可食性花生分离蛋白膜对风味物质的缓释效应研究毕业论文
2020-06-26 19:48:16
摘 要
花生蛋白膜是一种新型材料,由于其绿色和环保的特性,可以应用于食品包装。但它同时具有不耐水且质地比较脆的缺点,限制了它在食品包装中的应用。本研究采用糖基化改性来改善花生分离蛋白膜,并探讨了糖基化反应对花生分离蛋白膜物理性能及风味缓释效应的影响。
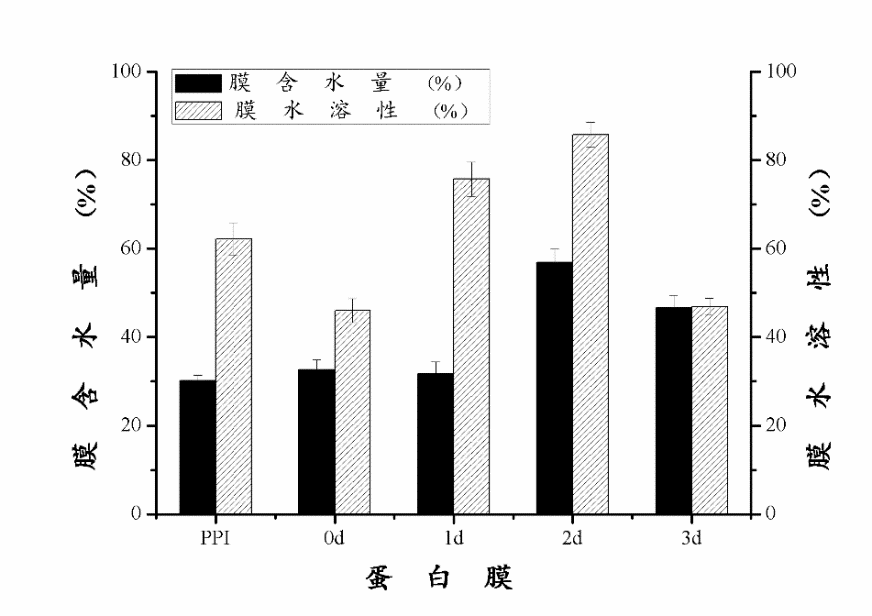
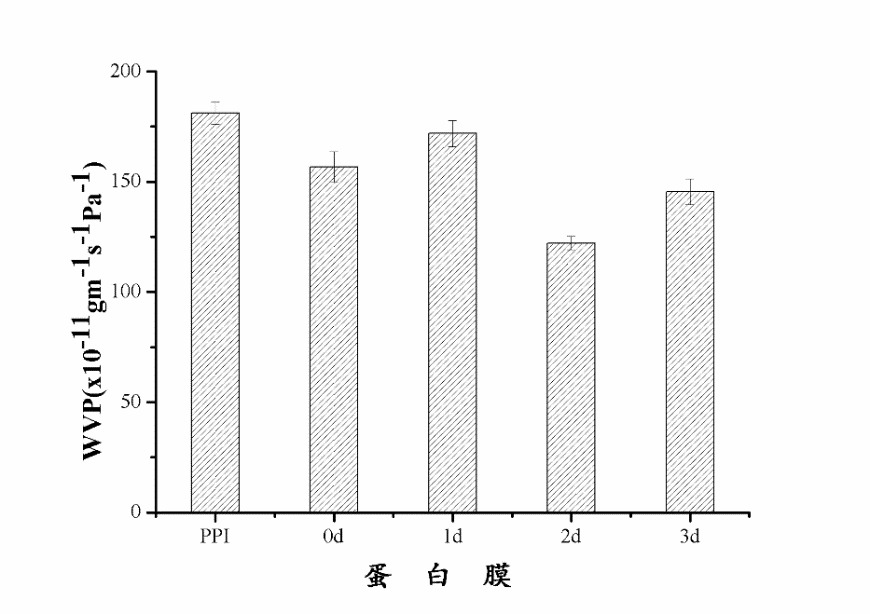
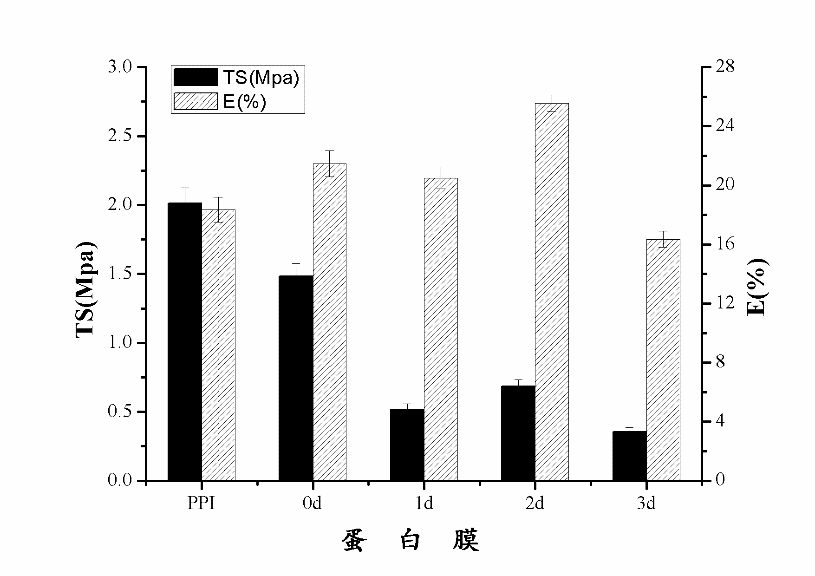
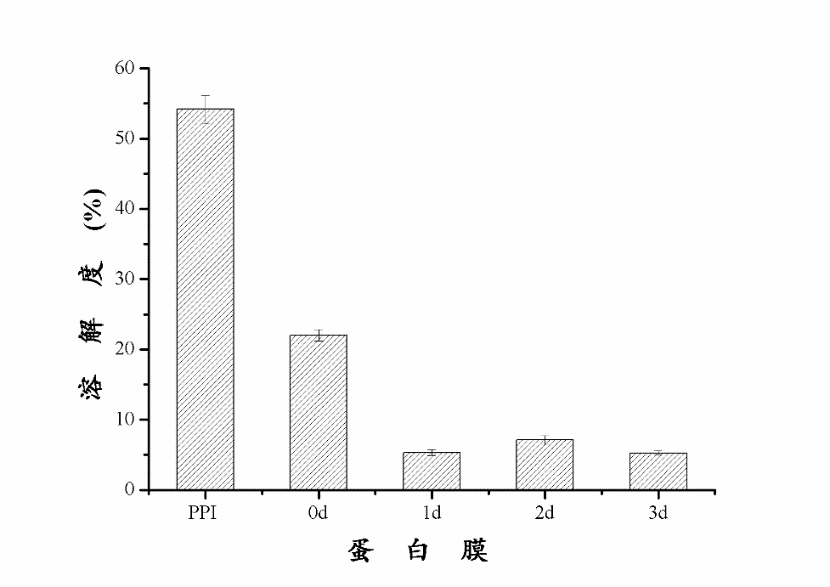
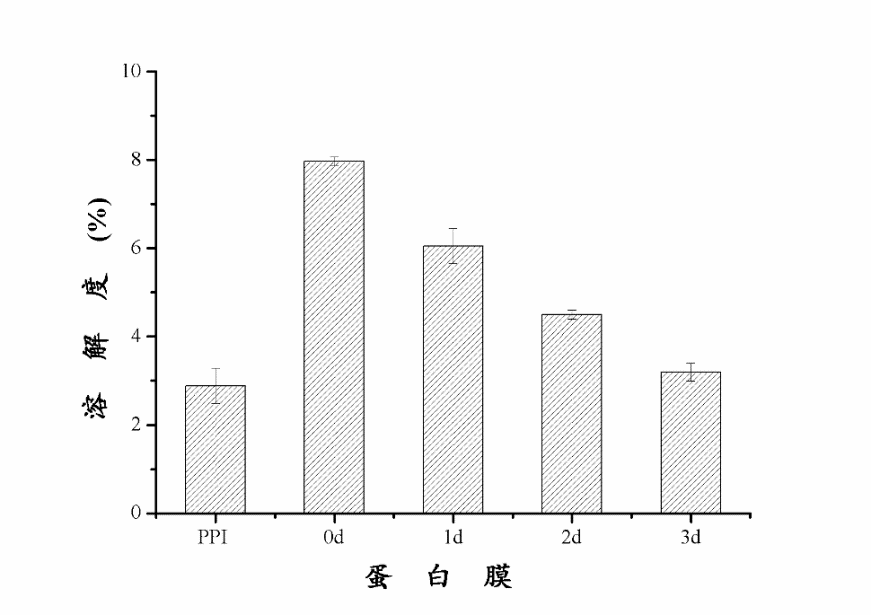
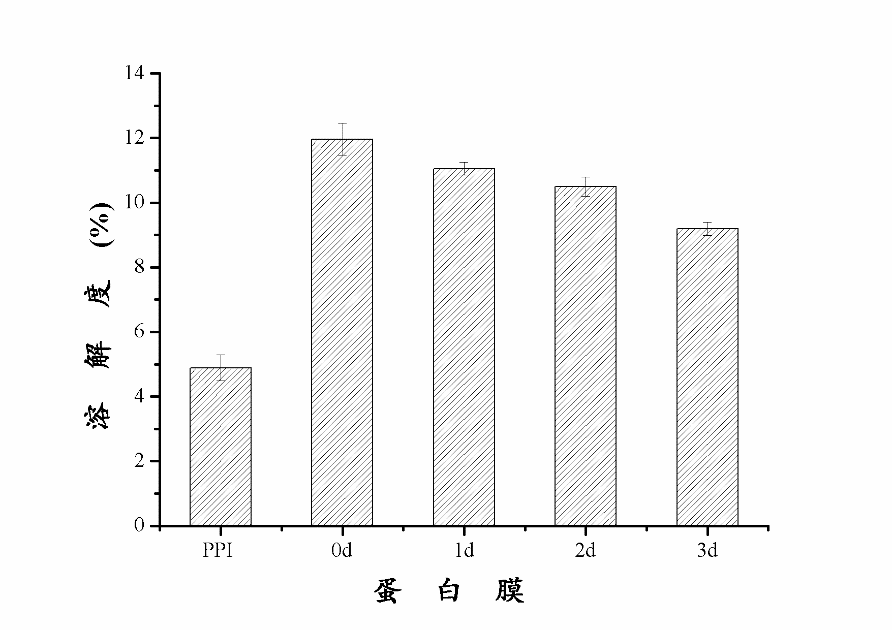
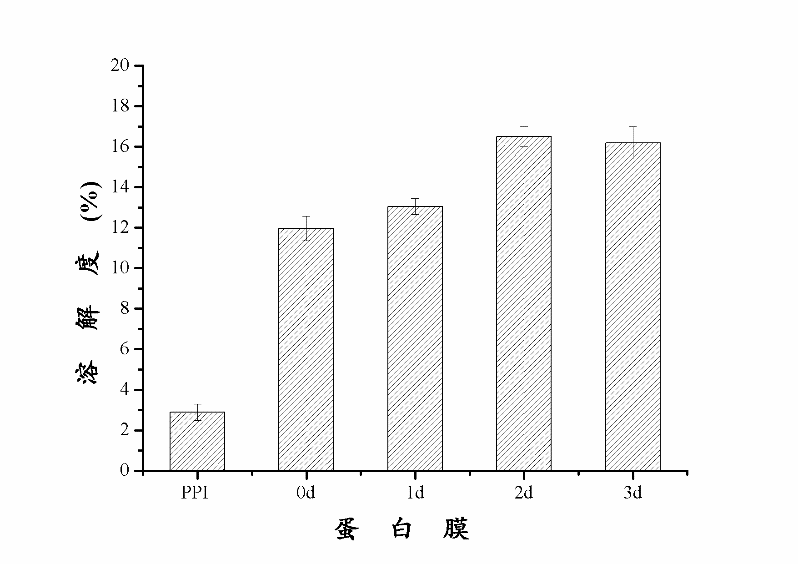
通过实验,可以得出下列结论:进行糖基化反应后,0天、1天的花生蛋白膜样品的含水量与PPI样品基本相同,2天样品的含水量有显著提升。在膜水溶性方面,糖基化反应1-2天样品的膜水溶性有所增加,而反应3天的样品膜水溶性显著降低。在水蒸气渗透率的测定中发现,随着糖基化反应的进一步发生,蛋白膜的水蒸气渗透率有所下降。在对样品进行机械性能的测定中发现,经过糖基化反应后,蛋白膜的拉伸强度显著下降,其中糖基化反应3天样品的拉伸强度最低。糖基化反应的程度对延长率影响较大,其中在反应2天时达到最大值,而反应时间达到3天时,延长率最低。在对蛋白膜内的非特异性交联、氢键、疏水作用力、二硫键以及静电相互作用五种化学作用力的测定中发现,在非特异性交联中,通过糖基化反应制备成的蛋白膜之间的溶解率无显著变化。在对氢键影响的研究中发现,PPI样品溶解度较低,0天样品显著升高,随后不断降低,0天样品中氢键作用力最强。在探讨阿拉伯胶对蛋白膜中二硫键的影响时,可以清晰地看到逐级增长的趋势,且在所有五种膜内作用力中,二硫键的影响最为明显,趋势最为清晰,影响数值也最大,是影响膜的性质的主要化学作用力。在对膜的风味控释的拟合曲线进行分析的过程中发现,混入多糖且经过糖基化反应后的花生蛋白膜,缓释速率常数随着糖基化反应的发生逐渐降低,由此可以看出,糖基化反应能够显著降低柠檬烯在膜中的释放速率。3天样品的缓释速度最慢,且较为稳定,适宜作为包装膜内材料。
在PPI中混入阿拉伯胶,并经过3天的糖基化反应后,花生蛋白膜的各项理化性能及缓释效能最佳,适合作为食品包装膜内材料。
关键词:花生分离蛋白;糖基化反应;缓释
Study on Controlled Effect of Edible Peanut Protein Isolate Film on Flavor Substances
Abstract
Peanut protein film is a new type of material that can be applied to food packaging due to its green and environmentally friendly properties. However, due to the lack of flexibility and large amount of hydrophilic group contained in the peanut protein membrane, the peanut protein membrane has the disadvantages of being permeative to water and extremely brittle. The presence of these defects will limit its application in food packaging. In this study, glycosylation was used to improve the membrane of peanut protein isolate, and the effect of glycosylation on the physical properties and flavor slow release effect of peanut protein isolate was investigated.
Through the experiment, the following conclusions can be drawn: After the glycosylation reaction, the water content of the peanut protein film sample on day 0 and day 1 was basically the same as that of the PPI sample, and the water content of the sample on the 2nd day was significantly improved. In the aspect of water solubility of the membrane, the water solubility of the membranes of the 1-2 day sample of the glycosylation reaction increased, and the water solubility of the membrane of the sample that was reacted for 3 days significantly decreased. In the determination of the water vapor permeability, it was found that the water vapor permeability of the protein film decreased as the glycosylation reaction proceeded.In the determination of the mechanical properties of the sample, it was found that after the glycosylation reaction, the tensile strength of the protein film decreased significantly, and the glycosylation reaction sample had the lowest tensile strength at 3 days. It can also be seen from the figure that the extent of the glycosylation reaction has a great influence on the elongation rate, in which the maximum value is reached at the 2nd day of the reaction, and the minimum elongation rate is reached at the 3rd day of the reaction time. In the determination of non-specific cross-links, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interaction forces, disulfide bonds, and electrostatic interactions within the protein membrane, it was found that in the non-specific cross-linking, the glycosylation reaction prepared There was no significant change in the dissolution rate between protein films.In the study of the effect of hydrogen bonding, it was found that the solubility of PPI sample was low, and the sample on day 0 increased significantly, and then decreased continuously. The hydrogen bonding force in the sample on day 0 was the strongest. When discussing the effect of gum arabic on the disulfide bond in the protein membrane, the gradual growth trend can be clearly seen, and among all five kinds of intramembrane forces, the effect of disulfide bond is the most obvious, and the trend is clearest. The largest value is the main chemical force that affects the properties of the membrane.In the process of analyzing the curve of the controlled release of the flavor of the film, it was found that the sustained release rate constant of the peanut protein film mixed with the polysaccharide and subjected to the glycosylation reaction gradually decreased with the occurrence of the glycosylation reaction, and thus It can be seen that the glycosylation reaction can significantly reduce the release rate of limonene in the membrane. Combining the two calculation methods, the release rate of the three-day sample is the slowest, and it is relatively stable, which is suitable as the material in the packaging film.After mixing with Arabia gum in PPI and after 3 days of glycosylation, the physical and chemical properties of the peanut protein membrane and the best release efficiency are best. It is suitable to be used as the internal material in the food packaging film.
Keywords: Peanut protein isolate; Glycosylation;Controlled release;
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 花生蛋白简介 1
1.1.1 花生蛋白结构 1
1.1.2 花生蛋白应用 1
1.1.3 花生蛋白的功能性质研究现状 2
1.2 糖基化反应 3
1.2.1 糖基化改性 3
1.2.2 糖基化反应产物中蛋白和多糖之间的作用力 4
1.3 可食性蛋白膜对风味物质的缓释效应 5
1.4 立题意义 5
第二章 实验材料与方法 7
2.1 材料与方法 7
2.1.1 材料与试剂 7
2.1.2 仪器设备 7
2.2 试验方法 8
2.2.1 蛋白质与多糖共价交联产物的制备 8
2.2.2 添加柠檬烯的花生蛋白膜制备 8
2.2.3 水溶性测定 8
2.2.4 水蒸气渗透率的测定 8
2.2.5 机械性能的测定 9
2.2.6 膜内化学作用力的测定 9
2.2.7 膜的风味缓释 10
第三章 实验结果与讨论 11
3.1 水溶性的测定 11
3.2 水蒸气渗透率的测定 11
3.3 机械性能的测定 12
3.4 膜内化学作用力的测定 13
3.4.1 糖基化反应对蛋白膜中的非特异性交联的影响 13
3.4.2 糖基化反应对蛋白膜中的静电相互作用的影响 14
3.4.3 糖基化反应对蛋白膜中氢键的影响 14
3.4.4 糖基化反应对蛋白膜中疏水相互作用的影响 15
3.4.5 糖基化反应对蛋白膜中二硫键的影响 16
3.4.6 蛋白膜内主要化学作用力的讨论 17
3.5 膜的风味缓释 17
第四章 实验结论与展望 22
4.1 结论 22
4.2 不足与展望 23
参考文献 24
致 谢 27
第一章 绪论
1.1 花生蛋白简介
花生作为一种油料农作物,在世界范围内占有重要的比例,我国是世界上第二大花生生产国[1]。根据资料统计显示,我国每年生产花生约1600多万吨,约占世界产量的1/3。花生由于其富含大量的蛋白质,且具有可再生性以及分布广泛性等特点,逐渐成为我国植物蛋白的主要来源。而且花生蛋白富含各种氨基酸,其营养价值与动物蛋白的营养价值相接近,逐渐被用来作为动物蛋白的替代物[2,3]。
1.1.1 花生蛋白结构
花生蛋白中主要部分是由花生球蛋白和伴花生球蛋白构成的,花生球蛋白占了大部分约63%,而伴花生球蛋白只占了小部分约33%[4]。花生球蛋白主要是以α-花生球蛋白为主,分子量在600 kDa附近,含有40.5、37.5、35.5以及23.5 kDa 4种不同分子量的亚基。而伴花生球蛋白又分为伴花生球蛋白Ⅰ和伴花生球蛋白Ⅱ,其中伴花生球蛋白Ⅰ主要是以142 kDa分子量的亚基存在,伴花生球蛋白Ⅱ主要是以290 kDa分子量的亚基存在[5]。
1.1.2 花生蛋白应用
花生蛋白由于其功能性质以及具有高营养性的特点,在食品行业中得到了广泛的应用。常见的应用方式主要有:作添加剂、作发泡稳定剂、制作花生蛋白肉以及花生蛋白膜等。花生蛋白由于具有较好的水溶性,其溶解度较高,并具有其独特的香味,因此,在饮料和乳制品的加工过程中会加入一些花生蛋白作为添加剂,会得到具有独特风味的产品。花生蛋白粉在经过一些处理后,如碱法和酶法,可以作为一种发泡稳定剂,在糖果加工过程中,加入25%浓度的花生蛋白发泡稳定剂,并控制适宜的温度,可以起到明胶和蛋白干的作用,也常用于汽水和饮料行业中。花生蛋白是一种高营养性植物蛋白,因此会被用于代替动物蛋白,在保证营养成分的同时降低加工成本,可以在香肠、火腿加工中得以应用,同时也可以成为猪肉、牛肉等替代品。近些年来,随着科学家对花生蛋白不断的研究发现了一种新型应用方式,花生蛋白制作成花生蛋白膜应用于食品中。花生蛋白膜能够降低O2以及CO2的透过作用,将其包裹于食品表面可以提高食品的抗氧化性延长食品的保质期,是一种新型的包装材料[6]。与现有的合成包装材料相比,由花生蛋白制成的花生蛋白膜能够更容易被微生物降解,对环境几乎零污染,在食品包装行业中具有更加广泛的应用前景[7]。因此,进行花生蛋白膜功能性质的研究,对于花生蛋白膜的进一步应用,以及拓宽花生蛋白的应用领域具有非常重要的意义。
1.1.3 花生蛋白的功能性质研究现状
一般对于蛋白的功能特性介绍,主要是包括其溶解性、乳化性、凝胶性以及成膜性等。根据近年来花生蛋白的研究重点以及本论文的研究方向,接下来主要介绍花生蛋白的溶解性和成膜性。
1.1.3.1 溶解性
相关图片展示: