水分子在陶瓷纳滤膜孔内的传递过程研究毕业论文
2020-04-20 13:52:40
摘 要
纳滤技术是介于超滤及反渗透之间的一种新型压力驱动型膜分离技术,对分子量处于200-1000 Da的物质具有较高的截留性。纳滤技术可用于替代针对小分子物质的传统分离方法(如高效液相色谱法、蒸发结晶、真空浓缩、生物降解法等),在食品、医药、环保、水资源、化工等领域中均有良好的应用前景。
纳滤过程是限域传质的一种,其传质过程涉及三个部分,即流体在膜材料表面的吸附、流体在膜孔中的传质以及流体离开膜材料。流体在纳滤膜受限界面内的传递过程存在复杂的传质机制膜,流体分子与限域壁面的作用与和流体分子间的相互作用决定了传质效率。此时流体分子的行为也变得难以调控,因此这成为了现代化工新技术(如膜过程、多相催化)突破的瓶颈。
基于上述问题,本文综述了近年来陶瓷纳滤膜及其限域传质过程的研究进展,基于现有纯水渗透通量与膜微结构的H-P传质模型,初步描述了限域传质过程中各影响因素的作用关系,主要研究在不同温度、不同压力下温度以及黏度对纯水渗透通量的影响。通过实验数据分析在一种材料的陶瓷纳滤膜内水分子的传递过程,研究温度以及黏度在其中的作用效果。研究发现,当水分子传递孔道的特征尺寸减小到一定程度时,黏度对传递过程的作用效果被显著放大。此外,本文展望了其他可以应用于纳滤膜传递过程的传质模型,如溶解扩散模型,为进一步研究流体在陶瓷纳滤膜内的传递过程以及具有限域传质效应分离膜的设计与制备提供了参考。
关键词:陶瓷膜;纳滤;限域传质;黏度;水分子
Study on Water Molecule Transfer in Ceramic Nanofiltration Membrane
Abstract
Nanofiltration (NF) ,which is defined as a process between ultrafiltration(UF) and Reverse osmosis(RO). It has high rejection for substance with molecular weight of 20-10000 Da. Nanofiltration technology can be used to replace traditional separation methods for small molecular substances (such as high performance liquid chromatography, evaporative crystallization, vacuum concentration, biodegradation, etc.). It has good application prospects in food, medicine, environmental protection, water resources, chemical industry and other fields.
Nanofiltration process is a kind of limited mass transfer, which involves three parts: the adsorption of fluids on the surface of membrane materials, the mass transfer of fluids in the membrane pore and the separation of fluids from the membrane materials. There is a complex mass transfer mechanism in the fluid transfer process at the confined interface of nanofiltration membrane. The intermolecular forces between the fluids and channel wall become the most prominent ones in nanoconfined systems and determine the mass transfer efficiency,and because the molecular behaviors of nanoconfined fluid at interface are difficult to control which becomes a bottleneck of new technology development (e.g. membrane process, heterogeneous catalysis) in modern chemical industry.
Taking this problem into consideration,this article reviews the progress of ceramic nanofiltration membranes and their transfer processes in a confined space in recent years. We adopt the classical mass transfer model to study the effect of temperature and viscosity on the permeation flux of pure water under different temperatures and pressures and Obtain the relationship between the influencing factors in the process of limited mass transfer. Through the experimental data, the transfer process of water molecules in ceramic nanofiltration membranes is analyzed, and the effect of temperature and viscosity on the permeation flux is studied. In this paper, when the characteristic size of water molecule transport channels is reduced to a certain extent, the effect of viscosity on this transfer process is greatly enhanced. In addition, other transfer models, such as dissolution-diffusion model, which can be applied to the transfer process of nanofiltration membranes are prospected. This paper will provide valuable guidance for the further study of fluid transfer process in ceramic nanofiltration membranes as well as the design and application of separation membranes in a confined space.
Key Words: Ceramic membrane; Nanofiltration; Confinement mass transfer; Viscosity; Water molecule
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.1纳滤膜分离技术概述 1
1.1.2纳滤膜的应用领域 2
1.2 陶瓷纳滤膜传递过程研究进展 3
1.2.1限域传质研究进展 3
1.2.2水分子限域传质过程分析 4
1.2.3传质机制模型简述 5
1.3本文的研究目标、内容和意义 6
1.3.1研究目标和内容 7
1.3.2研究意义 7
第二章 实验部分 9
2.1陶瓷纳滤膜的前期表征 9
2.1.1实验材料与试剂 9
2.1.2 实验仪器 9
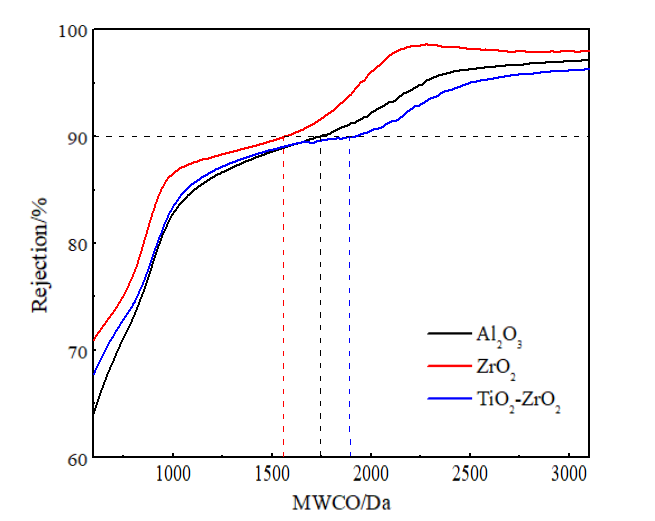
2.1.3 纳滤膜的截留性能测试及结果 10
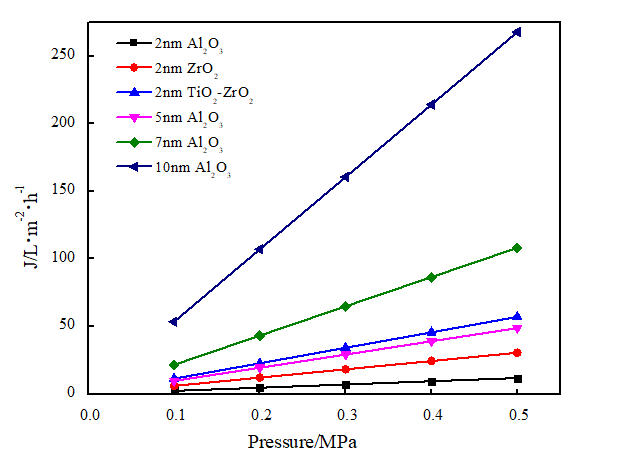
2.1.4 纳滤膜的渗透性能测试及结果 12
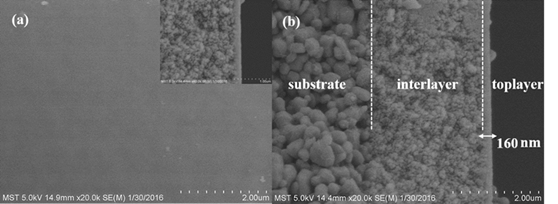
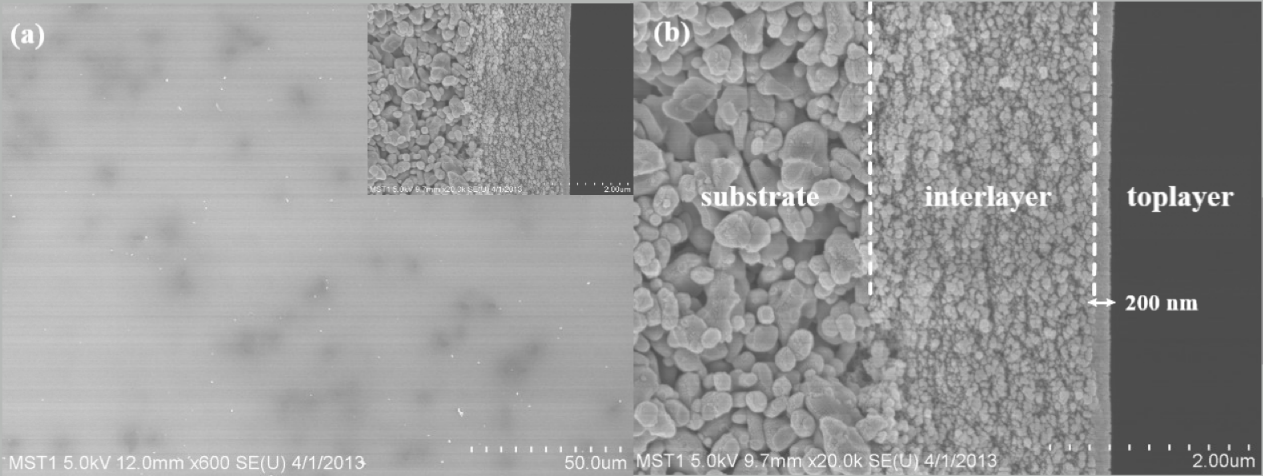
2.1.5 纳滤膜的膜厚表征 13
2.2陶瓷纳滤膜内纯水渗透实验 14
2.2.1 实验材料及试剂 14
2.2.2 实验仪器 14
2.2.3 水分子传递实验 15
第三章 实验结果分析与讨论 16
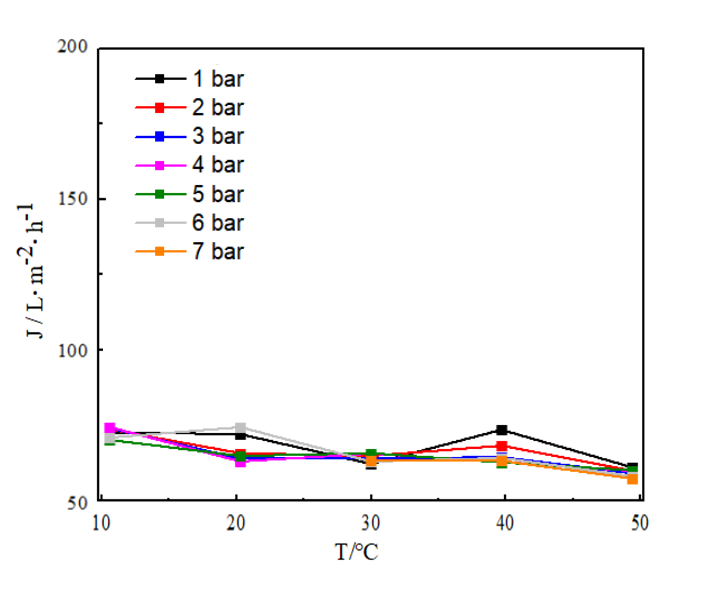
3.1 温度对不同孔径膜管校正通量影响 16
3.1.1不同孔径膜管中温度对校正通量的影响 16
3.1.2 影响结果分析 17
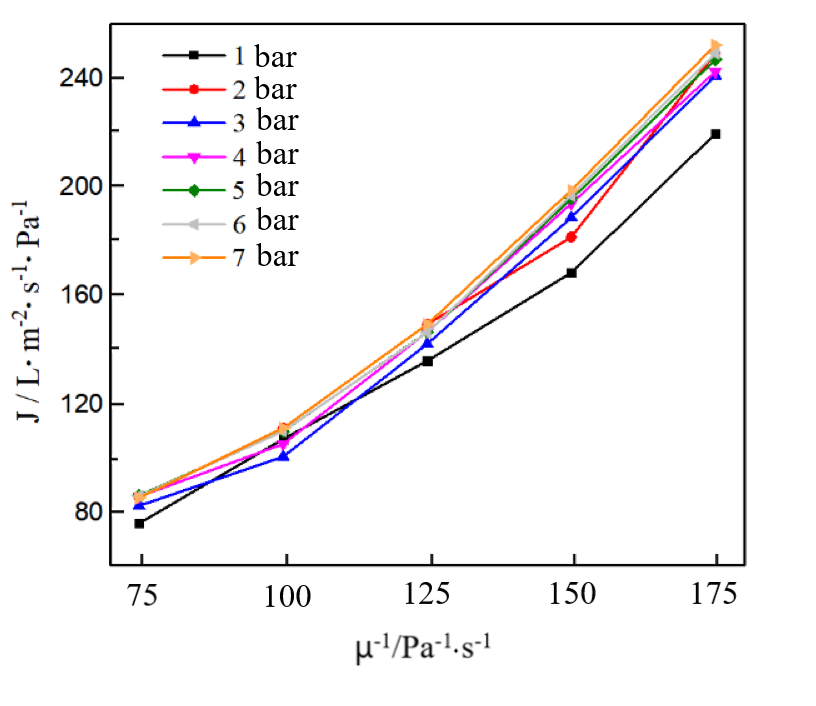
3.2 黏度对不同孔径膜管渗透率影响 18
3.2.1 不同孔径膜管中黏度对渗透率的影响 18
3.2.2 影响结果分析 21
3.3 验证实验 21
3.3.1 实验方案 22
3.3.2 结果及讨论 22
第四章 小结与展望 26
4.1小结 26
4.2展望 26
参考文献 27
致谢 30
第一章 文献综述
研究背景
1.1.1纳滤膜分离技术概述
物质分离的能耗占据人类日常活动总能耗的10 %~15 %[1],其分离成本也占据化工总生产成本的60 %以上。传统的化工分离方法是以塔器为基础的单元操作,依据连续介质假设的宏观传质理论,在精馏、吸收、蒸发、干燥等大型分离过程中应用良好。
膜分离技术是兴起于20世纪末的新型分离技术,具有高效、节能、工艺简单、无环境污染等优点,目前膜分离技术作为新型的分离过程,已广泛应用于化工、电子、医药、食品、环保等行业中,并被认为是21世纪最具应用前景的高新技术之一[2]。膜分离技术可以广泛应用于现代工业中对节能降耗、污染物控制减排、资源高效利用等方面的需求要求[3],同时在生物医药(如血液毒素透析等)中也有广泛的需求前景。
根据膜材料的不同,可将纳滤膜分为有机纳滤膜和无机陶瓷纳滤膜两类。其中有机纳滤膜(如聚乙烯醇、醋酸纤维素、聚酰亚胺等)制备工艺相对简单且大规模生产成本低,已在水处理领域得到了广泛的应用,如法国Mery-sur-Oise纳滤饮用水处理示范厂,产水量达14000 m3/d,该厂负责巴黎西郊6500居民的饮用水供给,目前运行状况良好。然而,有机膜材料稳定性差,其固有的缺点将会造成膜的操作条件(如操作压力、温度、溶液酸碱性等)的诸多限制,极大地限制了有机纳滤膜在苛刻环境体系中的推广应用,尽管目前已有大量研究致力于改进有机膜的性能,但仍无法满足工业生产中对材料长期稳定性的要求,如美国博芒特炼油厂采用纳滤技术进行溶剂回收,使单套装置年效益增长600万美元,每年可节约燃油36000桶[4],但由于聚酰亚胺纳滤膜材料固有的缺点限制了其广泛应用。因此,开发适合苛刻环境应用的纳滤膜材料成为推动纳滤膜发展的迫切要求。近十年来,制备具有良好的热稳定性、化学稳定性和溶剂稳定性的陶瓷纳滤膜成为多孔膜领域的研究热点之一。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: