氮化碳材料的调控改性及其光催化分解水产氢性能研究毕业论文
2020-07-09 20:27:09
摘 要
石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)由于其合适的能隙和高的化学稳定性,在光催化领域引起了广泛的关注,目前已经报道的合成g-C3N4的方法有电化学沉积法,溶剂热法,固相法和高温结烧法。但是单一的g-C3N4半导体也有其缺陷,使得g-C3N4在光催化方面的应用面对重重困难。本文用三聚氰胺和镍膜为原料,采用热缩聚法制备不同比例氮缺陷的氮化碳材料。
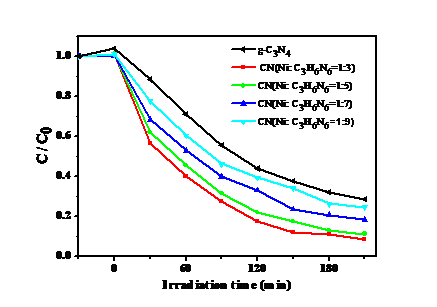
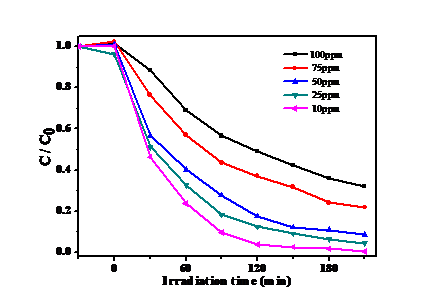
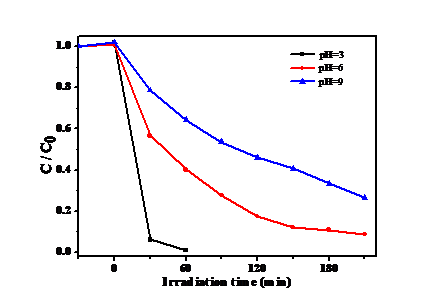
将制备的一系氮化碳材料置于可见光下,测试其催化降解Cr6 的活性。结果显示:在没有光照时,氮化碳材料并没有表现出催化活性;在光照一段时间后,Cr6 的浓度开始降低,这表明氮化碳材料具有光催化降解能力。此外,实验环境也会氮化碳材料的光催化能力有着一定的影响,例如:Cr6 的浓度,溶液的初始pH等。因此,本次实验也探究了Cr6 的浓度,溶液的初始pH对催化剂活性的影响,结果表明溶液的pH和Cr6 浓度越低,催化剂的催化活性反而越好。
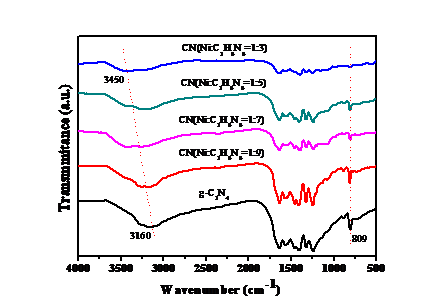
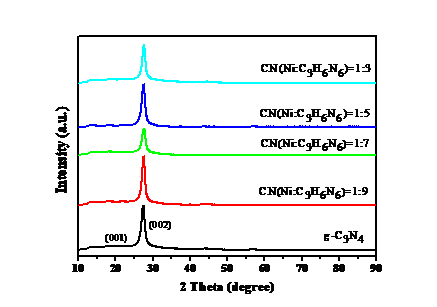
此外本实验还通过其他的表征手段(如X射线衍射、紫外漫反射光谱等)对该样品进行表征。XRD的表征结果显示出随着引入Ni的减少,横向峰值向2θ大角方向偏移,表明纳米片之间的堆积距离逐渐缩小。在FT-IR光谱中可以观察到,对于CN(Ni: C3H6N6=1:x)样品,随着Ni比例的增加,在810cm-1处的峰逐渐减弱,说明三嗪环的结构被破坏;在3160cm-1处的峰在逐渐减弱,同时在3450cm-1出现一个由弱至强的特征峰,对应-NH2的伸缩振动峰,说明镍膜的加入使氮化碳被还原。同时紫外显示出CN(Ni: C3H6N6=1:x)样品在可见光区域的吸收强度增强,并且整个样品体系向可见光偏移,说明该材料更易对可见光响应,这与以上表征结果是相一致的。
关键词:光催化 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4) 氮缺陷的氮化碳材料 降解铬
Modification of Carbon Nitride Material and Its Photocatalytic Performance
Abstract
Graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4) has attracted extensive attention in the field of photocatalysis because of its suitable energy gap and high chemical stability. Currently reported methods of synthesizing g-C3N4 include electrochemical deposition method and solvent thermal method, solid phase method and high-temperature sintering method. However, a single g-C3N4 semiconductor also has its defects, making it difficult to use g-C3N4 in photocatalysis applications. This article uses melamine and nickel film as raw materials, using thermal condensation method to prepare different proportions of nitrogen deficient carbon nitride material.
A series of prepared carbon nitride materials were placed under visible light to test the catalytic degradation of Cr6 . The results show that in the absence of light, the carbon nitride material does not show catalytic activity; after a certain period of light exposure, the Cr6 concentration begins to decrease, indicating that the carbon nitride material has photocatalytic degradation capability. In addition, the experimental environment also has a certain influence on the photocatalytic ability of carbon nitride materials, such as the concentration of Cr6 and the initial pH of the solution. Therefore, this experiment also explored the lower the pH and Cr6 concentration of the solution, the better the catalytic activity of the catalyst.
In addition, this experiment was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-vis DRS (UV-vis DRS) and other characterization methods. XRD shows that as the introduction of Ni decreases, the lateral peak shifts toward the larger angle of 2θ, indicating that the stacking distance between the nanosheets gradually decreases. In the FT-IR spectrum, it can be observed that for the CN (Ni:C3H6N6=1:x) sample, the peak at 810cm-1 gradually weakens as the proportion of Ni increases, indicating that the structure of the triazine ring is destroyed; The peak at 3160 cm-1 is gradually weakening, and a weak to strong characteristic peak appears at 3450 cm-1, indicating that the addition of the nickel film causes the carbon nitride to be reduced. At the same time, UV shows that the absorption intensity of CN (Ni:C3H6N6=1:x) in the visible light region is obviously enhanced, indicating that CN (Ni:C3H6N6=1:x) (x=3,5,7,9) enhances the absorption. The ability of visible light, and the shift of the entire sample system to visible light, indicates that the material is more responsive to visible light, which is consistent with the above characterization results.
Key Words: Photocatalysis; Graphitic carbon nitride; Nitrogen defective carbon nitride materials; Degradation of chromium
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 光催化简介 2
1.2.1 光催化原理 2
1.2.2 光催化剂 3
1.3 石墨相氮化碳结构、性质及制备方法 4
1.3.1 氮化碳结构 4
1.3.2 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)的性质 5
1.3.3 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)的制备方法 6
1.3.3 石墨相氮化碳的光催化应用 7
1.4 石墨相氮化碳的改性方法综述 10
1.4.1 形貌调控 10
1.4.2 元素掺杂 11
1.4.3 形成异质结 12
1.5 本文研究内容及意义 12
第二章 实验与表征 14
2.1 实验药品与仪器 14
2.2 样品制备 15
2.2.1 CN(Ni:C3H6N6=1:x)样品制备 15
2.2.2 g-C3N4的制备 15
2.3 光催化降解Cr6 活性测定 15
2.3.1 配制溶液 15
2.3.2 测试不同催化剂的催化剂活性 15
2.3.3 测试不同pH条件下的催化剂活性 16
2.4 样品的表征与光电性能测试 16
2.4.1 红外光谱(FT-IR) 16
2.4.2 X-射线衍射仪(XRD) 17
2.4.3 紫外-可见漫反射吸收光谱(UV-vis DRS) 17
2.5 结果与讨论 17
2.5.1 活性及实验条件探究 17
2.5.2 红外光谱(FT-IR) 19
2.5.3 X-射线衍射仪(XRD) 20
第三章 总结与展望 22
3.1研究总结 22
3.2展望 22
致谢 24
参考文献 25
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
随着社会生产力的发展以及科技的进步,给自然环境带来了诸多问题,例如生态破坏、全球变暖以及水体污染,尤其是对水体的污染。工业废水的超量排放,生活污水的随意排放,严重破坏了水体环境,对水体生物的生存以及人类的生产生活造成了严重的威胁。据环保部门统计,2006-2014年我国的工业用水总量平均高达1400亿立方米/年,大量工业用水加剧水资源的紧张局面,并由此而引起的水体污染进一步恶化[1]。近年来,国民的环保意识正在逐渐加强,尤其认识到是水资源的重要性,同时我国政府也出台了关于环境保护的法律法规,加大了治理环境污染的的力度,并收到了一定的成效。目前我国的废水排放量正在逐年减少,但由于我国的体量大,水体环境仍然面临着巨大的威胁,如何高效治理水体污染等问题依旧突出。
水体的污染源大致可分为有机染料、内分泌干扰物、抗生素以及含金属废水等,这些都是水污染治理的重点对象。其中,工业废水中含有许多的重金属离子如铜、锌、六价铬等,但由于我国的工业废水排放量巨大,从而我国金属废水的污染问题也十分突出。因此,如何高效治理重金属废水问题引起了国内外研究人员的广泛关注。金属铬及铬的化合物是重要的化工原料,在冶金、化工、医药等行业被广泛应用。重金属铬,尤其是六价铬,是一种迁移性强、易扩散的致癌金属之一。我国是通过物化和生化工艺联合法来处理含铬废水,其中物化方法有:直接回收法、加碱沉淀法、离子交换法、膜技术吸附法等,铬废水经物化处理后排入生化处理系统再次处理。这些方法都不能够彻底的处理含铬废水,且能耗高,一次投资较高,运行费用高,操作管理要求严格,会对环境造成二次污染等众多不足,因此我们需要更加便捷,更加高效,更加环保的方法来处理铬废水。
光催化是近年来兴起的,在新能源开发,有机合成,环境治理等领域都有应用的高新技术。应用光催化技术来降解铬废水,能够将铬废水中高毒的六价铬还原成毒性较低的三价铬,并且不会对环境造成二次污染。光催化是一种高效、节能、绿色环保的新兴技术,有着非常广阔的应用前景,因此将光催化技术用来治理水体污染问题成为广受关注的课题。
1.2 光催化简介
1.2.1 光催化原理
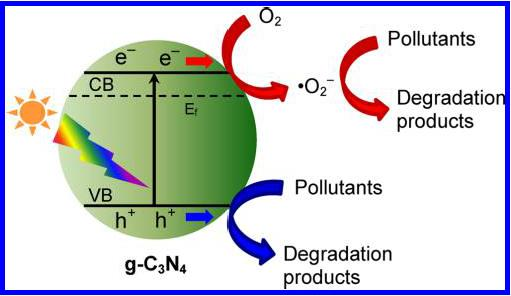
1972年Fujishima和Honda发现,在可见光照射下的TiO2表面可以析出氢气和氧气[2],之后的人们开始认识到在可见光的照射下的光催化剂可以催化水制氢,并将这种方法当做是解决能源危机的一种途径。实际上,光催化技术不仅可用于光解水制氢从而来解决能源不足问题,而且还可用于降解大气或水中的污染物从而解决一些环境污染问题[3]。因此,利用半导体光催化剂来解决环境和能源问题引起了许多科研工作者的研究兴趣。
相关图片展示: