磁性离子筛的合成研究毕业论文
2020-07-07 22:16:21
摘 要
金属锂作为21世纪重要的能源材料,被广泛应用于各种行业,包括冶金、润滑脂和润滑剂、铝的生产、医药和锂离子电池工业。近年来,市场对锂的需求逐年增加。盐湖以及海水中都储藏着丰富的锂资源,目前工业提锂还是以盐湖卤水为主要原料。盐湖卤水中锂的含量较高,资源丰富以及提取成本低廉,在所有的锂离子提取方法中,吸附法以其最环保、工艺简单和成本低廉的优点脱颖而出,被公认为是从海水和盐湖卤水中回收锂的最有前途的方法之一。尖晶石型锂吸附剂(来源于尖晶石型锂锰氧化物)是从卤水和海水中提取锂的极具应用前景的锂离子筛分吸附剂,具有选择性高、毒性低、成本低和化学稳定性高等优点,有望用于高镁锂比的盐湖卤水中提取锂。
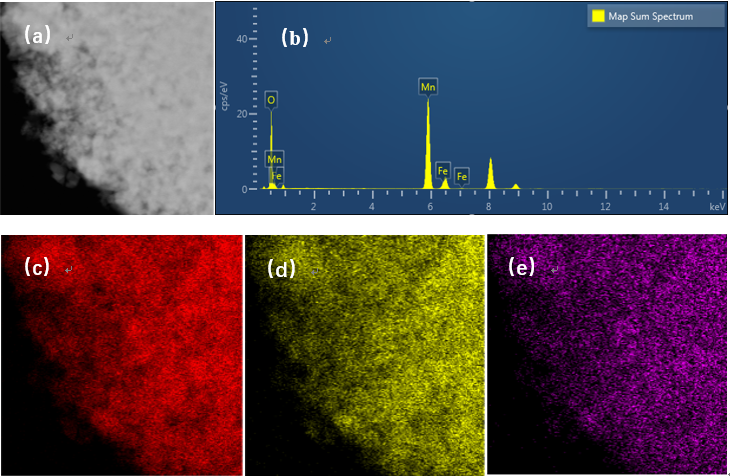
为了克服离子筛的回收困难的问题,本文主要讲述Fe3O4改性Li1.6Mn1.6O4型离子筛的方法及对其吸附性能的研究,探究掺杂量对制得离子筛的结构及其吸附性能的影响,对吸附和脱附实验数据进行分析,得出掺杂量为0.1g就可以使得固液分离,该操作方法简单和成本低廉,而且对离子筛晶体结构的影响不大。通过EDS可以发现,Fe3O4成功生长在晶体内部且分布均匀。吸附脱附实验说明Fe3O4的掺杂对离子筛的吸附性能影响不大。拟合吸附等温线得出LMO-0.1对Li 的吸附是一个化学过程,且LMO-0.1表面仅发生单分子层吸附。对前驱体、离子筛和吸附后的样品进行XRD表征发现晶体结构没有发生明显的变化。最后对HMO-0.1进行稳定性研究,5次循环之后吸附量仍然接近首次吸附量的80%,表明掺杂Fe3O4后的离子筛稳定性较高,从富锂溶液提锂的过程中,该离子筛可以实现循环使用,从而实现工业化应用。
关键词:改性 离子筛 吸附 脱附 稳定性
Abstract
As an important energy material in the 21st century, lithium metal is widely used in various industries, including metallurgy, grease and lubricants, aluminum production, medicine and lithium ion battery industry. In recent years, the market demand for lithium has increased year by year. Salt lake and sea water are rich in lithium resources. At present, the main raw material is salt lake brine. The content of lithium in brine of salt lake is high and the cost of extraction is low. Among all the methods of extracting lithium ion, adsorption method stands out because of its environmental protection, simple process and low cost. It is recognized as one of the most promising ways to recover lithium from seawater and salt lake brine. Spinel lithium adsorbent (derived from spinel lithium manganese oxide) is a promising lithium ion sieving adsorbent for lithium extraction from brine and seawater. It has the advantages of high selectivity, low toxicity, low cost and high chemical stability. It is expected to be used to extract lithium from brine of salt lake with high ratio of magnesium to lithium.
In order to overcome the difficulty of recovering ion sieve, this paper mainly describes the preparation of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 ion screen doped with Fe3O4 and its adsorption performance, and probes into the influence of doping amount on the structure and adsorption performance of the ion screen. By analyzing the experimental data of adsorption and desorption, it is concluded that the solid-liquid separation can be made when the doping amount is 0.1g, the operation method is simple, the cost is low, and the crystal structure of the ionic sieve is not affected much. It can be found by EDS that Fe3O4 successfully grows in the crystal and its distribution is uniform. The adsorption and desorption experiments show that the doping of Fe3O4 has little effect on the adsorption performance of the ion sieve. By fitting the adsorption isotherm, it is found that the adsorption of Li on the magnetic lithium-ion sieve with doping amount of 0.1 g is a chemical process, and only monolayer adsorption occurs on the adsorbent surface. Finally, the stability of magnetic lithium-ion screen with doping amount of 0.1 g is studied. The results show that the stability of the ion sieve doped with Fe3O4 is high. In the process of extracting lithium from lithium-rich solution, the ion screen can be recycled and used in industry.
Keywords:Modification;Ionic sieve;Adsorption;Desorption;Stability;
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract i
目录 1
第1章 文献综述 1
1.1课题背景 1
1.2盐湖提锂技术研究进展 1
1.3锂离子筛的概念 2
1.4锂离子筛研究进展 3
1.4.1锰系锂离子筛现状 3
1.5改性锂锰氧化物离子筛 4
1.6课题的主要内容及研究意义 5
第2章 Fe3O4改性离子筛的性能研究 7
2.1引言 7
2.2实验部分 7
2.2.1实验试剂 7
2.2.2实验仪器 8
2.2.3实验步骤 8
2.2.4样品表征 10
2.3结果与讨论 12
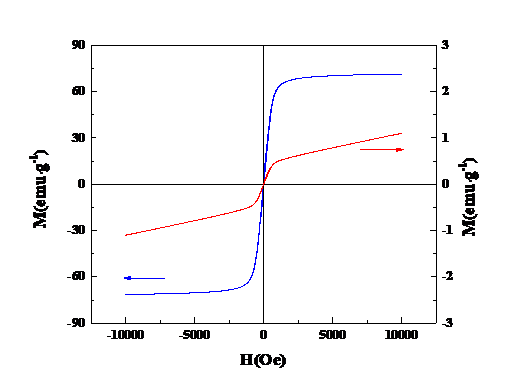
2.3.1掺杂量对离子筛前驱体以及磁性能的影响 12
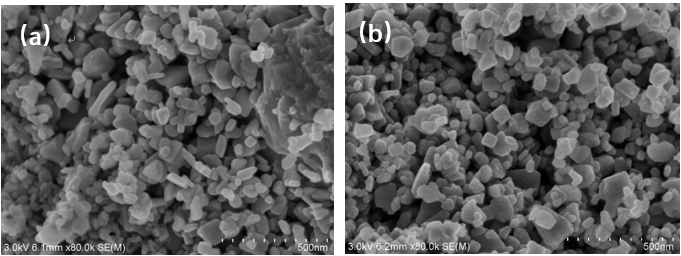
2.3.2 形貌分析 14
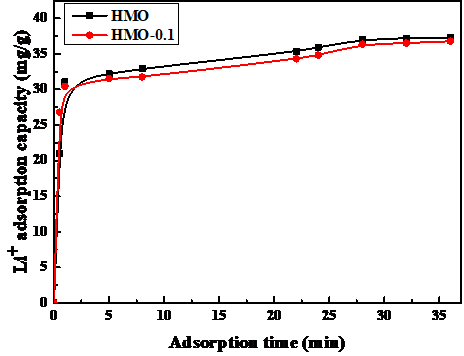
2.3.3 Fe3O4改性离子筛吸附性能测定 15
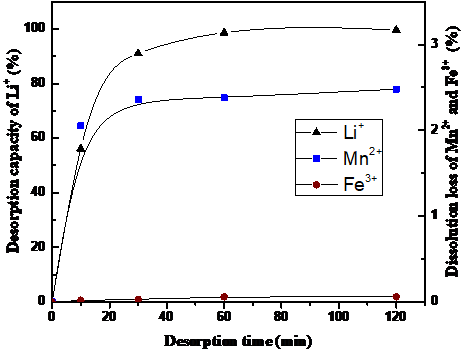
2.3.4 Fe3O4改性离子筛脱附性能测定 16
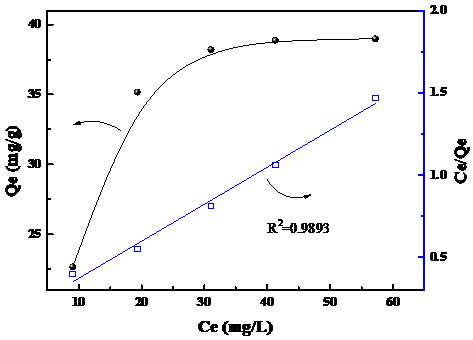
2.3.5 Fe3O4改性离子筛等温吸附模型拟合 17
2.3.6 Fe3O4改性离子筛的循环稳定性 18
第3章 实验结论与展望 21
3.1 结论 21
3.2 展望 21
参考文献 23
致谢 25
第1章 文献综述
1.1课题背景
锂由于“稀有金属”而著称,硬度和密度都很小,是世界上最轻的金属,也是关系到国计民生的重要资源。锂广泛应用于各种行业,包括冶金、润滑脂和润滑剂、铝的生产、医药和锂离子电池工业,近年来,对锂资源的需求也逐年增加。因此被誉为“新能源金属和推动世界前进的元素”[1, 2]。由于锂具有诱人的性能,而且没有任何其他元素可以替代它,再加上全球锂市场的快速发展,如今锂资源已无法满足全球市场的需求,因此它的消费量每年都在增加[3-7]。
自然界中的锂元素主要来自于卤水及各种矿物如辉石、透锂长石、锂云母和锂磷铝石。然而锂基矿物的丰度很低,并且提取锂产品的成本高、流程长、能耗大,无法满足市场的需求[8]。故对未来大力开发锂源的需求是一个不可避免的事实。尽管海水中锂的浓度很低(0.17 mg/g),但海水被认为是未来重要的锂源。海洋中的锂储量约为2.5×1014 kg,这是一个很有希望的来源[9]。近年来,海水淡化厂建设迅速增长。从浓缩海水中提取锂也因此成为学术研究者和产业界的重要挑战。一直以来人们对从海水中回收锂的技术很感兴趣,对此已经进行了一些研究[4]。
1.2盐湖提锂技术研究进展
目前工业提锂还是以盐湖卤水为主要原料。全球大于60%的锂资源存在于盐湖卤水中,我国也是锂资源大国,其中盐湖锂资源占我国已探明总储量的87%,主要分布在青海柴达木盆地和青藏高原,因此从盐湖中提取锂资源具有很大的市场应用前景[10]。
盐湖或海水中锂浓度很低,首先需要将原始卤水或海水进行蒸发浓缩,然后再采用适合的分离技术将锂从母液中分离出来。从盐湖卤水中分离锂的过程采用沉淀法、太阳能电池加热沉淀锂法、煅烧法、溶剂萃取法和吸附法等。其中吸附法就是利用有选择性的吸附剂选择性吸附盐湖卤水中的锂离子,然后再经酸洗将锂回收。吸附剂按性质可分为有机和无机两类,有机吸附剂有机离子交换树脂对高价离子吸附性能较好,对一价离子如Li 吸附困难,相比而言,无机离子交换吸附剂的研究较多,它具有较高吸附选择性,较高吸附容量的优点。吸附法因最环保、工艺简单和成本低廉的优点脱颖而出,被公认为是从海水和盐湖卤水中回收锂的最有前途的方法之一[9, 11, 12]。
相关图片展示: