不同粒径大小PAM微球的连续制备毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:51:32
摘 要
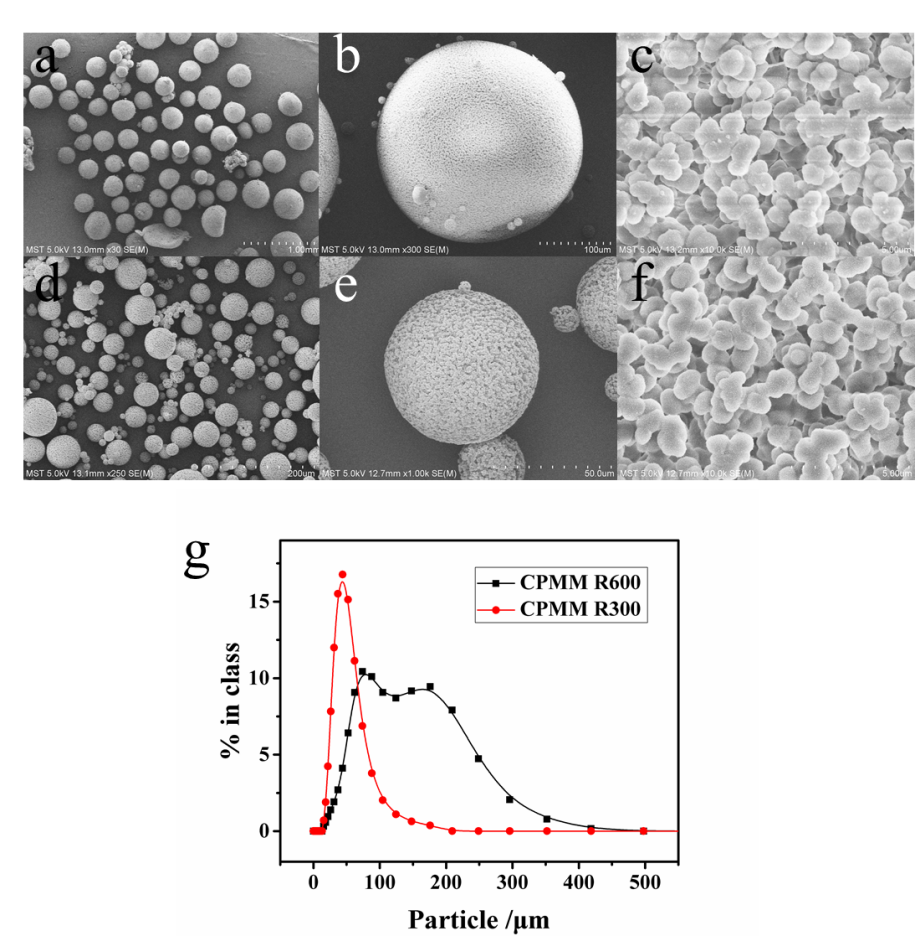
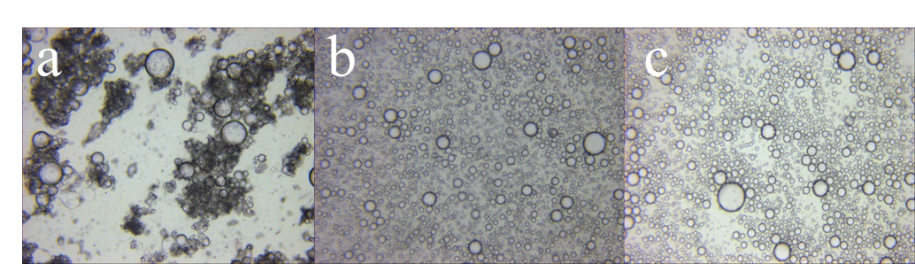
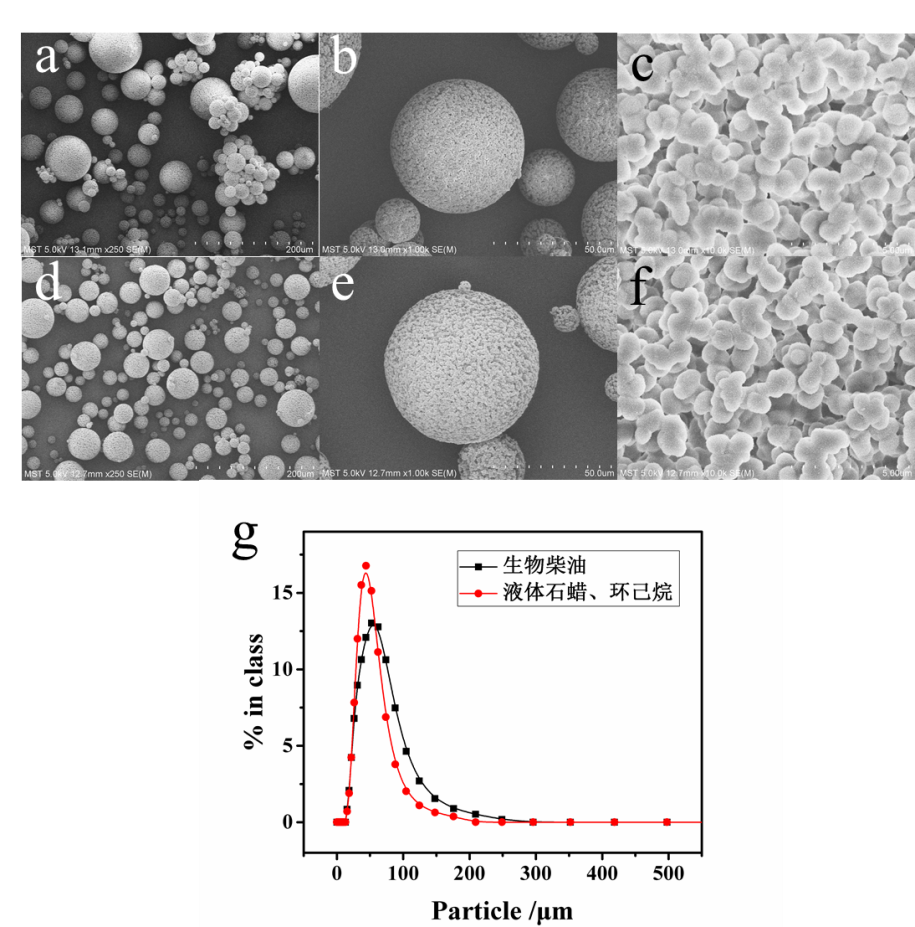
聚合物微球在药物传递、催化、太阳能电池、传感器等领域的应用非常普遍,其中聚丙烯酰胺微球由于其更加复杂的结构而使其在应用方面具有更多的优势。然而目前制备这种微球的方法步骤较多且繁杂,一般分为悬浮聚合法、反相乳液聚合法、分散聚合法等。近几年来,微流体技术在多种形貌和结构高分子材料的制备方面显现出优异的灵活性和可调性,所以本实验采用微混合器技术制备聚丙烯酰胺微球,制备连续且在传质传热方面效果好,具有较高的产品转化率和选择性。考察了微混合器装置及其混合方式、连续相与分散相的流速比、两相总流速以及单体含量对PAM微球粒径大小的影响,可得出混合强度越强、流速比越大、总流速越大以及单体量越高,得到的PAM微球尺寸越小,粒径分布相对较窄。通过调变微混合器混合通道的尺寸,使用CPMM R600微混合器,水相和油相的流速大小分别为5、25 ml/min,制得的PAM微球平均粒径为290 μm且粒径分布较窄。使用CPMM R300微混合器制备PAM微球,通过调变油相和水相流速比分别为3:1、9:1,总流速为30 ml/min时,制备的PAM微球的平均粒径分别为103.2、40.20 μm且粒径分布相对较窄;保持油水两相流速比为5:1,将总流速增大至48 ml/min时,制得PAM微球30.44 μm且粒径分布相对较窄。使用CPMM R300微混合器制备PAM微球,聚合反应时间从3 h缩短至20min,大大的缩短制备时间,实现了PAM微球连续高效制备。
关键词:聚合物微球 聚丙烯酰胺 粒径分析 微混合器技术 连续高效制备
Abstract
Polymer microspheres are widely used in the fields of drug delivery, catalysis, solar cells, sensors, etc. Among them, polyacrylamide microspheres have more advantages in application due to their more complex structure. However, at present, the method for preparing such microspheres has many steps and is complicated. Generally, it is divided into a suspension polymerization method, an inverse emulsion polymerization method, a dispersion polymerization method, and the like. In recent years, microfluidic technology has shown excellent flexibility and tunability in the preparation of a variety of morphological and structural polymer materials, so in this experiment, micro-mixer technology was used to prepare polyacrylamide microspheres to prepare continuous and Good mass transfer and heat transfer, with high product conversion and selectivity. The effects of the micromixer device and its mixing method, the ratio of the flow rate of the continuous phase to the dispersed phase, the total flow rate of the two phases, and the monomer content on the particle size of the PAM microspheres were investigated. The stronger the mixing strength and the greater the flow rate ratio, the higher the mixing intensity. The larger the total flow rate and the higher the monomer amount, the smaller the size of the obtained PAM microspheres and the narrower the particle size distribution. By adjusting the size of the micromixer mixing channel, the CPMM R600 Micromixer was used. The flow rates of the aqueous phase and the oil phase were 5 and 25 ml/min respectively. The average particle size of the PAM microspheres was 290 μm and the particle size was obtained. The distribution is narrow. Preparation of PAM microspheres using a CPMM R300 micromixer. The average particle size of the prepared PAM microspheres was determined by adjusting the ratio of the oil and water phase ratios to 3:1, 9:1, respectively, and the total flow rate to 30 ml/min. It is 103.2 and 40.20 μm and the particle size distribution is relatively narrow. When the ratio of the oil-water two-phase flow rate is 5:1 and the total flow rate is increased to 48 ml/min, the PAM microspheres are 30.44 μm and the particle size distribution is relatively narrow. . The PAM microspheres were prepared using the CPMM R300 Micromixer. The polymerization time was shortened from 3 h to 20 min. The preparation time was greatly shortened, and continuous and efficient preparation of PAM microspheres was achieved.
KEYWORDS: Polymer;microspheres;Polyacrylamide;Particle size analysis;Micro-mixer technology;Continuous efficient preparation
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2聚合物微球 1
1.2.1聚合物微球简介 1
1.2.2聚合物微球制备方法 2
1.3 PAM微球 5
1.3.1 PAM简介 5
1.3.2 PAM微球的性能及应用 5
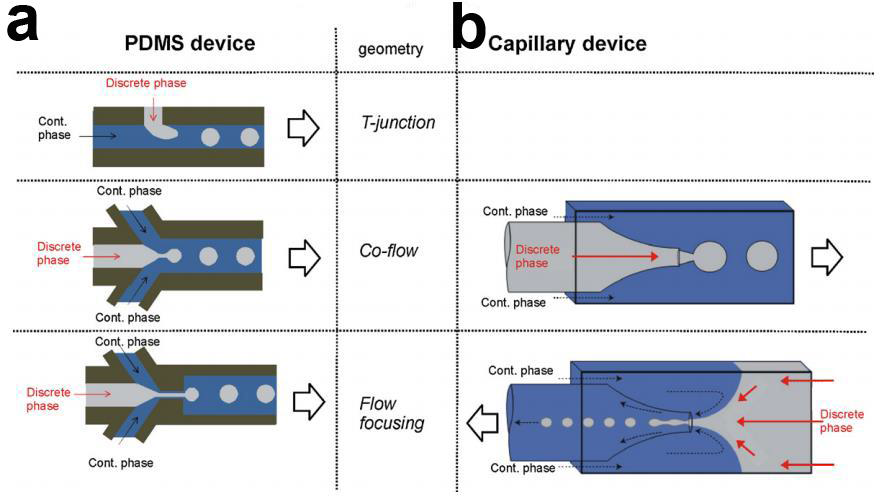
1.4微流体技术在微球制备方面的研究 6
1.5本文研究目的和内容 7
第二章 实验部分 9
2.1实验试剂及仪器 9
2.2实验流程 10
2.2.1实验装置图 10
2.2.2溶液的配置 10
2.2.3液滴制备 11
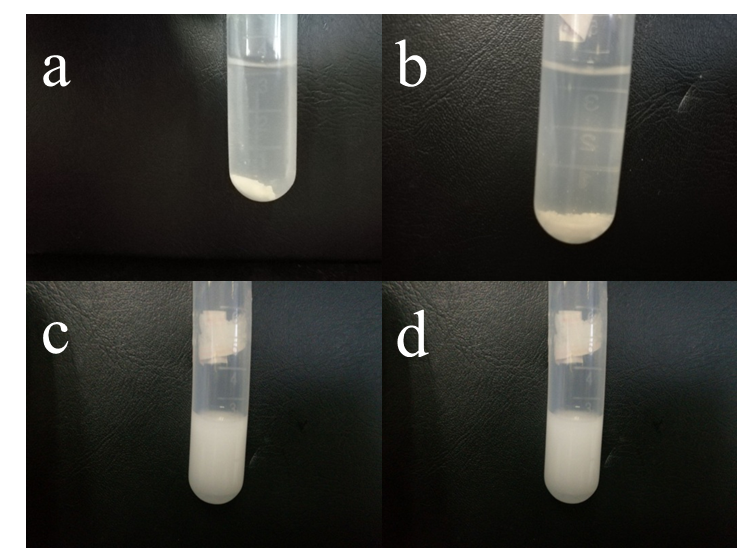
2.3.4样品洗涤及干燥 11
2.3样品表征与分析 11
第三章 结果与讨论 13
3.1引言 13
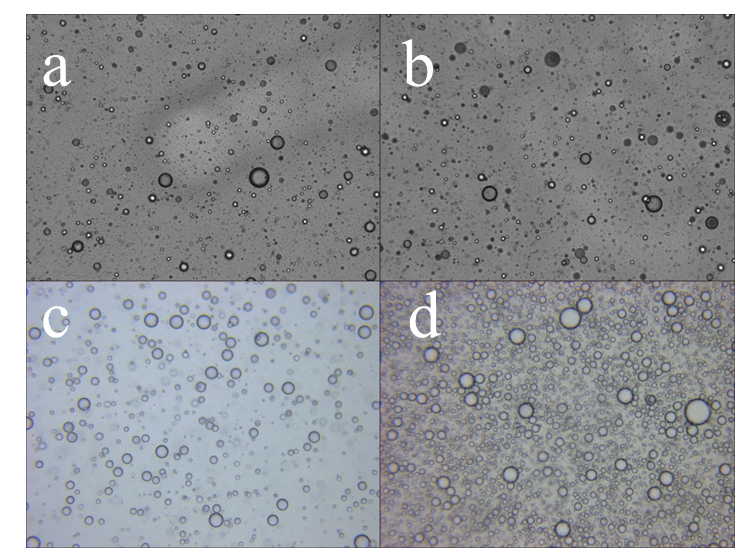
3.2微混合器类型及其混合方式的影响 13
3.3连续相的选择 16
3.4流速比的影响 18
3.5总流速大小的影响 20
3.6丙烯酰胺(AM)含量的影响 22
第四章 结论 25
参考文献 27
致 谢 31
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)是一种有着广泛应用前景的水性聚合物,通过与分散在溶液中的悬浮微粒架桥吸附,可形成具有极强絮凝作用的絮体,因此PAM微球在机械强度、抗污等方面有着良好表现,且其特性堆积比高,常被选作合成复合微球等载体或模板,在理论和实践中具有较高的研究价值与发展空间[1]。
随着各国对生态环境的重视,PAM在污水处理方面的应用也越来越强。作为一个人口数量多、人均淡水量少的大国,我国对水资源的管理更是尤为重视。“十二五”规划中建设和改建污水处理厂等项目被列为政府部门重点排查对象,新修订的《环境保护法》、《环境影响评价法》也在不断预防和解决造成的水污染问题。由于PAM在城市及工业环节处理污水的作用不可替代,其需求量逐年升高,像大庆、宝莫、天润生产PAM的企业在发展中已跻身为世界前列,这也越来越促进了对PAM的研究。而研究中,其孔隙度和孔径等性质与其应用方面要求不尽相同,因而,制备不同粒径大小的PAM微球对现代工业进步具有极其重要的意义。
1.2聚合物微球
1.2.1聚合物微球简介
聚合物微球通常指直径在纳米级或微米级,形状为球形或其他几何形状的高分子材料或高分子复合材料[2]。而由于不同工艺方法制备的聚合物微球,其形貌上的孔隙率也受调控,可分为有孔的聚合微球和无孔的聚合微球。在实际应用中因为多数的无孔微球在其内部分布着孔结构,在相比于有孔的聚合微球,不利于制备,且在应用上也利用率较低,因此本课题对聚合物的研究主要以有孔微球为主。通过对有孔微球孔径及孔隙率的分析调变,其应用效果将进一步被放大。在调变有孔微球的制备方法上,目前应用较多的是化学工艺上的调变,但也有物理方法作为补充,两者互相影响。下面则对这两种工艺方法进行简单介绍。物理方法是在物质聚合过程中制备聚合物微球,不经过物质的单聚或多聚,只在物质物理性质上作出改变,一般比较常见的有乳化-固化法,沉淀法以及喷雾干燥法。而化学方法则种类较多,不同种制备方法下各有其优点,但总体而言都是经过了化学合成这一基本步骤,聚合的微球在乳液、悬浮液、分散液中各表现出不同的性质,具有十分广泛的研究性。考虑到聚合物微球尺寸小、比表面积大及易被功能化等优良特性,其被广泛应用在生物医药、生物催化以及太阳能电池制备等领域[3]。
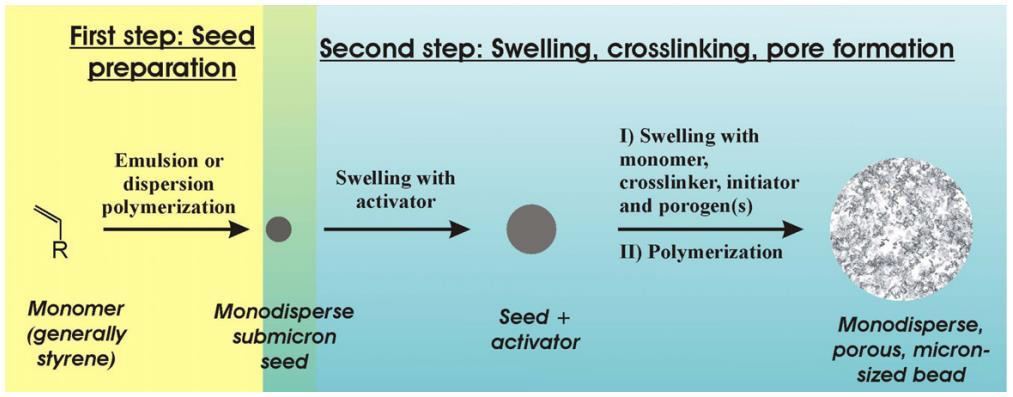
1.2.2聚合物微球制备方法
聚合物微球在药物传递、催化、太阳能电池、传感器等领域的应用非常普遍,其在应用方面具有更多的优势,目前制备聚合物微球的方法较多,下面对制备方法做简要介绍:
相关图片展示: