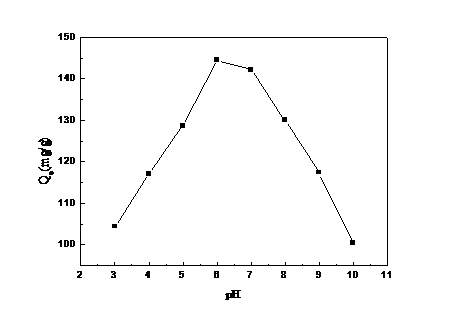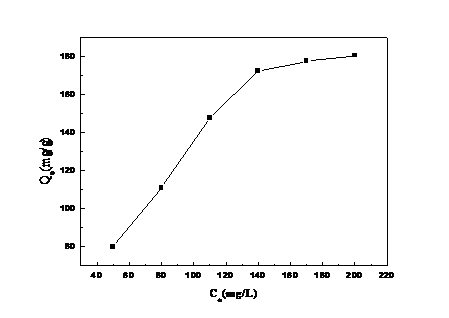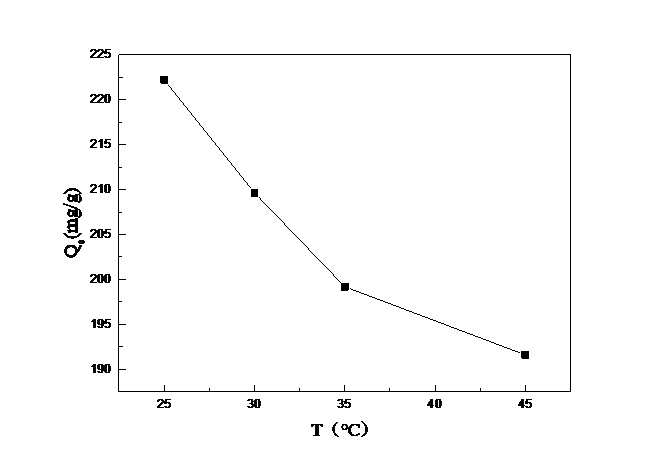氧化石墨烯壳聚糖复合微球对Cu2 的吸附研究毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:48:23
摘 要
由于工业的发展以及人们的大规模生产活动,工业废水去环境的污染日益严重。其中,Cu2 就是一种具有严重危害的物质,它可能会引起人体的各种疾病,乃至死亡。对此,我们不得不采取有效地方法去处理工业废水和其中的Cu2 。目前,比较常见的方法包括离子交换法、膜分离法、沉淀法和吸附法等等。本课题采用的方法是快速、高效、无污染的吸附法。
吸附法之所以具有的快速、高效、无污染等优点,不仅是吸附原理本身的高明,也在于选取的吸附剂的好坏。本课题采用的吸附剂,是含有大量含氧官能团的氧化石墨烯(GO)与含有大量氨基的壳聚糖(CS)反应制备而成。这种反应形成的符合材料,不仅具有GO、CS本身具有的优点,同时又弥补了二者或多或少的缺点,是一种用途广泛的复合吸附材料。而本课题的实验重点,就在于探究吸附时间、吸附温度、初始金属离子浓度、吸附剂用量、吸附pH五个方面对吸附过程的影响。
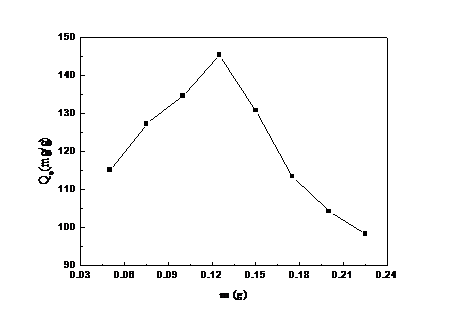
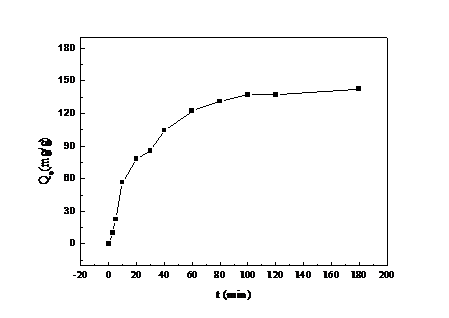
通过实验测定,我们发现制备得到的GO/CS吸附剂在处理含铜离子溶液时,具有以下特征:(1)通过吸附温度和吸附时间的实验结果以及动力学数据拟合,可以看出该吸附过程为放热反应,同时吸附的速率控制步骤为化学吸附反应。(2)通过初始金属离子浓度的实验以及等温模型数据拟合,会发现当浓度提高时,GO/CS复合材料会利用水溶液和材料之间的质量梯度压力来克服传质阻力。与此同时,针对Langmuir模型拟合得到的回归系数更接近于1,也证明了Cu2 在GO/CS上的吸附更倾向于单分子层吸附。(3)吸附pH、吸附剂用量的实验,使我们得到在实验中吸附反应的最佳条件为pH=6,吸附剂用量为0.125 g。这些实验数据,一方面证明了实验所制备的GO/CS复合材料对Cu2 具有良好的吸附性能,可以在工业废水处理中起到很大的作用;另一方面也有助于我们深入了解吸附反应的原理和条件,利于对其进行进一步的研究、改进。
关键词:含Cu2 废水处理 吸附 复合材料
Adsorption Of Cu2 On Graphene Oxide / Chitosan Composite
Microspheres
Abstract
Due to industrial development and people's large-scale production activities, the pollution of industrial waste water to the environment has become increasingly serious.Among them, Cu2 is a substance with serious hazards. He may cause various diseases and even death.In this regard, we have to take effective measures to treat industrial waste water and Cu2 .At present, the more common methods include ion exchange method, membrane separation method, precipitation method, adsorption method and the like, which are the preferred methods for treating industrial waste water.The method used in this topic is the adsorption method.
Adsorption method has the advantages of fast, high efficiency, no pollution, not only is the adsorption principle itself smart, but also lies in the quality of the selected adsorbent.The adsorbent used in this project was prepared by reacting graphene oxide (GO) containing a large amount of oxygen-containing functional groups with chitosan (CS) containing a large amount of amino groups.The conformal material formed by this reaction not only has the advantages of GO and CS itself, but also compensates for more or less shortcomings. It is a composite adsorption material with a wide range of applications.The research focus of this topic is to explore the adsorption capacity of the GO/CS composite in various complex environments, including pH, adsorbent dosage, adsorption time, adsorption temperature, and initial metal ion concentration.The focus of this project is to explore the effects of adsorption time, adsorption temperature, and initial metal ion concentration on the adsorption process.
Through the experimental measurement, we found that the prepared GO/CS adsorbent has the following characteristics in the treatment of copper ion-containing solutions:(1) Through the experimental results of adsorption temperature and adsorption time and the kinetic data fitting, it can be seen that the adsorption process is an exothermic reaction, and the adsorption rate control step is a chemical adsorption reaction.(2) Through the initial metal ion concentration experiment and isothermal model data fitting, it is found that when the concentration is increased, the GO/CS composite will use the mass gradient pressure between the aqueous solution and the material to overcome the mass transfer resistance.At the same time, the regression coefficient for the Langmuir model fitting is closer to 1 and it is also proved that the adsorption of Cu2 on GO/CS is more prone to monolayer adsorption.(3) The experiment of adsorbing pH and adsorbent dosage gave us the optimum conditions for the adsorption reaction in the experiment: pH=6, and the adsorbent dosage was 0.125 g.These experimental data, on the one hand, prove that the GO/CS composites prepared by the experiment have good adsorption properties for Cu2 and can play a significant role in industrial wastewater treatment.On the other hand, it also helps us to understand in depth the principles and conditions of adsorption reactions, which will facilitate further research and improvement.
Key Words: Cu2 Sewage treatment; Adsorption; Composite materials
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 重金属离子的危害 1
1.2 重金属离子的治理手段 1
1.2.1 物理处理法 1
1.2.2 化学处理法 2
1.2.3 生物处理法 2
1.3 吸附法优点及氧化石墨烯与壳聚糖结合的优点 2
1.3.1 吸附法介绍及优点 2
1.3.2 氧化石墨烯结合壳聚糖的优点 3
1.4 GO/CS复合材料的研究进展 4
1.4.1 氧化石墨烯/壳聚糖的研究概况 4
1.4.2 氧化石墨烯/壳聚糖的研究应用 4
1.5 研究内容 5
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1 仪器及试剂 6
2.1.1 仪器 6
2.1.2 药品和试剂 6
2.2 制备实验 6
2.3 吸附影响条件实验步骤 7
第三章 实验结果与分析 10
3.1 吸附影响条件 10
3.1.1 pH的影响 10
3.1.2 吸附剂用量对吸附量的影响 11
3.1.3 金属离子浓度对吸附量的影响 12
3.1.4 吸附时间对吸附量的影响 12
3.1.5 吸附温度对吸附量的影响 13
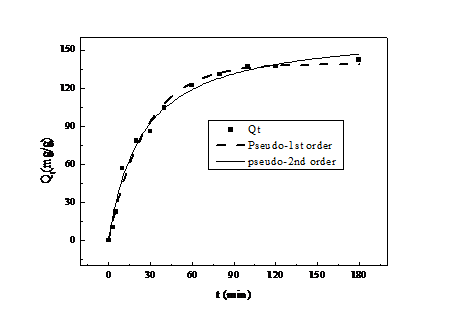
3.2 吸附动力学 14
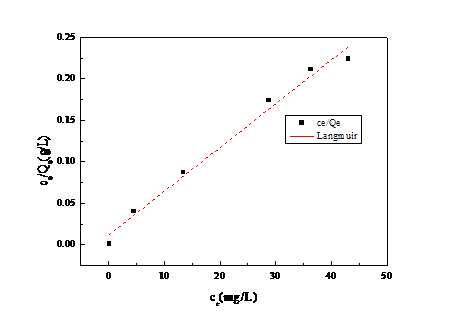
3.3 吸附等温模型 16
第四章 结论 18
参考文献 19
致谢 21
第一章 文献综述
1.1 重金属离子的危害
随着工业的发展,环境污染越来越严重,水污染问题已经成为当今最严重的问题之一。废水中的重金属离子及染料的成分相对复杂,毒性大色度深、并且难于生化降解,若不经处理会对自然生态环境造成极大地破坏。流入水体会对水生生物产生毒害作用,对水体的气体溶解度和水体透光率造成影响,影响水生植物的光合呼吸作用和水生动物的生长繁殖。并且,累计在水生动植物体内的重金属离子及有毒物质,通过生物链的传递,会进入人体,可诱发崎形、癌变,危害人类的健康[1]。例如铜会通过对人体短期或长期接触产生严重的毒性作用,如胃肠道疾病、呕吐、痉挛、抽搐、甚至死亡。因此,探索新型高效的污水处理工艺是非常有必要的。
1.2 重金属离子的治理手段
处理重金属废水与染料废水的方法目前主要有三大类[2]:一、物理处理法,即不改变化学形态实现对金属离子与染料污染物分子的去除;二、化学处理法,改变重金属离子或染料分子的化学形态通过化学方法去除;三、生物处理法、借助水生生物的新陈代谢作用对重金属离子与染料分子进行处理的方法。
1.2.1 物理处理法
1. 溶液萃取分离法
萃取分离法是利用重金属离子在水中和在有机相中具有不同的溶度积而使其浓缩于溶剂中,从而使其去除的方法[3]。由于萃取效果主要取决于萃取剂的性质,因此,选择分离性好、萃取能力大、容易回收溶质的萃取剂尤为重要。尽管如此,萃取分离法存在着成本高、溶剂流失严重、能源消耗大等缺点。
2. 膜分离法
膜分离技术是指在压力的驱动下利用高分子的选择性对废水中的某些成分进行渗透,将溶质和溶剂分离的方法。主要包括扩散超滤、隔膜电解、纳滤、反渗透等种类。膜分离过程对温度需求小,常温就可以进行,并且具有装置简单、操作方便、易维护且可实现重金属的回收利用、无二次污染等优点。
吸附法
吸附法主要利用吸附材料的特性,是溶液的污染物通过自由能的吸引聚集在吸附材料的表面或内部,从而完成对污染物的部分去除。吸附法是一种简单、有效的方法。但需要选取合适的吸附剂,以及控制吸附过程的外部条件,不然很难完成有效的去除。
1.2.2 化学处理法
化学处理法是通过化学反应,达到去除金属离子的目的,包括电解法和沉淀法。工业废水常用的处理方法为沉淀法。
化学沉淀法通过加入特殊的沉淀剂,与溶液中的重金属离子反应生成难溶或不容的物质,最后得到的沉淀物进行处理。这种方法比较常用,但面对浓度低的废水就难以起到效果。并且沉淀物的处理也是一大难题。
1.2.3 生物处理法
生物法是指利用动植物和微生物的新陈代谢并经过富集、絮凝和沉积等作用对水中重金属离子进行去除的方法[3]。其主要依靠的是微生物的细胞,它可以讲水中的金属离子聚集并运输到细胞内部,已达到取出的目的。这种方法虽无毒害且环境友好,但细胞培育复杂难以适应苛刻的环境。
1.3 吸附法优点及氧化石墨烯与壳聚糖结合的优点
1.3.1 吸附法介绍及优点
吸附法主要是利用吸附材料的高比较面积和高孔隙率的特性,使溶液中的重金属离子或染料等溶质在吸附剂的表面或者内部聚积,完成对污染物的去除。当液相中的重金属离子或染料等溶质碰撞到吸附剂表面时,由于受到表面上自由能的吸引而被截留下来,通过分离可使污染物被去除。吸附剂和被吸附物质的作用方式主要包括以下三种:物理吸附、化学吸附、离子交换吸附[4],[5]。(1)其中,物理吸附主要依赖于分子间引力(范德华力、静电力)相互作用;(2)化学吸附则是需要当吸附剂和吸附质发生化学反应时,才会产生作用力。所以化学吸附需要的活化能高,速率慢;(3)离子交换吸附经由静电吸引作用使金属离子聚集在吸附材料表面。一般情况下,重金属离子的吸附作用主要是依靠化学吸附或离子交换吸附。
相关图片展示: