响应面法优化桑木耳多糖水提工艺毕业论文
2020-07-02 22:39:55
摘 要
黑木耳(Auricularia auricula)属于木耳系真菌类担子菌纲,是我国珍贵的食用胶质真菌。黑木耳中含有丰富的营养物质,如多糖、蛋白质、脂肪、氨基酸、纤维素以及多种微量元素等,具有很高的营养价值。大量研究结果表明,多糖是木耳的主要功效组分,具有激发细胞免疫活性、有效延缓衰老、辅助降血脂、降血糖、抗凝血、抗癌和抗氧化等生物学活性,并可作为益生元,促进肠道益生菌的生长。桑木耳(Mulberry fungus),是黑木耳中的一种,以桑枝屑为主要基料通过人工培植而成。但目前国内外对于桑木耳的研究报道很少,有关桑木耳黄酮、多糖的提取,结构的分析及功能性评价均未见报道。为此,本文以云南昆明石林地区的桑木耳为原料, 优选桑木耳多糖水提工艺,通过红外光谱(FT-IR)、凝胶色谱(HPGPC)和离子色谱(HPAEC)对得到的多糖组分进行表征。
为此,本文以云南昆明石林地区的桑木耳为原料,优选桑木耳多糖水提工艺,通过红外光谱(FT-IR)、凝胶色谱(HPGPC)和离子色谱(HPAEC)对得到的多糖组分进行表征。
具体研究内容和结论如下:
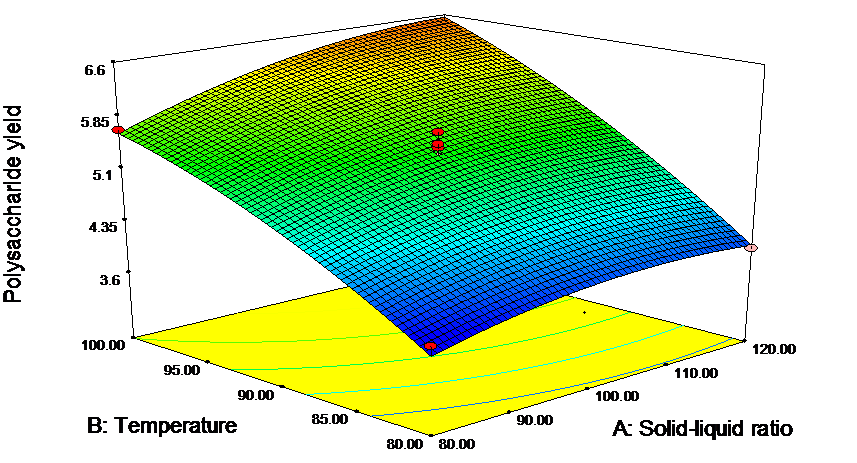
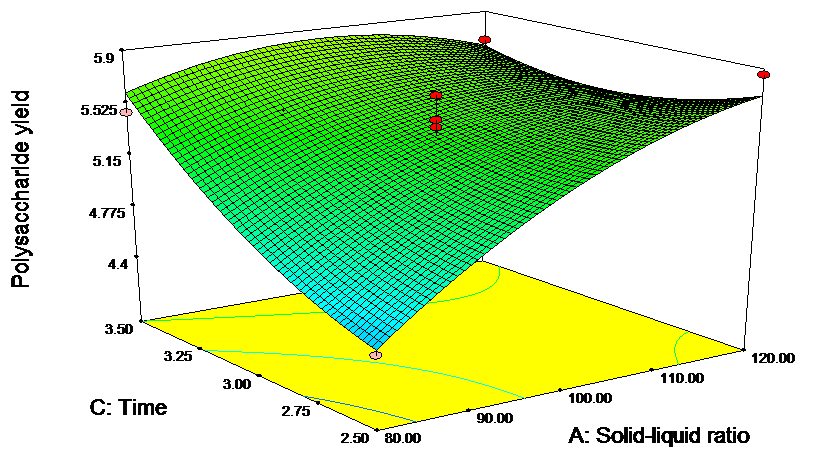
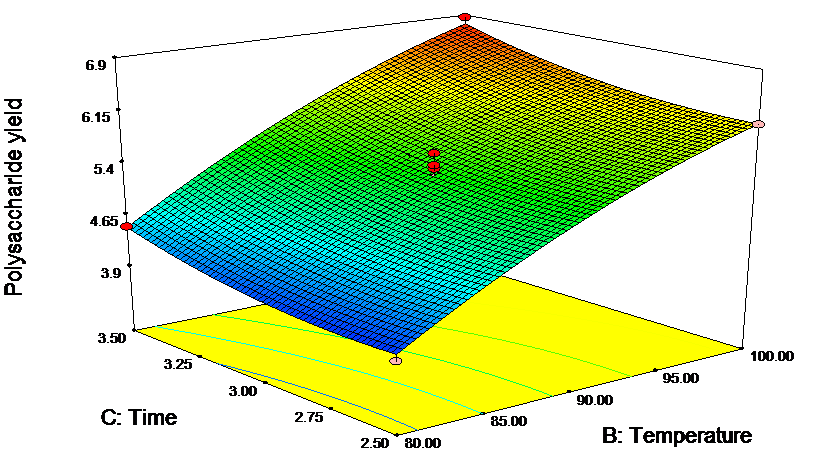
(1)通过单因素实验结合响应面优化法得到桑木耳多糖的最佳提取条件为:料液比1:108(w/v),提取温度100 °C,提取时间3.5 h,桑木耳多糖的一次提取率为6.96%。经10次重复提取,桑木耳多糖的总得率达34.18%。
(2)经测定,桑木耳多糖主要由葡萄糖、木糖和甘露糖,其比例近似为1.18: 0.65: 2.88。FT-IR分析显示,桑木耳多糖提取物中存在O-H、CH2-(或H-C=O)、C=O(或C=C)和C-H等官能团的特征吸收峰,以及吡喃型糖苷环骨架C-O变角振动吸收峰(说明分子中存在C-O-H和糖环C-O-C结构)和β-型糖苷键的特征吸收。
关键词:桑木耳多糖 提取 优化 表征
Response Surface Methodology to Optimize Mulberry Water Extraction Process
ABSTRACT
Auricularia auricula, also called black fugus, belonging to heterobasidiae of basidiomycetes, is frequently consumed as a food and a traditional medicine in China. It is believed to be of high nutritional value since it has the high content of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, amino acids, cellulose, and trace elements. Many studies have reported that polysaccharides were the main efficacy composition in A. auricula, because of their wide variety of pharmacological activities, such as immunomodulation, anti-aging, hypolipidemic, hypoglycemic, anticoagulant, antitumor, and antioxidant activity. Moreover, recent research has found that polysaccharides from edible fungi could be used as prebiotics to promote the growth of intestinal probiotics. Mulberry fungus, which is a kind of Auricularia auricula, is cultivated artificially with mulberry branch powder as the main raw material. The mulberry branchs are rich in cellulose and have developed phloem, therefore, the yield of cultivation can be increased by 10% to 20% by using them as raw materials.
In this study, To characterize the structural features of MFP, fourier transforminfrared (FT-IR) spectrometry, high performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC) and high-performance anion exchange chromatography (HPAEC) were used.
The contents and conclusions are as follows:
(1)The extraction condition of MFP were optimized with single factor and response surface experiments. The results showed that extraction once with the solid-liquid ratio of 1:100 in 100 °C for 3.5 hours, the experimental yield was 6.96%. After 10 times, the polysaccharide yield was as high as 34.18%.
(2)Analysis of monosaccharide compositions showed that MFP mainly contained glucose, xylose, and mannose, and the molar mass ratio was 1.18: 0.65: 2.88, respectively. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) results showed that there were characteristic absorption peaks in the Mulberry fungus polysaccharide extract, such as O-H, CH2-(or H-C=O), C=O (or C=C) and C-H. The angle-shifted vibrational absorption peak of C-O indicated C-O-H groups or C-O-C groups in structures. Moreover, the bands at the range of 902 cm-1 suggested the presence of β-glucopyranoside bonds in MFP.
Key words: Mulberry fungus polysaccharide; Extract; Optimization; Characterization
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 8
1.1 黑木耳多糖 8
1.2黑木耳多糖提取方法的研究现状 8
1.2.1 热水浸提法 8
1.2.2 超声辅助提取法 9
1.2.3 微波辅助提取法 9
1.2.4 酶解法 10
1.2.5 其他方法 10
1.3 黑木耳多糖的表征 10
1.3.1 凝胶色谱(HPGPC) 10
1.3.2 紫外分光光度法与红外光谱法 10
1.3.3 离子色谱(HPAEC) 11
1.4 本文的研究目的、意义及主要内容 11
1.4.1 研究目的和意义 11
1.4.2 主要研究内容 11
第二章 桑木耳多糖含量测定 12
2.1 实验材料与仪器 12
2.1.1 实验材料 12
2.1.2 实验试剂 12
2.1.3 实验仪器 13
2.2 实验方法 13
2.2.1 原料预处理 13
2.2.2 多糖含量的测定 13
2.3 结果与讨论 15
2.3.1 桑木耳、黑木耳和椴木耳多糖含量的测定 15
2.4 本章小结 16
第三章 桑木耳多糖提取条件优化及表征 16
3.1 实验材料与仪器 16
3.1.1 实验方法 16
3.1.2 实验仪器 17
3.2 实验方法 17
3.2.1 桑木耳多糖的提取 18
3.2.2 桑木耳多糖提取的工艺优化 18
3.2.3 桑木耳多糖的表征 19
3.3 结果与讨论 20
3.3.1 单因素实验结果 20
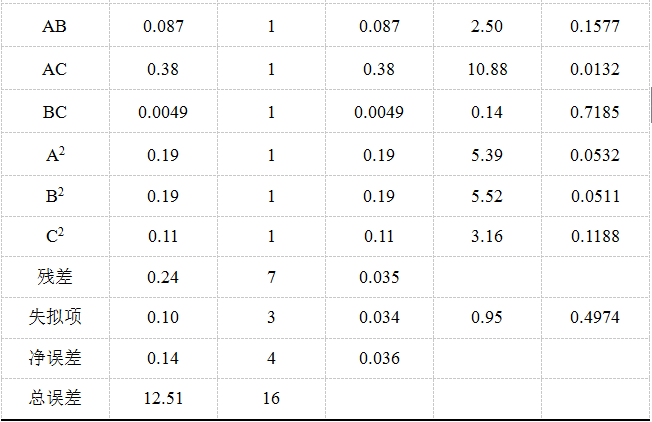
3.3.2 响应面实验结果与分析 22
3.3.3 最优条件下提取次数对多糖得率的影响 25
3.3.4 桑木耳多糖的表征 26
3.4 本章小结 28
第四章 结论与展望 29
4.1 结论 29
4.2 展望 29
参考文献 31
致 谢 35
第一章 文献综述
1.1 黑木耳多糖
多糖广泛存在于自然界的真菌、藻类和高等植物中,具有多种药理活性,且一般无毒副作用,因此吸引了众多研究者的关注。目前,对多糖的研究主要涉及来源、提取分离、结构鉴定、活性分析以及功能性产品开发等。
研究表明,黑木耳中富含多糖,且黑木耳多糖的组成和结构较为复杂,通常还会受产地、品种、提取剂和提取方法的影响。Shahzor等[1]从黑木耳中分离纯化出两种多糖组分AAPF和AAPP。Zhang等[2]从湖北房山黑木耳中分离出两种酸性多糖和三种D-葡聚糖,并通过纸层析法、GC、IR和13C NMR法对它们的结构进行分析。Zeng等[3]采用微波法提取四川黑木耳多糖AAP,结果显示,AAP是一种杂多糖,其骨架是由葡萄糖通过(1→3)糖苷键连接而成的,并由葡萄糖,半乳糖,甘露糖,阿拉伯糖和鼠李糖组成。
大量研究结果表明,多糖是木耳的主要功效组分,具有激发细胞免疫活性、有效延缓衰老、辅助降血脂、降血糖、抗凝血、抗癌和抗氧化等生物学活性[4-8],并可作为益生元,促进肠道益生菌的生长[9,10]。蔡铭等对黑木耳多糖的抑菌活性进行分析,发现黑木耳多糖对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌有明显的抑制作用[11]。Peng等的研究表明黑木耳多糖可明显降低皮肤中丙二醛(MDA)和脂褐素(LF)的含量,增强超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的活性,从而达到减缓皮肤老化的效果[12]。Ma等通过向高脂模型小鼠饮食中添加黑木耳多糖来考察其降脂活性,结果发现,黑木耳多糖可减少心血管疾病的发生[13]。
相关图片展示: