。PI自身特有的性能和合成上的优异特点,使得越来越多的人认识到其广阔的应用前景与潜在价值-聚酰亚胺被称为“解决问题的能手”,而且人们认为是它的神奇又优良的性能导致了今天微电子技术的蓬勃发展。
1.1.2 聚酰亚胺性能
聚酰亚胺的综合性能特别优秀,它具有非常优异的抗腐蚀,抗疲劳,耐磨损,耐冲击,密度小,使用寿命长等特点[2]。它在非常低和非常高的温度范围内依然可维持其形态不变,结构非常稳定;它还具有极好的耐蠕变和耐疲劳性,在极为广泛的温度范围内依旧可以保持其性能不变;它的密封性极好,这是由它对溶剂,燃料,以及化学品等具有很强的抗性决定的;它的抗拉强度和弯曲模量高,在280℃高温下依然可保持此性能,有些型号的聚酰亚胺的抗拉强度仅次于碳纤维[1];它的热膨胀系数低,大部分在2×10-5m/K与3×10-5m/K之间,尤为低的可达到10-7m/K;它的电气性能好,介电常数为3.4左右,介电损耗仅为10-3;它的水解能力低,吸水能力弱,将其放入高温水浴中半个月依旧不破损。
1.1.3 聚酰亚胺的合成途径
聚酰亚胺有多种形式和种类,因此它的合成方法也很多,因为二元酐和二胺
原料来源极为广泛,所以其中占主流的方法为由二元酐和二元胺合成,且此方法操作简单。
相关图片展示: