有机碳正离子Lewis酸催化剂的合成及聚合研究毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:58:07
摘 要
开环聚合是一种合成生物可降解以及生物可再生聚酯的强有力方法。但是,为了合成出能够用于生物医药并且具有明确结构的功能性脂肪族聚酯,要求开环聚合的过程是可控的。本文中,利用碳正离子Lewis酸有机分子催化环状碳酸酯的开环聚合反应,成功实现对三亚甲基碳酸酯(TMC)进行开环聚合反应。仅仅以1 mol%量的TrBF4 作为催化剂、甲苯作为溶剂、苄醇(BnOH)作为引发剂、TMC作为反应单体、当单体与引发剂投料比为 50:1 时,室温反应 3 h,转化率可高达到 95%,所得的聚三亚甲基碳酸酯(PTMC)分子量高达5.0kg mol-1,分子量分布窄,ÐM 值仅为 1.12。室温条件下,溶液聚合得到窄分布、精确分子量和高末端保真度的聚碳酸酯,且反应过程中没有脱羧反应的发生。聚合物的化学结构通过 1H NMR、13CNMR和MALDI-ToF MS 进行确认,证明三苯甲基四氟硼酸盐催化聚合反应的活性特征。
关键词:开环聚合 碳正离子 碳酸酯 有机分子催化
Organic carbon cation Lewis acid catalyzed ring-opening polymerization of trimethylene carbonate
ABSTRACT
Ring opening polymerization is a powerful method for synthesizing biodegradable and biorenewable polyesters. However, in order to synthesize a functional aliphatic polyester which can be used in biomedicine and has a well-defined structure, the process of ring-opening polymerization is required to be controllable. In this paper, the ring-opening polymerization of trimethylmethylene carbonate (TMC) was successfully carried out by the ring-opening polymerization of cyclic carbonates catalyzed by carbon cation Lewis acid organic molecules. Only 1 mol% of TrBF4 was used as a catalyst, toluene was used as a solvent, benzyl alcohol (BnOH) was used as an initiator, TMC was used as a reaction monomer, and when the ratio of monomer to initiator was 50:1, the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 3 h. The rate can be as high as 95%, and the obtained polytrimethylene carbonate (PTMC) has a molecular weight of up to 5.0 kg mol-1, a narrow molecular weight distribution, and a ÐM value of only 1.12. At room temperature, solution polymerization gave a polycarbonate with a narrow distribution, precise molecular weight and high terminal fidelity, and no decarboxylation reaction occurred during the reaction. The chemical structure of the polymer was confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR and MALDI-ToF MS to demonstrate the activity characteristics of the catalytic reaction of trityltetrafluoroborate.
Keywords: ring-opening polymerization; carbon cation,;carbonate,;organic molecular catalysis
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1有机分子催化 1
1.2 Lewis 酸有机分子催化剂 2
1.3碳正离子的介绍 2
1.4碳正离子的结构 3
1.4碳正离子 Lewis 酸催化的有机合成反应 4
1.5有机碳正离子作为路易斯酸催化剂在聚合方面的介绍 4
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1实验材料 6
2.1.1本实验过程所需要的试剂 6
2.2仪器与表征方法 6
2.2.1 核磁共振测试 6
2.2.2 体积排阻色谱 7
2.2.3 基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱表征 7
2.3 碳正离子催化剂的制备 7
2.3.2 五种催化剂的合成路线图 8
2.4 聚三亚甲基碳酸酯的制备 9
2.4.1 聚三亚甲基碳酸酯的合成方法 9
2.4.2 聚三亚甲基碳酸酯的合成路线 9
第三章 结果与讨论 11
3.1五种碳正离子结构表征 11
3.2聚三亚甲基碳酸酯结构表征 11
3.3五种碳正离子盐催化三亚甲基碳酸开环聚合的研究 12
3.3聚合反应条件的优化 13
3.4不同单体/引发剂比的聚合研究 14
3.5 基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱 15
第四章 结论与展望 17
4.1 结论 17
4.2 展望 18
参考文献 19
致谢 22
第一章 绪论
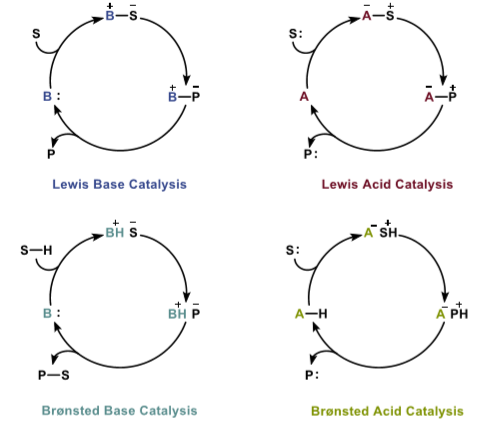
1.1有机分子催化
“有机分子催化”最早由 MacMillan 提出【1,2】。催化剂是一种参与反应,但不会消除,并且不会影响反应平衡常数的化合物。有机分子催化剂是由C,H,O,N,P,S与其它非金属元素组成的有机化合物,它的作用是从反应底物或过渡态中给出或移出正电(H)或负电(电子)。其催化机理如图1所示。有机分子催化剂分为布朗斯特酸(Brønsted acids)、布朗斯特碱(Brønsted bases)、路易斯酸(Lewis acids)和路易斯碱(Lewis bases)。近年来,将有机分子催化剂应用于高分子聚合反应成为人们研究热点。相比于金属催化与酶催化,有机分子催化展现出反应条件温和,无金属残留,反应效果好,反应稳定性高等优势。其缺陷在于,催化剂种类少,用量大,进而影响了有机分子催化的应用范围【3】。