TL-2 用于SCOT尾气吸附净化工艺研究毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:37:27
摘 要
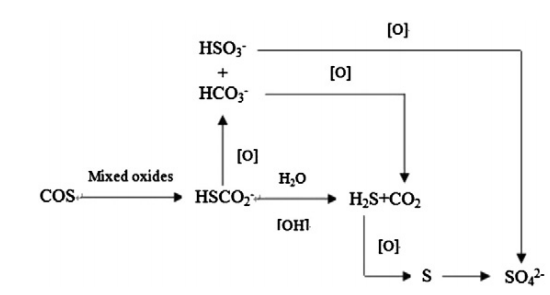
SCOT工艺是工业上Claus尾气处理主要工艺之一,Claus尾气中1-2 vol.%的硫化物在高温下还原为H2S,通入急冷塔冷却降温后用醇胺溶液(MDEA)吸收去除硫化物,但醇胺液吸收后尾气中仍有微量COS(约20-80 ppm)和H2S(约50 ppm),不能直接排放。本文配制了模拟SCOT尾气,采用实验室自制TL-2脱硫吸附剂,考察反应温度、进料空速、氧气含量和水汽含量对TL-2吸附脱除COS和H2S性能的影响;采用N2吸附/脱附等温线、FT-IR和元素分析等方法对脱硫前后的TL-2进行表征。结果表明,在进料空速2000 h-1,反应温度60 ℃,水汽含量2.16 vol.%,氧气含量3 vol.%的条件下,TL-2对COS和H2S的穿透硫容可达到7.91 mg S/g ads。TL-2对COS和H2S的吸附脱除机理为:COS和H2S在TL-2表面和0.8-0.9 mm的微孔孔道中吸附,并催化水解生成H2S,H2S进一步被氧化生成单质硫磺和硫酸。
关键词:SCOT尾气 TL-2 COS H2S 穿透硫容 脱硫机理
Study on Adsorption Purification Process of TL-2 for SCOT Tail Gas
ABSTRACT
The SCOT process is the most important Claus tail gas treatment process in the industry. The sulfide (1-2 vol.%) in the Claus tail gas is reduced to H2S at high temperature, and is cooled by the quenching tower and then absorbed by the alcohol amine solution (MDEA), but absorbed in the tail gas after absorption by the alkanolamine. There is still a small amount of COS (~20-80 ppm) and H2S (~50 ppm) that cannot be directly discharged. In this paper, the COS and H2S components in the simulated SCOT tail gas were subjected to adsorption purification experiments. The self-made TL-2 desulfurization adsorbent was used to investigate the reaction temperature, feed space velocity, oxygen content and water vapor content for TL-2 adsorption removal. The effects of COS and H2S were optimized to optimize the conditions of adsorption desulfurization. The TL-2 adsorbents before and after desulfurization were characterized by N2 adsorption/desorption isotherm, FT-IR and elemental analysis. The results show that when the simulated SCOT tail gas containing COS and H2S is removed, the TL-2 adsorbent is worn under the conditions of feed air velocity of 2000 h-1, reaction temperature of 60 °C, water vapor content of 2.16% and oxygen content of 3%. Breakthrough sulfur capacity reaches 7.91 mg S/g ads. according to the characterization results, the pores with a pore diameter of 0.8-0.9 mm on TL-2 act as the main adsorption desulfurization; the adsorption removal mechanism of COS and H2S on the TL-2 adsorbent is: COS and H2S enter the surface and pores of TL-2 The medium is converted into an adsorption state, and a catalytic hydrolysis reaction occurs to form H2S. H2S continues to be oxidized to form elemental sulfur and sulfuric acid.
KEYWORDS: SCOT tail gas; TL-2; COS; H2S; breakthrough sulfur capacity; desulfurization mechanism
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 概 述 1
1.1 背景 1
1.2 脱硫工艺研究进展 2
1.2.1克劳斯工艺 2
1.2.2 SCOT尾气处理工艺 3
1.3 含硫尾气脱硫吸附剂研究现状 3
1.3.1 H2S脱硫吸附剂 4
1.3.2 COS脱硫吸附剂 5
1.4 本文主要研究内容 6
第二章 实 验 7
2.1 主要原料和试剂 7
2.2 实验仪器和设备 7
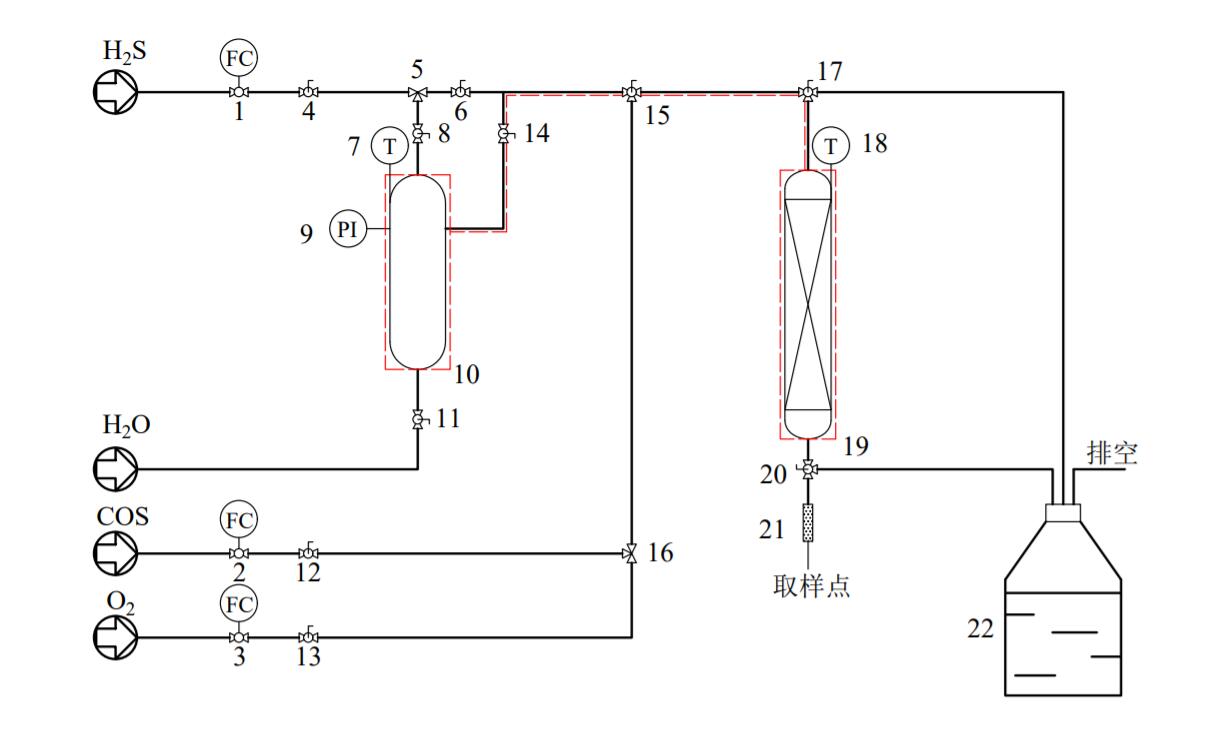
2.3 TL-2吸附净化脱硫实验 7
2.3.1 实验装置 7
2.3.2实验步骤 8
2.3.3 实验数据处理 8
2.4 脱硫吸附剂表征方法 9
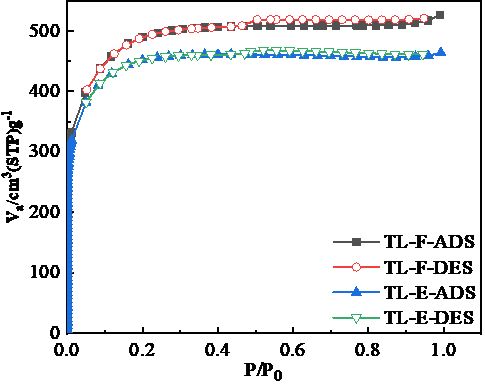
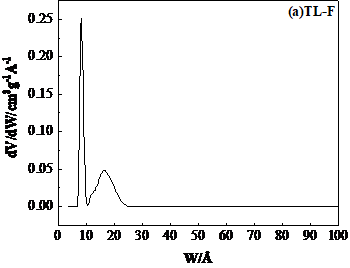
2.4.1比表面积、孔径和孔容分布测定 9
2.4.2 热重分析 9
2.4.3 红外光谱分析 9
2.4.4 元素分析 9
第三章 结果与讨论 10
3.1 TL-2吸附脱除COS/H2S工艺研究 10
3.1.1 进料空速对TL-2吸附脱除COS/H2S性能的影响 10
3.1.2 反应温度对TL-2吸附脱除COS/H2S性能的影响 10
3.1.3 温度空速正交实验优化 11
3.2 吸附脱硫前后TL-2吸附剂表征 12
3.2.1比表面积、孔径和孔容分析孔结构 12
3.2.2 FT-IR表征吸附剂表面官能团变化 14
3.2.3 TG-DSC分析吸附剂热稳定性及其表面物质 14
3.2.4 吸附剂元素组成及含量分析 15
3.3 TL-2吸附脱除COS/ H2S机理 15
第四章 结论与展望 17
4.1 结论 17
4.2 展望 17
参考文献 18
致谢 20
第一章 概 述
1.1 背景
随着环保和市场对石化生产中尾气的硫含量要求逐年上升,石油化工中针对有害的硫化物的脱除,尤其是其中较难被脱除的有机硫化物去除方法已成为石化行业中诸多研究者热切关注的问题。目前,SCOT工艺是工业上最主要的Claus尾气处理工艺。它们将尾气中的硫化物在高温下还原为H2S或氧化成SO2,通入急冷塔冷却降温后用醇胺溶液(MDEA)吸收,吸收后的尾气工业上含硫尾气经克劳斯和SCOT工艺脱硫反应后能够将绝大部分的硫化物脱除,但通过SCOT工艺反应后的尾气中有少量硫化氢(H2S)和羰基硫(COS)组分[1],因此不能直接排放。
含硫化合物不仅会造成环境污染、管道设备腐蚀损坏,同时还会造成催化剂硫中毒从而失去活性,而且微量硫组分的存在会严重影响产品质量。其中COS通常状况下是一种无色、有臭鸡蛋气味的气体,广泛存在于各种石油化工和煤化工的工业气体中,包括天然气、焦炉气、合成气、液化石油气等。王红妍等[2]指出,含硫尾气中的COS若不经处理直接排放能够在大气中转化为SO2,发生光化学反应,环境问题愈发突出;此外,Rhodes C等[3]发现,原料气中微量的COS成分会导致工业催化剂的含硫量大幅提升,当催化剂中的含硫量达到4 mg S/g cat时,催化剂的活性就会大幅下降50%之多,严重影响生产的有效进行;COS甚至会对设备造成腐蚀[4],影响设备的使用寿命。
现有的脱硫催化剂主要对H2S等无机硫能够起到很好的脱除效果,但是对COS的脱除效率较低,主要是由于COS的化学活性比无机硫的化学活性小得多,其酸性和极性均比无机硫的弱,一般用于脱除无机硫的方法不能有效地完全脱除COS。因此,需要研制一种能够同时脱除无机硫和有机硫能够的吸附剂,用于脱除SCOT尾气中的COS和H2S组分。
1.2 脱硫工艺研究进展
1.2.1克劳斯工艺
克劳斯工艺于1883年由英国科学家Carl Friedrich Claus发明,20世纪30年代受到德国法本公司的改进,如今成为世界上应用最为广泛的脱硫工艺。传统克劳斯工艺如图1-1所示。
相关图片展示: