碳化ZIF-8对单宁酸吸附性能的研究毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:51:38
摘 要
金属-有机骨架材料因其高比表面积、丰富的金属/有机种类及结构和组成的可调性,是制备具有多种孔道结构和表面功能的碳基纳米材料的理想的自我牺牲模板和前驱体。最近有文献报道,通过碳化ZIF-8得到的纳米多孔碳(NZIF-8)因其丰富的孔结构和良好的化学稳定性,对水中亚甲基蓝、环丙沙星和杀虫剂具有优异的的吸附能力。为此,本论文试图拓展NZIF-8对废水中有机大分子物质的吸附,研究了其对单宁酸的吸附。
在NZIF-8用于吸附单宁酸研究方面,优化了碳化ZIF-8纳米颗粒的温度对得到的NZIF-8纳米颗粒对单宁酸吸附的影响,发现碳化温度为750 oC时得到的NZIF-8纳米颗粒对单宁酸吸附量最大;在3h内对单宁酸达到吸附饱和。进一步探究了吸附温度、单宁酸初始浓度、吸附剂用量、吸附时间、离子强度等因素与NZIF-8纳米颗粒吸附单宁酸的关系,获得相应的平衡吸附数据,可用Langmuir模型可以很好的描述,并得到其最大吸附量为977.76 mg/g,高于活性炭、沸石、碳纳米管等的最大吸附量。采用拟二阶方程对吸附动力学数据进行拟合。吸附后的NZIF-8纳米颗粒在pH为9的水溶液中进行脱附,再用于单宁酸的吸附,吸附量略有下降,循环5次,吸附量维持在92%以上。
关键词: 吸附 多孔碳 纳米颗粒 单宁酸
ABSTRACT
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have proved to be promising self-sacrificing templates and precursors for preparing various carbon-based nanomaterials, benefiting from their high BET surface areas, abundant metal/organic species, and extraordinary tunability of structures and compositions. It is recently reported that, nano-porous carbon (NZIF-8) obtained by carbonized ZIF-8 has excellent adsorption ability to methylene blue, ciprofloxacin and insecticides in water, due to its rich pore structure and good chemical stability. Further, to expand the adsorption of organic macromolecules in wastewater by NZIF-8, the adsorption of tannic acid was studied.
For adsorption of tannic acid by NZIF-8, the effect of temperature of carbonized ZIF-8 nanoparticles on the adsorption of tannic acid was examined. It was found that the adsorption capacity of NZIF-8 nanoparticles to tannic acid was the largest when the carbonization temperature was 750 oC. The adsorption saturation of tannic acid was achieved within 3 h. The relationship between adsorption temperature, initial concentration of tannic acid, amount of adsorbent, adsorption time, ionic strength and the adsorption of tannic acid by NZIF-8 nanoparticles was further investigated. The corresponding equilibrium adsorption data were obtained, which can be described by Langmuir model. The maximum adsorption capacity is 977.76 mg/g, which is higher than those on activated carbon, zeolite and carbon nanotubes. The adsorption kinetic data were fitted by quasi second order equation. The adsorbed NZIF-8 nanoparticles were desorbed in aqueous solution with pH 9, and then used for the adsorption of tannic acid. The adsorption capacity decreased slightly, and the adsorption capacity remained above 92% after 5 cycles.
KEYWORDS:Adsorption;Porous carbon;Nanoparticles;Tannic acid
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.1 多孔碳材料的制备研究 1
1.1.2 含单宁酸废水处理的研究方法 4
1.2 本文研究目的和内容 10
第二章 实验部分 11
2.1 实验原料及仪器 11
2.2 ZIF-8碳化得到NZIF-8纳米颗粒及其吸附性能的研究 11
2.2.1 ZIF-8纳米颗粒的制备 11
2.2.2 NZIF-8纳米颗粒的制备 12
2.2.3 NZIF-8纳米颗粒对单宁酸吸附性能的研究 12
2.3 表征与分析 12
第三章 ZIF-8碳化得到NZIF-8纳米颗粒及其吸附性能的研究 15
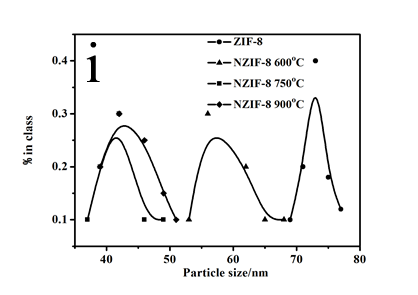
3.1 ZIF-8晶体和NZIF-8纳米颗粒的表征 15
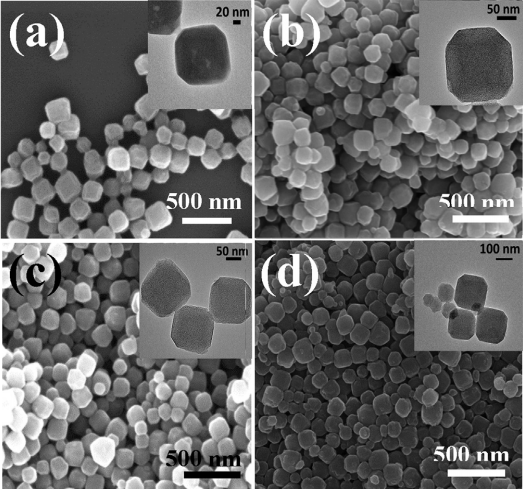
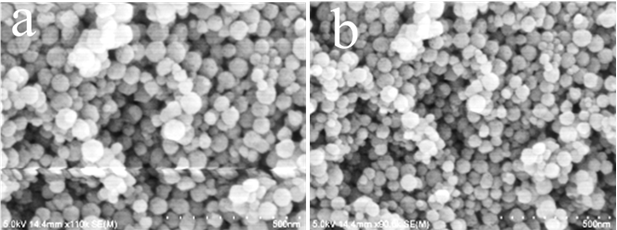
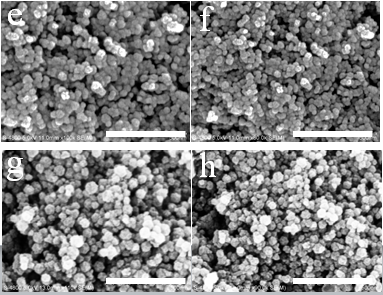
3.1.1 ZIF-8晶体和NZIF-8纳米颗粒的电镜表征 15
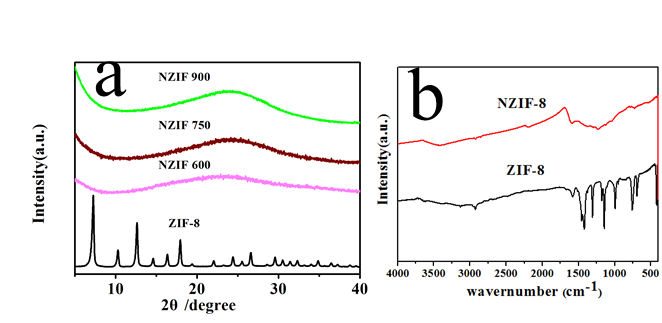
3.1.2 ZIF-8、NZIF-8纳米颗粒的XRD和FT-IR表征 17
3.1.3 NZIF-8纳米颗粒的比表面积和孔径表征 17
3.2 NZIF-8纳米颗粒对单宁酸吸附性能的研究 18
3.2.1 碳化温度的影响 18
3.2.2 溶液温度的影响 19
3.2.3 溶液浓度的影响 20
3.2.4 吸附剂用量的影响 22
3.2.5 溶液pH的影响 23
3.2.6 离子浓度影响 23
3.2.7 吸附剂的再生及循环利用 24
3.3 小结 25
第四章 结论与展望 27
4.1 结论 27
4.2 展望 27
参考文献 29
致 谢 33
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
近几年来,天然有机物和药物作为复杂的非均质有机混合物,普遍存在于地面、地下水中,对饮用水的处理和环境产生了不利的影响。混凝、吸附、氧化、膜、生物处理和光催化等多种处理方法已广泛应用于水净化工艺中[1]。其中,吸附分离法作为一种高效、经济、简便、可操作性强的净水方法,长期以来在各个方面都得到了广泛的研究和应用[2]。对于吸附分离法来说,性能优异对吸附剂的选择无疑是第一位的,而多孔碳材料因拥有丰富的孔道结构、良好的稳定性和较高的比表面积被大量地应用于从水溶液中移除有机物[3]和药物[4]。
最近,由于具有高比表面积和孔体积,基于MOFs为模板或前驱体制备的纳米碳材料已经得到广泛的应用[5]。基于MOFs制备得到的多孔碳骨架材料仍具有高比表面积和丰富的孔道结构,并且具有很大的潜在应用价值。一般地,通过对MOFs进行热分解形成多孔的碳材料。比如,MOF-5和它派生的MOF碳系列材料[6],ZIF-8和它派生的ZIF碳系列材料[7]以及含Al的MOF碳系列材料[8]等已经被广泛应用在气体存储、电容器、染料电池、传感器和催化剂等[9]。然而基于MOFs得到的纳米多孔碳材料应用于水处理方面的研究较少,因此仍需开发其在该领域的中更多应用。
相关图片展示: